ASTM D3606-07
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Benzene and Toluene in Finished Motor and Aviation Gasoline by Gas Chromatography
Standard Test Method for Determination of Benzene and Toluene in Finished Motor and Aviation Gasoline by Gas Chromatography
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Benzene is classed as a toxic material. A knowledge of the concentration of this compound can be an aid in evaluating the possible health hazard to persons handling and using the gasoline. This test method is not intended to evaluate such hazards.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of benzene and toluene in finished motor and aviation gasolines by gas chromatography.
1.2 Benzene can be determined between the levels of 0.1 and 5 volume % and toluene can be determined between the levels of 2 and 20 volume %.
1.3 The precision for this test method was determined using conventional gasoline as well as gasolines containing oxygenates (ethers such as methyl tert-butyl ether, ethyl tert-butyl ether and tert-amyl methyl ether).
1.4 Methanol may cause interference. Appendix X1 provides an option for modifying the test method for analyzing samples containing ethanol.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D3606 – 07
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Benzene and Toluene in Finished Motor
1
and Aviation Gasoline by Gas Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3606; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* E1293 Specification for Glass Measuring Pipets
1.1 This test method covers the determination of benzene
3. Summary of Test Method
and toluene in finished motor and aviation gasolines by gas
3.1 An internal standard, methyl ethyl ketone (MEK), is
chromatography.
added to the sample which is then introduced into a gas
1.2 Benzene can be determined between the levels of 0.1
chromatograph equipped with two columns connected in
and 5 volume % and toluene can be determined between the
series.The sample passes first through a column packed with a
levels of 2 and 20 volume %.
nonpolar phase such as dimethylpolysiloxane (8.1.1) which
1.3 The precision for this test method was determined using
