ASTM D5466-21
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Volatile Organic Compounds in Atmospheres (Canister Sampling, Mass Spectrometry Analysis Methodology)
Standard Test Method for Determination of Volatile Organic Compounds in Atmospheres (Canister Sampling, Mass Spectrometry Analysis Methodology)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 VOCs are emitted into ambient, indoor, and workplace air from many different sources. These VOCs are of interest for a variety of reasons including participation in atmospheric chemistry and contributing to air toxics with their associated acute or chronic health impacts.
5.2 Canisters are particularly well suited for the collection and analysis of very volatile and volatile organic compounds because they collect whole gas samples.
5.3 Chemically stable selected VOCs have been successfully collected in passivated stainless steel canisters. Collection of atmospheric samples in canisters provides for: (1) convenient integration of air samples over a specific time period (for example, 8 to 24 h), (2) remote sampling and central laboratory analysis, (3) ease of storing and shipping samples, (4) unattended sample collection, (5) analysis of samples from multiple sites with one analytical system, (6) dilution or additional sample concentration to keep the sample size introduced into the analytical instrument within the calibration range, (7) collection of sufficient sample volume to allow assessment of measurement precision through replicate analyses of the same sample by one or several analytical systems, (8) sample collection using a vacuum regulator flow controller if electricity is not available, and (9) grab sample collection for survey or screening purposes.
5.4 Interior surfaces of the canisters may be treated by any of several proprietary passivation processes including an electropolishing process to remove or cover reactive metal sites on the interior surface of the vessel and a fused silica coating process.
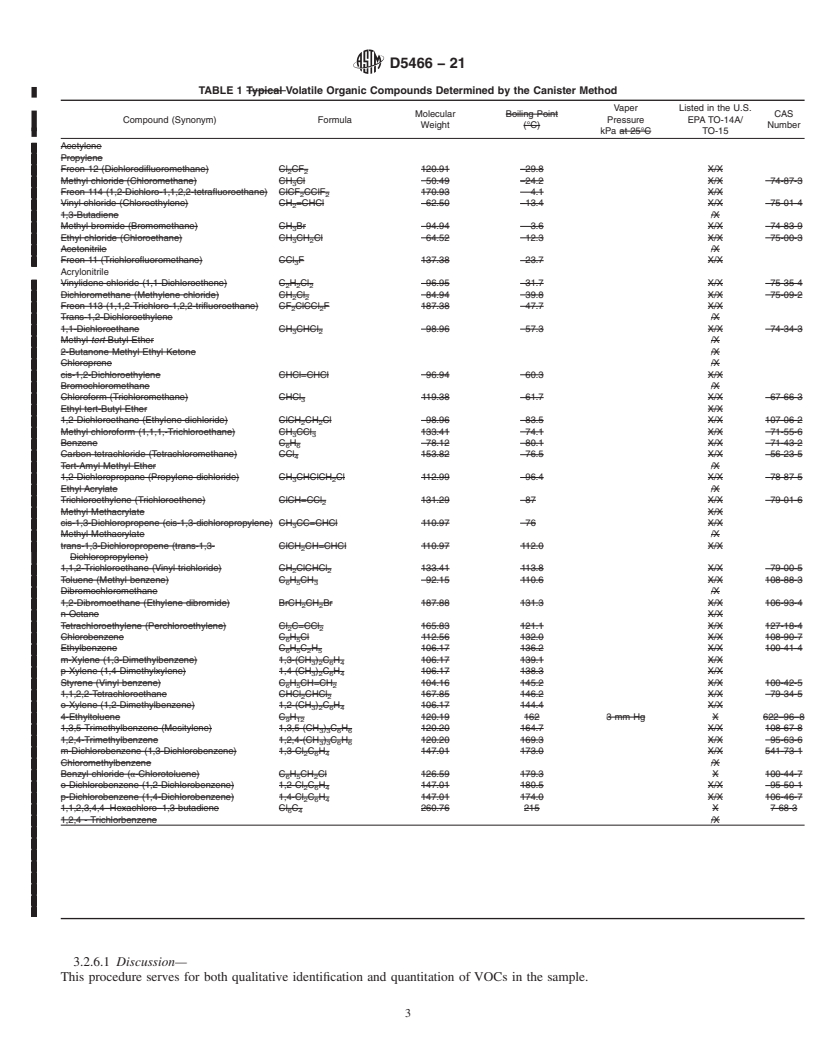
5.5 For this test method, VOCs are defined as organic compounds that can be quantitatively recovered from the canisters having a vapor pressure greater than 10-2 kPa at 25ºC (see Table 1 for examples).
5.6 Target compound polarity is also a factor in compound recovery. Aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons from C1 to C13 have been successfull...
SCOPE
1.1 This test method describes a procedure for sampling and analysis of selected volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in ambient, indoor, and workplace atmospheres. The test method is based on the collection of whole air samples in stainless steel canisters with specially treated (passivated) interior surfaces.
