ASTM F2414-04
(Practice)Standard Practice for Sealing Sewer Manholes Using Chemical Grouting
Standard Practice for Sealing Sewer Manholes Using Chemical Grouting
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This practice is used as a guide for the installation of chemical grout in the practice of sealing sewer manholes from leaks, cracks, and around penetrations. It is attended to assist sewer owners and engineer, owner’s representative, or authorized inspectors for installation method specification and for contractors to refer to during installations of chemical grout for manhole sealing.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice covers proposed selection of materials, installation techniques, and inspection required for sealing manholes using chemical grout. Manholes or sections of manholes with active leaks shall be repaired. Manholes to be grouted are of brick, block, cast-in-place concrete, precast concrete, or fiberglass construction. Manholes or sections of manholes with active leaks will be designated by the engineer, owners representative, or authorized inspector, for manhole grouting.
1.2 The contractor shall be responsible for furnishing all labor, supervision, materials, equipment, and inspection follow-up required for the completion of chemical grouting of manhole defects in accordance with the contract documents.
1.3 Materials, additives, mixture ratios, and procedures utilized for the grouting process shall be in accordance with manufacturers recommendations and shall be appropriate for the application.
1.4 The values stated in inch/pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:F2414–04
Standard Practice for
Sealing Sewer Manholes Using Chemical Grouting
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 2414; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope form. The greatest use of acrylamide is as a coagulant aid in
drinking water treatment. Other major uses of acrylamide are
1.1 This practice covers proposed selection of materials,
in soil stabilization, in grout for repairing sewers and in
installation techniques, and inspection required for sealing
acrylamide gels used in biotechnology laboratories.
manholes using chemical grout. Manholes or sections of
3.1.2 acrylate—a general term applied to various water-
manholes with active leaks shall be repaired. Manholes to be
soluble acrylic resinous materials.
grouted are of brick, block, cast-in-place concrete, precast
3.1.3 authorized inspector—the person(s) contracted or ap-
concrete, or fiberglass construction. Manholes or sections of
proved by the owner or owner’s representative to do inspec-
manholes with active leaks will be designated by the engineer,
tions.
owner’s representative, or authorized inspector, for manhole
3.1.4 catalyst—substance which markedly speeds up the
grouting.
cure of an adhesive when added in small quantities as
1.2 The contractor shall be responsible for furnishing all
compared to the amounts of primary reactants.
labor, supervision, materials, equipment, and inspection
3.1.5 chemical grout—injection repair media other than
follow-up required for the completion of chemical grouting of
cementitious grout that may be multi-component, with or
manhole defects in accordance with the contract documents.
without additives, and based on either polyurethane resin or
1.3 Materials, additives, mixture ratios, and procedures
acrylic resin.
utilized for the grouting process shall be in accordance with
3.1.6 control agent—substance added which controls the
manufacturer’s recommendations and shall be appropriate for
viscosity or flow properties of the material it is added to.
the application.
3.1.7 engineer—an engineer registered in the state where
1.4 The values stated in inch/pound units are to be regarded
the work is to be done who has been contracted by or is acting
as the standard. The values in parentheses are for information
on behalf of the owner or the owner’s representative.
only.
3.1.8 exfiltration—leaking or weeping to the external areas
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
outside the barrier from a source inside the barrier.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
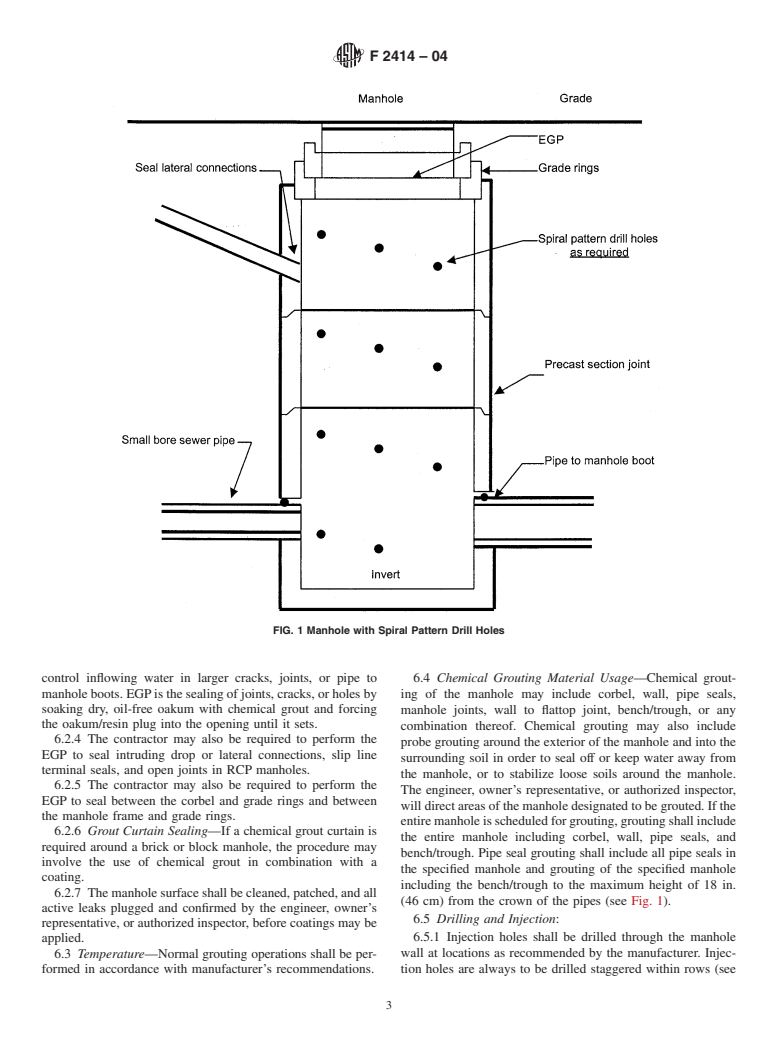
3.1.9 expanded gasket procedure (EGP)—EGP is the seal-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
ing of joints, cracks, or holes by soaking dry, oil-free oakum
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
with chemical grout and forcing the oakum/resin plug into the
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
opening until it sets.
