ASTM E10-01e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Brinell Hardness of Metallic Materials
Standard Test Method for Brinell Hardness of Metallic Materials
SCOPE
1.1 This test method (Test Method A) covers the determination of the Brinell hardness of metallic materials, including methods for the verification of Brinell hardness testing machines (Test Method B) and the calibration of standardized hardness test blocks (Test Method C).
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
Note 1—In common terminology, the equivalent force in kgf is substituted for N.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
American Association State Highway
e1
Designation:E10–01 and Transportation Officials Standard
AASHTO No.: T70–86
Standard Test Method for
1
Brinell Hardness of Metallic Materials
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationE10;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginal
adoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1
e NOTE—Section 8.4.1 was editorially updated in June 2004.
1. Scope* curved surface area of the indentation which is assumed to be
spherical and of the diameter of the ball.
1.1 This test method (Test Method A) covers the determi-
nation of the Brinell hardness of metallic materials, including 2F
HBW 50.102 3 ~SeeTable1! (1)
2 2
methods for the verification of Brinell hardness testing ma-
p D~D 2 =D 2 d !
chines (Test Method B) and the calibration of standardized
where:
hardness test blocks (Test Method C).
D = diameter of the ball, mm,
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
F = test force, N, and
standard.
d = mean diameter of the indentation, mm.
NOTE 1—In common terminology, the equivalent force in kgf is
The Brinell hardness is denoted by the symbol: HBW.
substituted for N.
3.1.1.1 Discussion—In former standards, a steel ball was
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
allowed for hardness values below 450. In cases when a steel
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
ballwasused,theBrinellhardnesswasdenotedbyHBorHBS.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.1.1.2 Discussion—The symbol HBW is preceded by the
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
hardness value. When conditions other than those specified in
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
11.1.2 are used, the hardness value is supplemented by an
index indicating the test conditions in the order:
2. Referenced Documents
(1) Diameter of the ball, in mm,
2.1 ASTM Standards:
(2) A value representing the test force in kg/f (see Table 3), and,
2
E4 Practices for Force Verification of Testing Machines
(3) Duration of loading, in s.
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
Examples:
3
Determine Conformance with Specifications
350 HBW 5/750 = Brinell hardness of 350 determined with a ball of 5-mm diam-
eter and with a test force of 7.355 kN (750 kgf) applied for 10 to 15 s.
E74 Practice of Calibration of Force-Measuring Instru-
600 HBW 1/30/20 = Brinell hardness of 600 determined with a ball of 1-mm di-
ments for Verifying the Force Indication of Testing Ma-
ameter and with a test force of 294.2 N (30 kgf) applied for 20 s.
2
chines
3.1.1.3 Discussion—Brinellhardnessnumbersvarywiththe
E140 HardnessConversionTablesforMetalsRelationship
test force used; however, test results will generally be in
Among Brinell Hardness, Vickers Hardness, Rockwell
agreement when the ratio of the test force to the square of the
Hardness, Rockwell Superficial Hardness, Knoop Hard-
ball diameter is held constant (see Table 3).
2
ness, and Scleroscope Hardness
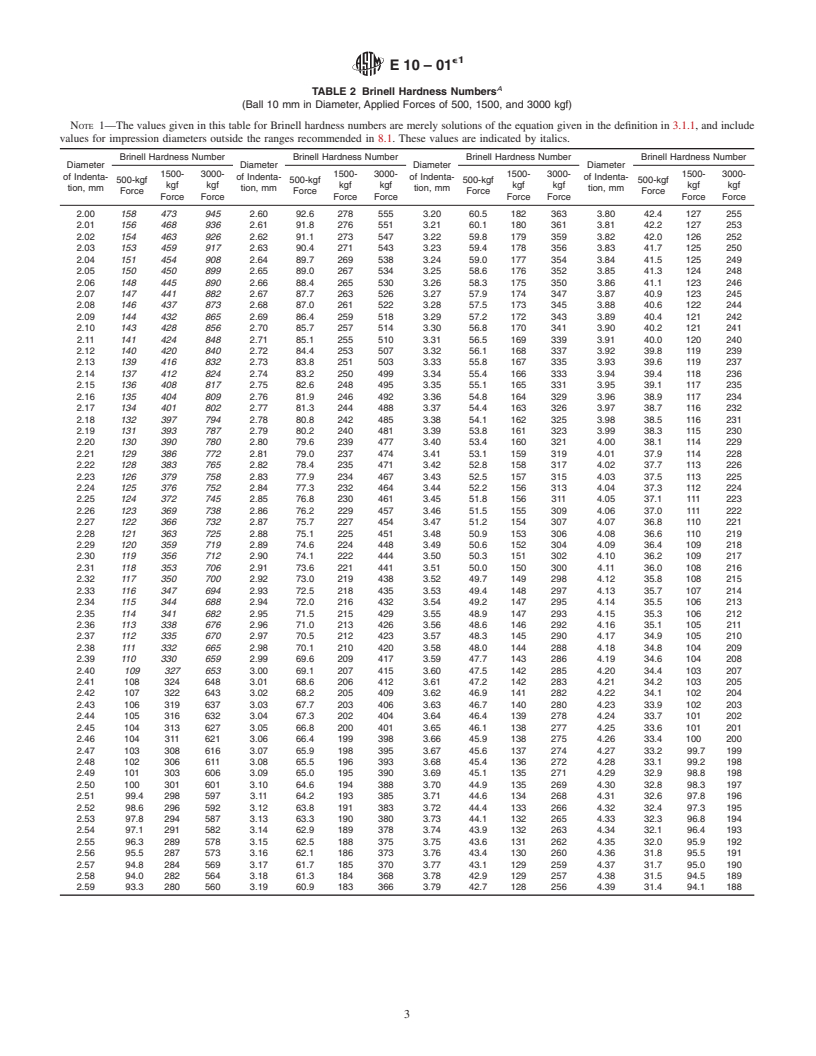
3.1.1.4 Discussion—Table 2 lists the Brinell hardness num-
bers corresponding to various diameters of indentations for
3. Terminology
29.4kN(3000kgf),14.7kN(1500kgf),and4.90kN(500kgf)
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
test forces making it unnecessary to calculate for each test the
3.1.1 Brinell hardness number—a number, which is propor-
value of the Brinell hardness number by the above equation in
tional to the quotient obtained by dividing the test force by the
Table1whentheseforcesareusedwitha10-mmdiameterball.
3.1.2 Brinell hardness test—an indenter (tungsten carbide
1
ball with diameter D) is forced into the surface of a test piece
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E28 on
Mechanical Testing and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E28.06 on
and the diameter of the indentation d left in the surface after
Indentation Hardness Testing.
removalofthetestforce,F,ismeasured.(seeTable1andFigs.
Current edition approved February 10, 2001. Published April 2001. Originally
1 and 2.)
published as E10–24T. Last previous edition E10–00a.
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.01.
3
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
e1
E10–01
TABLE 1 Symbols and Designations
and tolerances indicated in Table 4 may be used also provided
the precautions set forth in 8.1 are observed.
1 1
NOTE 1— Constan
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.