ASTM D7136/D7136M-20
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Measuring the Damage Resistance of a Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Matrix Composite to a Drop-Weight Impact Event
Standard Test Method for Measuring the Damage Resistance of a Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Matrix Composite to a Drop-Weight Impact Event
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
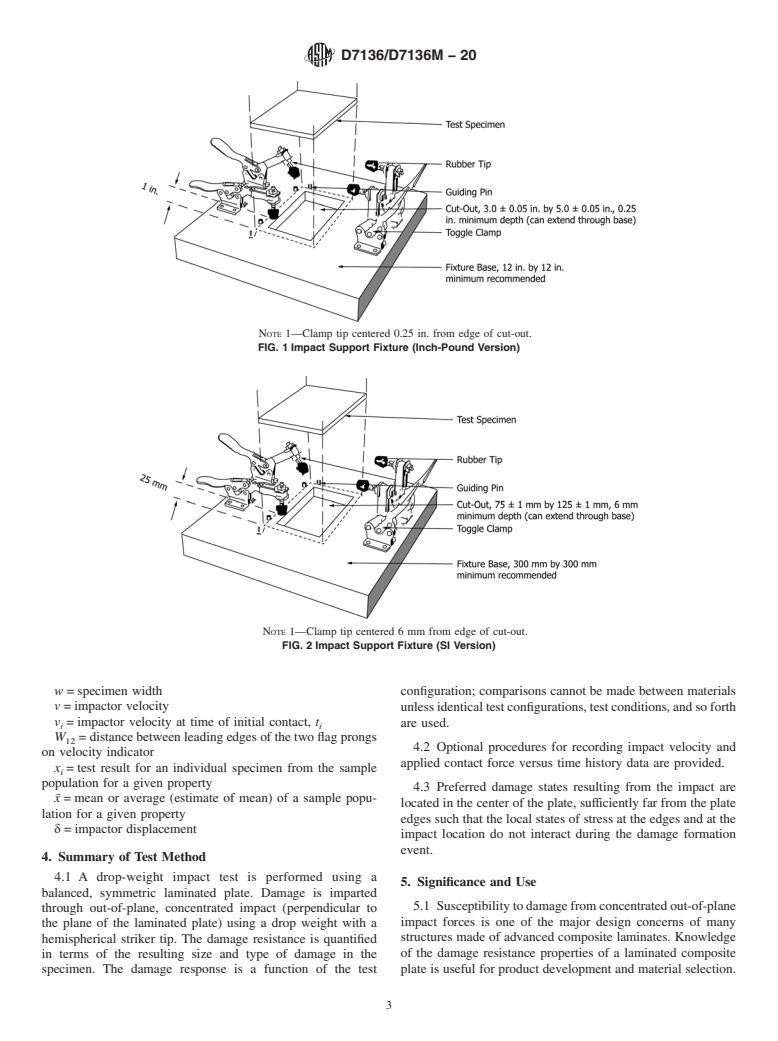
5.1 Susceptibility to damage from concentrated out-of-plane impact forces is one of the major design concerns of many structures made of advanced composite laminates. Knowledge of the damage resistance properties of a laminated composite plate is useful for product development and material selection.
5.2 Drop-weight impact testing can serve the following purposes:
5.2.1 To establish quantitatively the effects of stacking sequence, fiber surface treatment, variations in fiber volume fraction, and processing and environmental variables on the damage resistance of a particular composite laminate to a concentrated drop-weight impact force or energy.
5.2.2 To compare quantitatively the relative values of the damage resistance parameters for composite materials with different constituents. The damage response parameters can include dent depth, damage dimensions, and through-thickness locations, F1, Fmax, E1, and Emax, as well as the force versus time curve.