2. Referenced Documents
3.1.10 hydrophilic grout—hydrophilicgroutwillabsorband
react with the water it comes into contact with.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.1.11 hydrophobic grout—hydrophobic grout will repel
F 2304 Practice for Rehabilitation of Sewers Using Chemi-
water and push it away.
cal Grouting
3.1.12 manhole—vertical shafts that intersect with sewers
3. Terminology
to allow transitions in alignment and grade and to allow entry
for cleaning, inspection, and maintenance.
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.13 oakum—loose hemp or jute fiber, sometimes treated
3.1.1 acrylamide—organic solid of white, odorless, acrylic
with resin or grout, used chiefly for caulking seams in
resinous material available in flake-like crystals and in liquid
structures and boats as well as packing pipe joints.
3.1.14 owner’s representative—the individual who has been
This practice is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F36 on Technology
contracted to act on behalf of the owner for project planning
and Underground Utilities and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F36.20
and supervision.
on Inspection and Renewal of Water and Wastewater Infrastructure.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2004. Published December 2004. 3.1.15 polyurethane resin—any of various polymer resins
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
containing the urethane radical; a wide variety of synthetic
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
forms are made and used as adhesives, plastics, foams, paints,
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
or rubber-like materials.
the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
F2414–04
3.1.16 RCP—reinforced concrete pipe. tion requirements must be thoroughly reviewed by the contrac-
3.1.17 rehabilitated manhole—a manhole restored to its tor or engineer when choosing or approving the appropriate
intended capacity or use per the specifications. type of chemical grout.
3.1.18 repaired or sealed manhole—a manhole that has 5.2.8 Careful consideration of water type (storm water
been sealed from detected infiltration or exfiltrations, but not versus waste water) is to be considered when choosing or
necessarily restored to its original designed capacity. approving the appropriate type of materials.
3.1.19 sewer—waste water sewer or storm drain sewer. 5.3 Additives—The chemical grout must be applied so as to
have the grout material flow freely into the defects. To avoid
4. Significance and Use
any wasting of the material flowing through the defects gel
4.1 This practice is used as a guide for the installation of
control agent may be added. Grout additions may also be used
chemical grout in the practice of sealing sewer manholes from
forcatalyzingthereaction,inhibitingthereaction,bufferingthe
leaks, cracks, and around penetrations. It is attended to assist
solution, lowering the freezing temperature of the solution,
sewer owners and engineer, owner’s representative, or autho-
acting as filler, providing strength, or inhibition of root growth.
rized inspectors for installation method specification and for
5.3.1 Additivesmustnotalterotherintendedfinalproperties
contractors to refer to during installations of chemical grout for
and characteristics of the original material other than the
manhole sealing. properties targeted for improvement.
5.4 Material Identification—The contractor shall com-
5. Materials
pletely identify the types of grout, sealant, root control chemi-
5.1 Grouting Materials—Chemical grout sealing material:
cals, or any combination thereof, used and provide case
5.1.1 Acrylamide base gel,
histories of successful use or defend the choice of grouting
5.1.2 Acrylic base gel,
materials based on chemical and tested physical properties,
5.1.3 Hydrophilic polyurethane foam or gel,
ease of application, and expected performance to the satisfac-
5.1.4 Hydrophobic polyurethane foam or gel, and,
tion of the engineer, owner’s representative, or authorized
5.1.5 Oil-free, oakum-soaked polyurethane resin.
inspector. The grout materials’Technical Data Sheets, Material
5.2 Grouting Materials Characteristics—Specific charac-
Safety Data Sheets, and the manufacturer’s application instruc-
teristics that pertain to the application requirements are to be
tions are to be submitted for approval by the engineer, owner’s
defined and approved by the owner’s representative or project
representative, or authorized inspector.
engineer of record. The following general characteristics or
5.5 Mixing and Handling:
properties shall be exhibited by the chemical grout:
5.5.1 Hazards—Mixing and handling of chemical grout,
5.2.1 The chemical grout shall have documented service of
which may be toxic under certain conditions, shall be in
satisfactory performance in similar usage and should have a
accordance with the recommendations of the manufacturer and
manufacturer’s written guarantee of performance for the appli-
in such a manner as to minimize hazard to personnel. It is the
cation of sewer manhole sealing under intended conditions and
responsibility of the contractor to provide appropriate protec-
when installed per the manufacturer’s instructions.
tive measures to ensure that the chemicals are handled by
5.2.2 The chemical grout shall have controllable reaction
authorized personnel and in the proper manner.
times and minimal shrinkage, as specified by the owner,
5.5.2 All equipment shall be subject to the approval of the
owner’s representative, or engineer, through the use of chemi-
engineer, owner’s representative, or authorized inspector. Only
cals supplied by the same manufacturer.The minimum set time
personnel thoroughly familiar with the handling of the grout
shall be established so that adequate grout travel is achieved.
material and additives shall perform the grou
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.