separates the components according to boiling point. After
conventional gasoline as well as gasolines containing oxygen-
octane has eluted, the flow through the nonpolar column is
ates (ethers such as methyl tert-butyl ether, ethyl tert-butyl
reversed, flushing out the components heavier than octane.The
ether and tert-amyl methyl ether).
octane and lighter components then pass through a column
1.4 Methanol may cause interference. Appendix X1 pro-
packed with a highly polar phase such as 1,2,3-tris(2-
vides an option for modifying the test method for analyzing
cyanoethoxy)propane(8.1.2)whichseparatesthearomaticand
samples containing ethanol.
nonaromatic compounds. The eluted components are detected
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
by a thermal conductivity detector. The detector response is
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
recorded,thepeakareasaremeasured,andtheconcentrationof
only.
each component is calculated with reference to the internal
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
standard.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4. Significance and Use
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
4.1 Benzene is classed as a toxic material. A knowledge of
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
the concentration of this compound can be an aid in evaluating
2. Referenced Documents the possible health hazard to persons handling and using the
2 gasoline. This test method is not intended to evaluate such
2.1 ASTM Standards:
hazards.
D4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
Petroleum Products
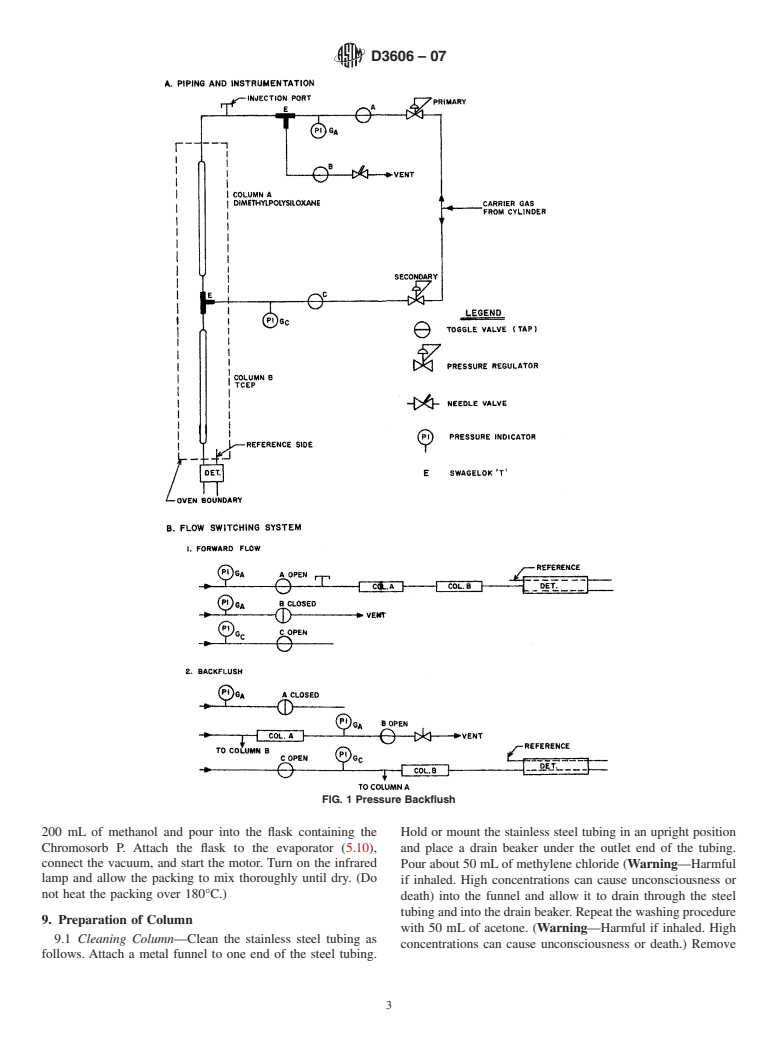
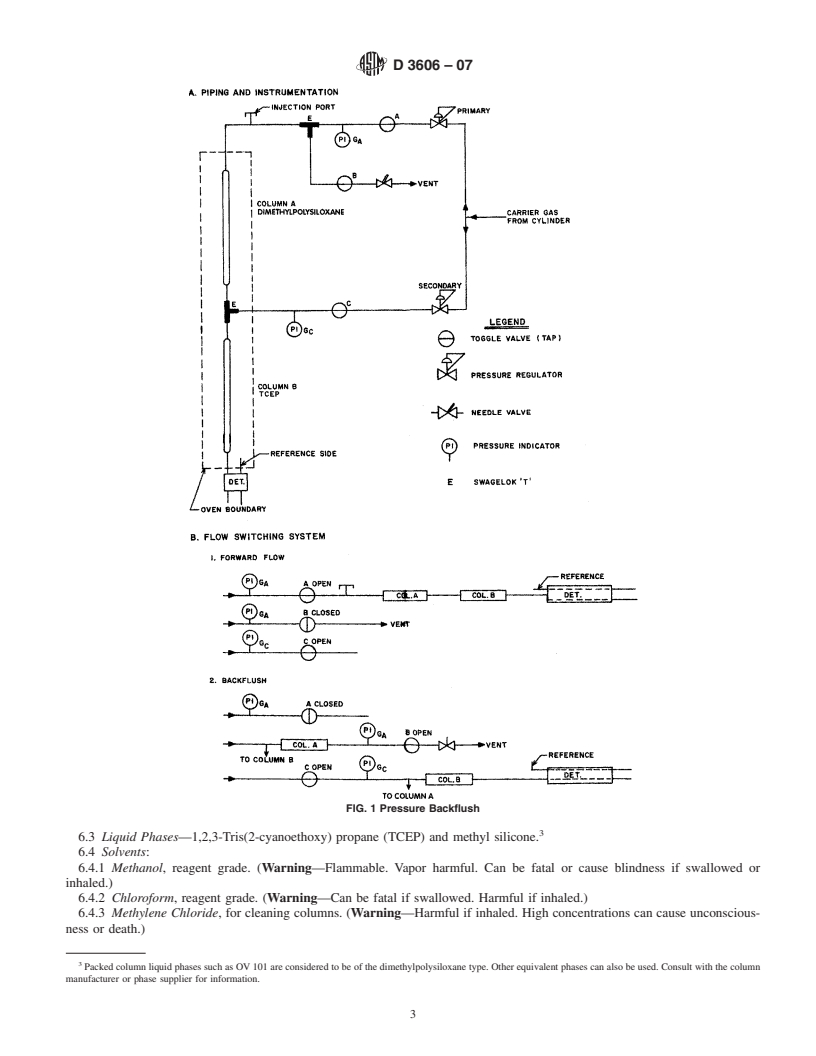
5. Apparatus
E694 Specification for Laboratory Glass Volumetric Appa-
5.1 Chromatograph—Any chromatographic instrument that
ratus
has a backflush system and thermal conductivity detector, and
E969 Specification for Glass Volumetric (Transfer) Pipets
that can be operated at the conditions given in Table 1, can be
E1044 Specification for Glass Serological Pipets (General
employed. Two backflush systems are shown. Fig. 1 is a
Purpose and Kahn)