5.2.3 To impart damage in a specimen for subsequent damage tolerance tests, such as Test Method D7137/D7137M.
5.3 The properties obtained using this test method can provide guidance in regard to the anticipated damage resistance capability of composite structures of similar material, thickness, stacking sequence, and so forth. However, it must be understood that the damage resistance of a composite structure is highly dependent upon several factors, including geometry, thickness, stiffness, mass, support conditions, and so forth. Significant differences in the relationships between impact force/energy and the resultant damage state can result due to differences in these parameters. For example, properties obtained using this test method would more likely reflect the damage resistance characteristics of an unstiffened monolithic skin or web than that of a skin attached to substructure which resists out-of-plane deformation. Similarly, test specimen properties would be expected to be similar to those of a ...
SCOPE
1.1 This test method determines the damage resistance of multidirectional polymer matrix composite laminated plates subjected to a drop-weight impact event. The composite material forms are limited to continuous-fiber reinforced polymer matrix composites, with the range of acceptable test laminates and thicknesses defined in 8.2.
1.1.1 Instructions for modifying these procedures to determine damage resistance properties of sandwich constructions are provided in Practice D7766/D7766M.
1.2 A flat, rectangular composite plate is subjected to an out-of-plane, concentrated impact using a drop-weight device with a hemispherical impactor. The potential energy of the drop-weight, as defined by the mass and drop height of the impactor, is specified prior to test. Equipment and procedures are provided for optional measurement of contact force and velocity during the impact event. The damage resistance is quantified in terms of the resulting size and type of damage in the specimen.
1.3 The test method may be used to screen materials for damage resistance, or to inflict damage into a specimen for subsequent damage tolerance testing. When the impacted plate is tested in accordance with Test Method D7137/D7137M, the overall test sequence is commonly referred to as the Compression After Impact (CAI) method. Quasi-static indentation per Test Method D6264/D6264M may be used as an alternate method of creating damage from an out-of-plane force and measuring damage resistance properties.
1.4 The damage resistance properties generated by this test method are highly dependent upon several factors, which include specimen geometry, layup, impactor geometry, impactor mass, impact force, impact energy, and boundary conditions. Thus, results are generally not scalable to other configurations, and are particular to the combination of geometric and physical conditions tested.
1.5 Units—The values stated in either SI units or inch-poun...
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D7136/D7136M − 20
Standard Test Method for
Measuring the Damage Resistance of a Fiber-Reinforced
1
Polymer Matrix Composite to a Drop-Weight Impact Event
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7136/D7136M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 1.5 Units—The values stated in either SI units or inch-
pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The
1.1 This test method determines the damage resistance of
values stated in each system are not necessarily exact equiva-
multidirectional polymer matrix composite laminated plates
lents; therefore, to ensure conformance with the standard, each
subjected to a drop-weight impact event. The composite
system shall be used independently of the other, and values
material forms are limited to continuous-fiber reinforced poly-
from the two systems shall not be combined.
mer matrix composites, with the range of acceptable test
1.5.1 Within the text, the inch-pound units are shown in
laminates and thicknesses defined in 8.2.
brackets.
1.1.1 Instructions for modifying these procedures to deter-
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
mine damage resistance properties of sandwich constructions
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
are provided in Practice D7766/D7766M.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
1.2 A flat, rectangular composite plate is subjected to an
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
out-of-plane, concentrated impact using a drop-weight device
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
with a hemispherical impactor. The potential energy of the
1.7 This international standard was developed in accor-
drop-weight, as defined by the mass and drop height of the
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
impactor, is specified prior to test. Equipment and procedures
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
are provided for optional measurement of contact force and
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
velocity during the impact event. The damage resistance is
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
quantified in terms of the resulting size and type of damage in
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
the specimen.
1.3 The test method may be used to screen materials for
2. Referenced Documents
damage resistance, or to inflict damage into a specimen for
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
subsequent damage tolerance testing. When the impacted plate
D792 Test Methods for Density and Specific Gravity (Rela-
is tested in accordance with Test Method D7137/D7137M, the
tive Density) of Plastics by Displacement
overall test sequence is commonly referred to as the Compres-
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
sion After Impact (CAI) method. Quasi-static indentation per
D2584 Test Method for Ignition Loss of Cured Reinforced
Test Method D6264/D6264M may be used as an alternate
Resins
method of creating damage from an out-of-plane force and
D2734 TestMethodsforVoidContentofReinforcedPlastics
measuring damage resistance properties.
