ASTM D3933-98(2017)
(Guide)Standard Guide for Preparation of Aluminum Surfaces for Structural Adhesives Bonding (Phosphoric Acid Anodizing)
Standard Guide for Preparation of Aluminum Surfaces for Structural Adhesives Bonding (Phosphoric Acid Anodizing)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 Durable adhesive bonds between metal to metal, metal to composites can be obtained reliably only through proper selection and careful control of the materials used and the steps in the bonding process. The preparation of the metallic substrates to obtain surfaces with appropriate characteristics is a critical step. Improper surface preparation can produce seemingly acceptable bonds that can degrade rapidly with time. This guide describes one method on how to properly prepare aluminum surfaces can be obtained.
4.2 The formation of reproducible, durable, adhesive bonds in structural assemblies requires great care in the selection of materials, the preparation of the surfaces of the components to be bonded, the fit of the components, and the performance of the steps in the bonding process. Experience has shown that when adhesively bonded aluminum surfaces which have been prepared in accordance with this guide produce relatively reproducible, durable bonds.
SCOPE
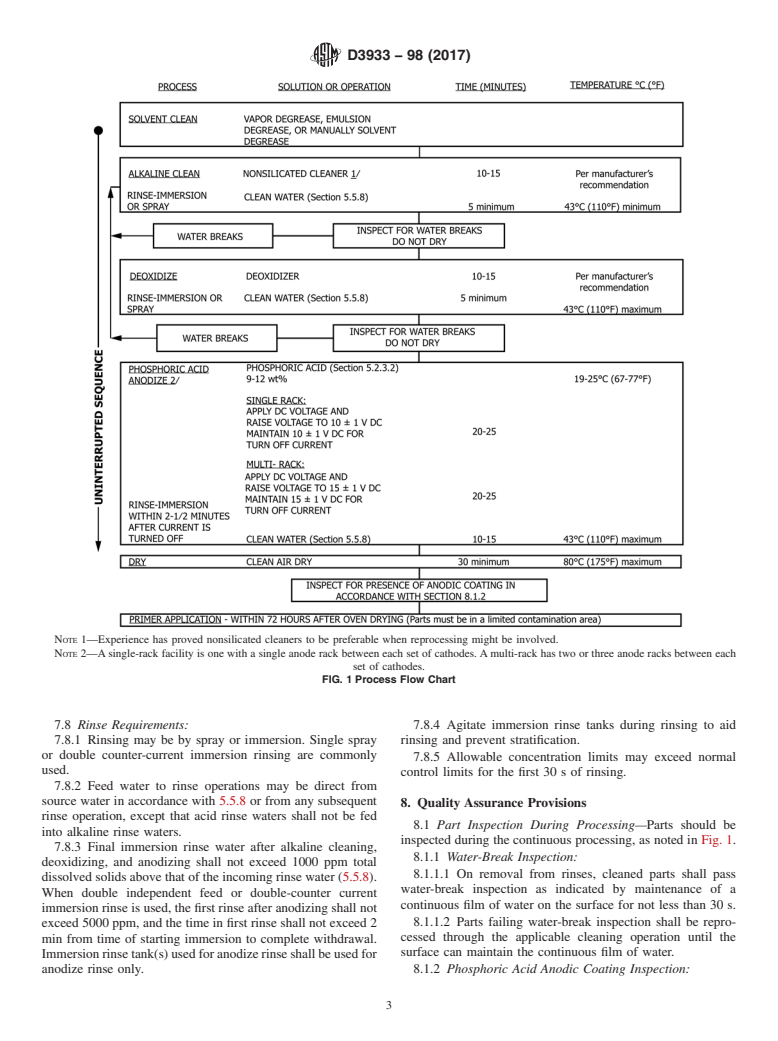
1.1 This guide describes the requirements for phosphoric acid anodizing of aluminum and its alloys for structural adhesive bonding.
1.2 The procedure included herein is based on the commercial practice of numerous agencies and organizations. The method may be revised or supplemented, as necessary, to include methods based on proven performance.
1.3 The surface preparation of metal systems used for qualification and quality-control testing of the adhesive should be agreed upon between the manufacturer and the user.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. A specific precaution is given in 5.5.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D3933 − 98 (Reapproved 2017)
Standard Guide for
Preparation of Aluminum Surfaces for Structural Adhesives
1
Bonding (Phosphoric Acid Anodizing)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3933; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2.2 Federal Specifications:
3
0-0-670 Orthophosphoric Acid, Technical
1.1 This guide describes the requirements for phosphoric
acid anodizing of aluminum and its alloys for structural
3. Terminology
adhesive bonding.
3.1 Definitions—Many terms in this guide are defined in
1.2 The procedure included herein is based on the commer-
Terminology D907.
cial practice of numerous agencies and organizations. The
method may be revised or supplemented, as necessary, to
4. Significance and Use
include methods based on proven performance.
4.1 Durable adhesive bonds between metal to metal, metal
1.3 The surface preparation of metal systems used for
to composites can be obtained reliably only through proper
qualification and quality-control testing of the adhesive should
selectionandcarefulcontrolofthematerialsusedandthesteps
be agreed upon between the manufacturer and the user.
in the bonding process. The preparation of the metallic
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the substrates to obtain surfaces with appropriate characteristics is
a critical step. Improper surface preparation can produce
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
only. seeminglyacceptablebondsthatcandegraderapidlywithtime.
This guide describes one method on how to properly prepare
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
aluminum surfaces can be obtained.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- 4.2 The formation of reproducible, durable, adhesive bonds
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
in structural assemblies requires great care in the selection of
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. A materials, the preparation of the surfaces of the components to
specific precaution is given in 5.5.
be bonded, the fit of the components, and the performance of
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
the steps in the bonding process. Experience has shown that
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
when adhesively bonded aluminum surfaces which have been
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
prepared in accordance with this guide produce relatively
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
reproducible, durable bonds.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
5. Apparatus
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
5.1 Locate surface preparation and drying facilities separate
2. Referenced Documents
from other activities or equipment, or both, to preclude
2
2.1 ASTM Standards: contamination by substances detrimental to adhesion.
D907 Terminology of Adhesives
5.2 Facilities should be arranged such that parts can flow
D2651 GuideforPreparationofMetalSurfacesforAdhesive
from the beginning of surface preparation to the priming
Bonding
operation without being touched.
5.3 Filtersortraps,orboth,shouldbeinstalledforremoving
1
airborne dust, moisture, and oil from all air lines or ducts used
ThisguideisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeD14onAdhesivesand
is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D14.80 on Metal Bonding Adhesives.
for solution agitation and parts drying. Periodically check,
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2017. Published November 2017. Originally
clean, or replace filters to ensure proper operation.
approved in 1980. Last previous edition approved in 2010 as D3933 – 98 (2010).
DOI: 10.1520/D3933-98R17.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
3
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM AvailablefromU.S.GovernmentPrintingOfficeSuperintendentofDocuments,
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on 732 N. Capitol St., NW, Mail Stop: SDE, Washington, DC 20401, http://
the ASTM website. www.access.gpo.gov.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D3933 − 98 (2017)
5.4 Surface preparation facilities should not be used for surfacesand
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.