ASTM A532/A532M-10(2023)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Abrasion-Resistant Cast Irons
Standard Specification for Abrasion-Resistant Cast Irons
ABSTRACT
This specification deals with abrasion-resistant cast irons used for mining, milling, earth-handling, and manufacturing industries. These alloys may be made by melting process and shall have microstructures that consist of carbides, martensite, bainite, austenite, and in exceptional cases, minor amounts of graphite or pearlite. The following conditions for casting will be supplied: as-cast, as-cast and stress relieved, hardened, hardened and stress relieved, or softened for machining. Heat treatment shall be done. The chemical composition of a class and type (that is, Class I, Type A) shall conform to the range of values specified for carbon, manganese, silicon, nickel, chromium, molybdenum, copper, phosphorus, and sulfur. Hardness test shall also be made.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers a group of white cast irons that have been alloyed to secure high resistance to abrasive wear in the applications of the mining, milling, earth-handling, and manufacturing industries.
1.2 Simple and low-alloy white cast irons that consist essentially of iron carbides and pearlite are specifically excluded from this specification.
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the standard.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: A532/A532M − 10 (Reapproved 2023)
Standard Specification for
Abrasion-Resistant Cast Irons
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A532/A532M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope E351 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Cast Iron—All
Types
1.1 This specification covers a group of white cast irons that
have been alloyed to secure high resistance to abrasive wear in
3. Ordering Information
the applications of the mining, milling, earth-handling, and
3.1 Orders for material in this specification should include
manufacturing industries.
the following information:
1.2 Simple and low-alloy white cast irons that consist
3.1.1 Quantity,
essentially of iron carbides and pearlite are specifically ex-
3.1.2 Specification number, class, and type,
cluded from this specification.
3.1.3 Description of the casting, pattern number, or drawing,
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
3.1.4 Chilling of the casting, if required (see 4.2),
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
3.1.5 Heat-treat condition (see 5.1),
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
3.1.6 Hardness level, if supplied hardened or hardened and
system shall be used independently of the other. Combining
stress relieved, and
values from the two systems may result in nonconformance
3.1.7 Hardness method, Brinell, Rockwell, Vickers (see
with the standard.
Section 9). If the hardness method is not specified, it shall be
at the manufacturer’s option.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
4. Method of Manufacture
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
4.1 These alloys may be made by any suitable melting
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
process.
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
4.2 If the casting is to be chilled or otherwise specially
treated on any portion, the inquiries and the purchase order
2. Referenced Documents
shall so state and a properly marked drawing of the casting will
2.1 ASTM Standards:
accompany both the inquiry and the purchase order.
E10 Test Method for Brinell Hardness of Metallic Materials
5. Heat Treatment
E18 Test Methods for Rockwell Hardness of Metallic Ma-
terials
5.1 The casting will be supplied in one of the following
E92 Test Methods for Vickers Hardness and Knoop Hard-
conditions:
ness of Metallic Materials
5.1.1 As cast,
E350 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Carbon Steel,
5.1.2 As cast and stress relieved,
Low-Alloy Steel, Silicon Electrical Steel, Ingot Iron, and
5.1.3 Hardened,
Wrought Iron
5.1.4 Hardened and stress relieved, or
5.1.5 Softened for machining.
5.2 Unless otherwise specified by the purchaser, the manu-
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A04 on Iron
facturer shall supply the castings in the heat treatment he
Castings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee A04.01 on Grey and White
deems best for the application.
Iron Castings.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2023. Published November 2023. Originally
5.3 If the heat treatment specified for delivered condition is
approved in 1965. Last previous edition approved in 2019 as A532/A532M – 10
not that of final use, it shall be the responsibility of the
(2019). DOI: 10.1520/A0532_A0532M-10R23.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or purchaser to provide the additional heat treatment.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
5.4 Class II and Class III alloys are frequently ordered in the
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. annealed condition with a maximum hardness of 400 HB. After
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
A532/A532M − 10 (2023)
machining operations are performed the castings may then be 6.3.2.1 Molybdenum by the Photometric Method.
hardened. If both annealing and machining are to be performed
by the manufacturer as specified in the inquiry, contract, or
7. Microstructure
order, the purchaser may then specify delivery in the hardened
7.1 The alloys covered by this specification are expected to
condition. If the purchaser specifies delivery in the annealed
have microstructures that consist essentially of carbides,
condition, subsequent hardening (and stress relief, if it is
martensite, bainite, austenite, and in exceptional cases, minor
desired) is the responsibility of the purchaser.
amounts of graphite or pearlite.
6. Chemical Composition 7.2 The microstructure will not be routinely determined nor
reported except in accordance with special agreement between
6.1 The composition of the metal of a class and type
the manufacturer and the purchaser, or in cases of dispute.
produced under this specification shall fall within the ranges
prescribed in Table 1 for that class and type.
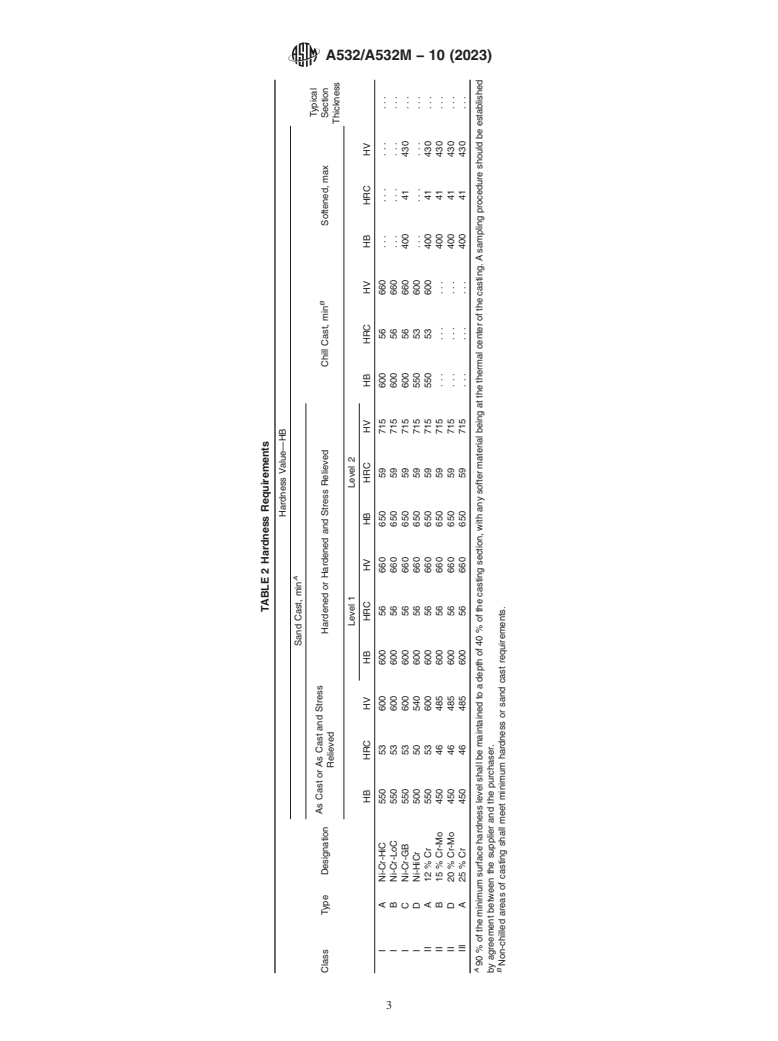
8. Hardne
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.