pressure system and Fig. 2 is a switching valve system. Either
one can be used.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
5.2 Columns:
Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
1
5.2.1 Column A—One 0.8-m (2.5-ft) by 3.2-mm ( ⁄8-in.)
D02.04.0L on Gas Chromatography Methods.
outsidediameterstainlesssteelcolumnpackedwith10mass%
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2007. Published January 2008. Originally
´1
approved in 1977. Last previous edition approved in 2006 as D3606–06 . DOI: dimethylpolysiloxane (for example, OV-101) on Chromosorb
10.1520/D3606-07.
W, 60 to 80 mesh.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D3606 – 07
TABLE 1 Instrument Parameters
6. Materials
Detector thermal conductivity
6.1 Carrier Gas—Helium, 99.99 % pure. (Warning—
Columns: two, stainless steel
Compressed gas under high pressure.)
Length, m (A) 0.8; (B) 4.6
Outside diameter, mm 3.2
6.2 Support—Crushed firebrick, acid-washed, 60 to 80-
Stationary phase (A) dimethylpolysiloxane, 10 mass %
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
An American National Standard
e1
Designation:D3606–06 Designation: D 3606 – 07
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Benzene and Toluene in Finished Motor
1
and Aviation Gasoline by Gas Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 3606; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
e NOTE—Updated 1.4 editorially in November 2006.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the determination of benzene and toluene in finished motor and aviation gasolines by gas
chromatography.
1.2 Benzene can be determined between the levels of 0.1 and 5 volume % and toluene can be determined between the levels
of 2 and 20 volume %.
1.3 The precision for this test method was determined using conventional gasoline as well as gasolines containing oxygenates
(ethers such as methyl tert-butyl ether, ethyl tert-butyl ether and tert-amyl methyl ether).
1.4Methanol may cause interference.
1.4 Methanol may cause interference. Appendix X1 provides an option for modifying the test method for analyzing samples
containing ethanol.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum Products
E 694 Specification for Laboratory Glass Volumetric Apparatus
E 969 Specification for Glass Volumetric (Transfer) Pipets
E 1044 Specification for Glass Serological Pipets (General Purpose and Kahn)
E 1293 Specification for Glass Measuring Pipets
3. Summary of Test Method
3.1 An internal standard, methyl ethyl ketone (MEK), is added to the sample which is then introduced into a gas chromatograph
equipped with two columns connected in series. The sample passes first through a column packed with a nonpolar phase such as
dimethylpolysiloxane (8.1.1) which separates the components according to boiling point.After octane has eluted, the flow through
the nonpolar column is reversed, flushing out the components heavier than octane. The octane and lighter components then pass
throughacolumnpackedwithahighlypolarphasesuchas1,2,3-tris(2-cyanoethoxy)propane(8.1.2)whichseparatesthearomatic
and nonaromatic compounds. The eluted components are detected by a thermal conductivity detector. The detector response is
recorded, the peak areas are measured, and the concentration of each component is calculated with reference to the internal
standard.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 Benzene is classed as a toxic material.Aknowledge of the concentration of this compound can be an aid in evaluating the
possible health hazard to persons handling and using the gasoline. This test method is not intended to evaluate such hazards.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D02.04.0L
on Gas Chromatography Methods.
Current edition approved May 1, 2006. Published June 2006. Originally approved in 1977. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as D3606–04a.
e1
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2007. Published January 2008. Originally approved in 1977. Last previous edition approved in 2006 as D 3606–06 .
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D3606–07
5. Apparatus
5.1 Chromatograph—Any chromatographic instrument that has a backflush system and thermal conductivity detector, and that
can be operated at the conditions given inTable 1, can be employed.Two backflush systems are shown. Fig. 1 is a pressure system
and Fig. 2 is a switching valve system. Either one can be used.
5.2 Columns:
1
5
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.