ASTM D1921-06
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Particle Size (Sieve Analysis) of Plastic Materials
Standard Test Methods for Particle Size (Sieve Analysis) of Plastic Materials
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
These test methods can be used to determine particle size distribution and therefore are useful for determining lot-to-lot uniformity.
The particle sizes of plastic materials affect the handling characteristics and sometimes will affect the processing characteristics of some polymers.
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover the measurement of the particle size of plastic materials in the powdered, granular, or pelleted forms in which they are commonly supplied. As these test methods utilize dry sieving, the lower limit of measurement is considered to be about 38 m (No. 400 sieve). For smaller particle sizes, sedimentation test methods are recommended.
1.2 Two test methods are described:
1.2.1 Test Method AThis test method uses multiple sieves selected to span the particle size of the material. This method is used to determine the mean particle diameter and particle size distribution.
1.2.2 Test Method BThis test method is an abbreviated version of Test Method A conducted with a few specific sieves. This test method determines "percent passing" or "percent retained" on a given sieve. Test Method B is applicable to materials which do not have a normal particle size distribution such as pellets and cubes.
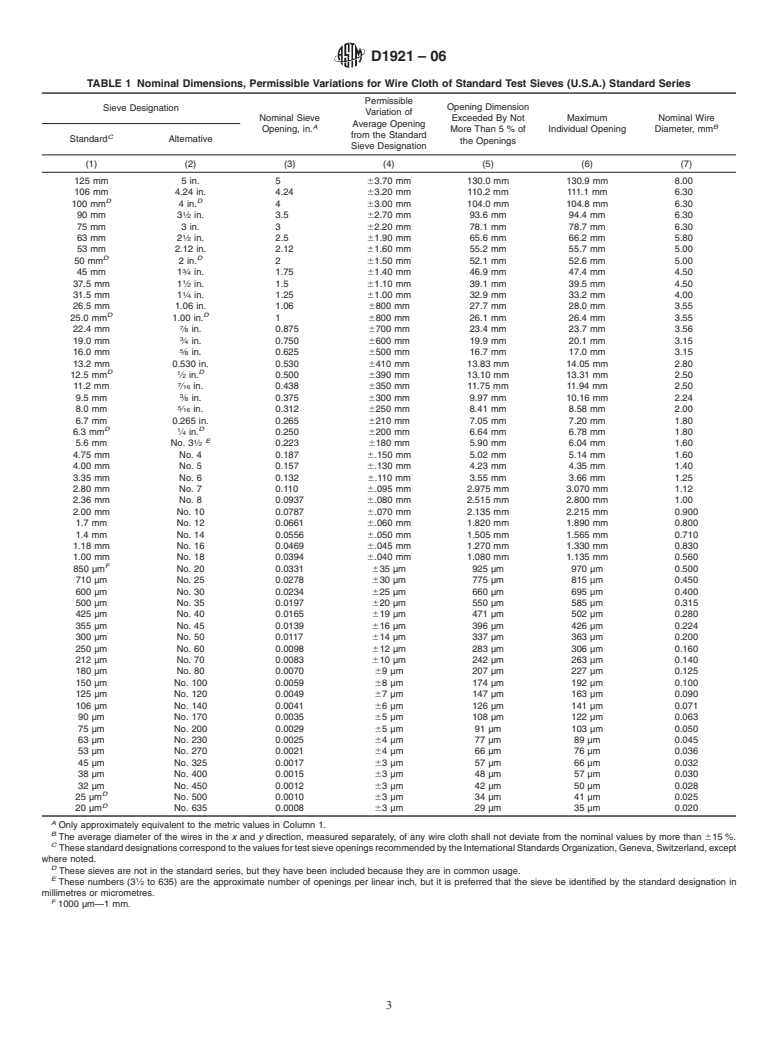
1.3 The values stated in SI units shall be considered standard for dimensions of the wire cloth openings and the diameter of the wires used in the wire cloth. The values stated in inch-pound units shall be considered standard with regard to the sieve frames.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
There is no technically equivalent ISO standard.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D1921–06
Standard Test Methods for
1
Particle Size (Sieve Analysis) of Plastic Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1921; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope* 2. Referenced Documents
2
1.1 These test methods cover the measurement of the 2.1 ASTM Standards:
particle size of plastic materials in the powdered, granular, or E11 SpecificationforWovenWireTestSieveClothandTest
pelleted forms in which they are commonly supplied.As these Sieves
test methods utilize dry sieving, the lower limit of measure- E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
ment is considered to be about 38 µm (No. 400 sieve). For Determine the Precision of a Test Method
smaller particle sizes, sedimentation test methods are recom-
3. Summary of Test Methods
mended.
3.1 A dry mass of plastic material is placed on a series of
1.2 Two test methods are described:
1.2.1 Test Method A—This test method uses multiple sieves sieves arranged in order of increasing fineness and the mass is
divided into fractions corresponding to the sieve opening.
selected to span the particle size of the material. This method
is used to determine the mean particle diameter and particle
4. Significance and Use
size distribution.
4.1 These test methods can be used to determine particle
1.2.2 Test Method B—This test method is an abbreviated
size distribution and therefore are useful for determining
version ofTest MethodAconducted with a few specific sieves.
lot-to-lot uniformity.
This test method determines “percent passing” or “percent
4.2 The particle sizes of plastic materials affect the handling
retained” on a given sieve. Test Method B is applicable to
characteristics and sometimes will affect the processing char-
materials which do not have a normal particle size distribution
acteristics of some polymers.
such as pellets and cubes.
1.3 The values stated in SI units shall be considered
5. Interferences
standard for dimensions of the wire cloth openings and the
5.1 Some materials develop a static charge during sieving.
diameter of the wires used in the wire cloth. The values stated
This charge interferes with the sieving process and results in a
in inch-pound units shall be considered standard with regard to
coarse bias. Use of an antistat is necessary to obtain meaning-
the sieve frames.
ful results.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
5.2 The choice of antistat (or slip agent) has been known to
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
affect the coarse bias. Some materials are more effective in
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
aiding the fines to separate from the mass.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
5.3 Too much material on a sieve causes mass blinding and
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
results in a coarse bias. The sieve selection and charge weight
NOTE 1—There is no technically equivalent ISO standard.
must be chosen to avoid overloading any sieve.
1
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on
Plastics and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.70 on Analytical
2
Methods (Section D20.70.01). For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved April 1, 2006. Published June 2006. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1961. Last previous edition approved in 2001 as D1921 - 01. DOI: Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/D1921-06. the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D1921–06
5.4 Wavy, improperly stretched wire-cloth may allow wires 11.2 If possible, condition the material to the laboratory
to separate without being visually damaged. Sieves with wavy temperature and humidity.
or torn wires shall not be used, as they no longer conform to
TEST METHOD A
Specification E11.
6. Apparatus
12. Procedure
6.1 Balance, 500-g minimum capacity with the capability of
12.1 Selectsievesinsufficientnumbertocovertheexpected
reading to the nearest 0.1 g.
range of particle sizes, and nest them together in order of
6.2 Mechanical Sieving Device and Time Switch—A me-
diminishing opening with the coarsest siev
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.