D3171 Test Methods for Constituent Content of Composite
1.4 The damage resistance properties generated by this test
Materials
method are highly dependent upon several factors, which
D3763 Test Method for High Speed Puncture Properties of
include specimen geometry, layup, impactor geometry, impac-
Plastics Using Load and Displacement Sensors
tor mass, impact force, impact energy, and boundary condi-
D3878 Terminology for Composite Materials
tions. Thus, results are generally not scalable to other
D5229/D5229M TestMethodforMoistureAbsorptionProp-
configurations, and are particular to the combination of geo-
erties and Equilibrium Conditioning of Polymer Matrix
metric and physical conditions tested.
Composite Materials
D5687/D5687M Guide for Preparation of Flat Composite
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D30 on
Composite Materials and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D30.05 on
2
Structural Test Methods. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2020. Published November 2020. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 2005. Last previous edition approved in 2015 as D7136/D7136M – 15. Standards volume information, refer to the
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D7136/D7136M − 15 D7136/D7136M − 20
Standard Test Method for
Measuring the Damage Resistance of a Fiber-Reinforced
1
Polymer Matrix Composite to a Drop-Weight Impact Event
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7136/D7136M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method determines the damage resistance of multidirectional polymer matrix composite laminated plates subjected
to a drop-weight impact event. The composite material forms are limited to continuous-fiber reinforced polymer matrix
composites, with the range of acceptable test laminates and thicknesses defined in 8.2.
1.1.1 Instructions for modifying these procedures to determine damage resistance properties of sandwich constructions are
provided in Practice D7766/D7766M.
1.2 A flat, rectangular composite plate is subjected to an out-of-plane, concentrated impact using a drop-weight device with a
hemispherical impactor. The potential energy of the drop-weight, as defined by the mass and drop height of the impactor, is
specified prior to test. Equipment and procedures are provided for optional measurement of contact force and velocity during the
impact event. The damage resistance is quantified in terms of the resulting size and type of damage in the specimen.
1.3 The test method may be used to screen materials for damage resistance, or to inflict damage into a specimen for subsequent
damage tolerance testing. When the impacted plate is tested in accordance with Test Method D7137/D7137M, the overall test
sequence is commonly referred to as the Compression After Impact (CAI) method. Quasi-static indentation per Test Method
D6264/D6264M may be used as an alternate method of creating damage from an out-of-plane force and measuring damage
resistance properties.
1.4 The damage resistance properties generated by this test method are highly dependent upon several factors, which include
specimen geometry, layup, impactor geometry, impactor mass, impact force, impact energy, and boundary conditions. Thus, results
are generally not scalable to other configurations, and are particular to the combination of geometric and physical conditions tested.
1.5 Units—The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
each system mayare not benecessarily exact equivalents; therefore, to ensure conformance with the standard, each system shall be
used independently of the other. Combiningother, and values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the
standard.shall not be combined.
1.5.1 Within the text, the inch-pound units are shown in brackets.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D30 on Composite Materials and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D30.05 on Structural Test
Methods.
Current edition approved March 15, 2015Oct. 1, 2020. Published March 2015November 2020. Originally approved in 2005. Last previous edition approved in 20122015
as D7136/D7136M - 12.D7136/D7136M – 15. DOI: 10.1520/D7136_D7136M-15.10.1520/D7136_D7136M-20.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7136/D7136M − 20
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D792 Test Methods for Density and Specific Gravity (Relative Density) of Plastics by Displacement
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
D2584 Test Method for Ignition Loss of Cured Reinforced Resins
D2734 Test Methods for Void Content of Reinforced Plastics
D3171 Test Methods for Constituent Content of Composite Materials
D3763 Test Metho
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.