ASTM C1399-07
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Obtaining Average Residual-Strength of Fiber-Reinforced Concrete
Standard Test Method for Obtaining Average Residual-Strength of Fiber-Reinforced Concrete
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of residual strength of a fiber-reinforced concrete test beam. The average residual strength is computed using specified beam deflections that are obtained from a beam that has been cracked in a standard manner. The test provides data needed to obtain that portion of the load-deflection curve beyond which a significant amount of cracking damage has occurred and it provides a measure of post-cracking strength, as such strength is affected by the use of fiber-reinforcement.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: C 1399 – 07
Standard Test Method for
Obtaining Average Residual-Strength of Fiber-Reinforced
1
Concrete
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C 1399; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* Fiber-Reinforced Concrete (Using Beam With Third-Point
Loading)
1.1 This test method covers the determination of residual
strength of a fiber–reinforced concrete test beam. The average
3. Terminology
residual strength is computed using specified beam deflections
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
that are obtained from a beam that has been cracked in a
3.1.1 deflection—mid–span deflection of the test beam ob-
standard manner. The test provides data needed to obtain that
tained in a manner that excludes deflection caused by the
portionoftheload–deflectioncurvebeyondwhichasignificant
following: (1) the flexural test apparatus, (2) crushing and
amount of cracking damage has occurred and it provides a
seating of the beam at support contact points, and (3) torsion of
measure of post–cracking strength, as such strength is affected
the beam; sometimes termed net deflection.
by the use of fiber–reinforcement.
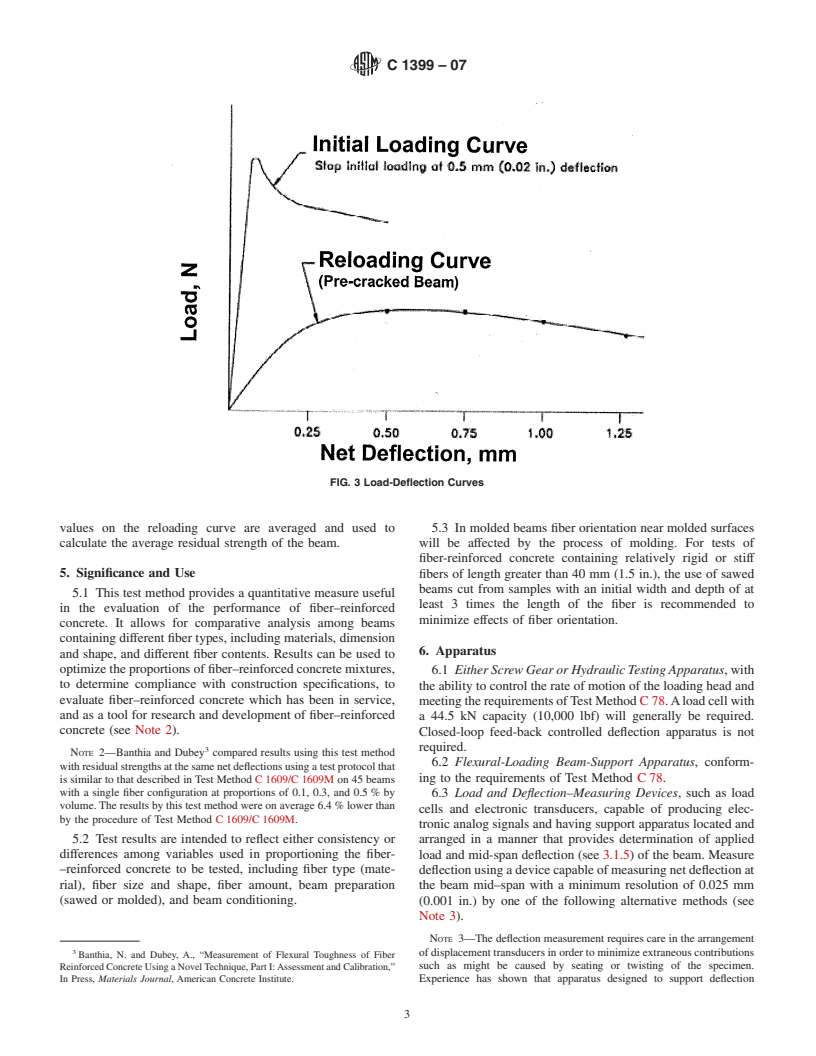
3.1.2 initial loading curve—the load–deflection curve ob-
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
tained by testing an assembly that includes both the test beam
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
and a specified steel plate (Fig. 1); plotted to a deflection of at
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
least 0.25 mm (0.010 in.) (Fig. 3).
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
3.1.3 reloading curve—the load–deflection curve obtained
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
by reloading and retesting the pre-cracked beam, that is, after
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
the initial loading but without the steel plate. (Fig. 3)
standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
3.1.4 reloading deflection—deflection measured during the
2. Referenced Documents reloading of the cracked beam and with zero deflection
2
referenced to the start of the reloading.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.1.5 residual strength—the flexural stress on the cracked
C 31/C 31M Practice for Making and Curing Concrete Test
beam section obtained by calculation using loads obtained
Specimens in the Field
from the reloading curve at specified deflection values (see
C 42/C 42M Test Method for Obtaining and Testing Drilled
Note 1).
Cores and Sawed Beams of Concrete
C78 Test Method for Flexural Strength of Concrete (Using
NOTE 1—Residual strength is not a true stress but an engineering stress
Simple Beam with Third-Point Loading)
computed using the flexure formula for linear elastic materials and gross
(uncracked) section properties.
C 172 Practice for Sampling Freshly Mixed Concrete
C 192/C 192M Practice for Making and Curing Concrete
3.1.6 average residual strength—the average stress–carry-
Test Specimens in the Laboratory
ing ability of the cracked beam that is obtained by calculation
C 823 Practice for Examination and Sampling of Hardened
using the residual strength at four specified deflections.
Concrete in Constructions
4. Summary of Test Method
C 1609/C 1609M Test Method for Flexural Performance of
4.1 Cast or sawed beams of fiber–reinforced concrete are
cracked using the third–point loading apparatus specified in
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C09 on
Test Method C78 modified by a steel plate used to assist in
Concrete and ConcreteAggregates and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
support of the concrete beam during an initial loading cycle
C09.42 on Fiber-Reinforced Concrete.
(Fig. 1). The steel plate is used to help control the rate of
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2007. Published February 2007. Originally
approved in 1998. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as C 1399–04.
deflection when the beam cracks. After the beam has been
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
cracked in the specified manner, the steel plate is removed and
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
the cracked beam is reloaded to obtain data to plot a reloading
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. load–deflection curve. Load values at specified deflection
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
--------
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.