1.2 For sample analysis, a portion of the sample is subsequently removed from the canister and the collected VOCs are selectively concentrated by adsorption or condensation onto a trap, subsequently released by thermal desorption, separated by gas chromatography, and measured by a low resolution mass spectrometric detector. This test method describes procedures for sampling into canisters to final pressures both above and below atmospheric pressure (respectively referred to as pressurized and subatmospheric pressure sampling).2
1.3 This test method is applicable to specific VOCs that have been determined to be stable when stored in canisters (see Table 1). Numerous compounds, many of which are chlorinated VOCs, have been successfully tested for storage stability in pressurized canisters (1-4).3 Information on storage stability is also available for polar compounds (5-7). This test method has been documented for the compounds listed in Table 1 and performance results apply only to those compounds. A laboratory may determine other VOCs by this test method after completion of verification studies that include measurement of recovery as specified in 5.7 and that are as extensive as required to meet the performance needs of the customer and the given application.
1.4 The procedure for collecting the sample involves the use of inlet lines, air filters, flow rate regulators for obtaining time-integrated samples, and in the case of pressurized samples, an air pump. Typical long-term fixed location canister samplers have been designed to automatically start and stop the sample collection process using electronically...
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D5466 − 21
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Volatile Organic Compounds in
Atmospheres (Canister Sampling, Mass Spectrometry
1
Analysis Methodology)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5466; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 1.4 Theprocedureforcollectingthesampleinvolvestheuse
of inlet lines, air filters, flow rate regulators for obtaining
1.1 Thistestmethoddescribesaprocedureforsamplingand
time-integrated samples, and in the case of pressurized
analysis of selected volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in
samples,anairpump.Typicallong-termfixedlocationcanister
ambient, indoor, and workplace atmospheres. The test method
samplershavebeendesignedtoautomaticallystartandstopthe
isbasedonthecollectionofwholeairsamplesinstainlesssteel
sample collection process using electronically actuated valves
canisters with specially treated (passivated) interior surfaces.
and timers (8-10). Temporary or short-term canister samplers
1.2 For sample analysis, a portion of the sample is subse-
may require the user to manually start and stop sample
quently removed from the canister and the collectedVOCs are
collection. A weatherproof shelter may be required if the
selectively concentrated by adsorption or condensation onto a
sampler is used outdoors. For the purposes of this test method,
trap,subsequentlyreleasedbythermaldesorption,separatedby
refer to Practice D1357 for practices and planning ambient
gas chromatography, and measured by a low resolution mass
sampling events.
spectrometric detector. This test method describes procedures
for sampling into canisters to final pressures both above and 1.5 The organic compounds that have been successfully
3
below atmospheric pressure (respectively referred to as pres- measured single-digit micrograms per cubic metre (µg/m (or
2
surized and subatmospheric pressure sampling). single digit parts-per-billion by volume (ppbv)) concentration
with this test method are listed in order of approximate
1.3 This test method is applicable to specific VOCs that
retentiontimeinTable1.ThetestmethodisapplicabletoVOC
havebeendeterminedtobestablewhenstoredincanisters(see
concentrations ranging from the detection limit to approxi-
Table 1). Numerous compounds, many of which are chlori-
3
mately 1000 µg/m (300 ppbv). Above this concentration,
natedVOCs,havebeensuccessfullytestedforstoragestability
3
smaller sample aliquots of sample gas may be analyzed or
in pressurized canisters (1-4). Information on storage stability
samples can be diluted with dry ultra-high-purity nitrogen or
is also available for polar compounds (5-7). This test method
air or equivalent.
has been documented for the compounds listed in Table 1 and
performance results apply only to those compounds.Alabora-
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
tory may determine other VOCs by this test method after
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
completion of verification studies that include measurement of
standard.
recovery as specified in 5.7 and that are as extensive as
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the
requiredtomeettheperformanceneedsofthecustomerandthe
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
given application.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D22 on Air
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Quality and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D22.05 on Indoor Air.
Current edition approved Aug. 15, 2021. Published September 2021. Originally
Safety practices should be part of the user’s SOP manual.
approved in 1993. Last previous edition approved in 2015 as D5466–15. DOI:
1.8 This international standard was developed in accor-
10.1520/D5466-21.
2
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
ThistestmethodisbasedonEPACompendiumMethodTO-15,“Determination
of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) in Air Collected in Specially-Prepared
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Canisters and Analyzed by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry (GC/MS)”
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
January 1999.
3
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Theboldfacenumbersinparenthesesrefertothelistofreferencesattheendof
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D5466 − 15 D5466 − 21
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Volatile Organic Compounds in
Atmospheres (Canister Sampling Sampling, Mass
1
Spectrometry Analysis Methodology)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5466; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method describes a procedure for sampling and analysis of selected volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in ambient,
indoor, and workplace atmospheres. The test method is based on the collection of whole air samples in stainless steel canisters with
specially treated (passivated) interior surfaces.
1.2 This standard describes a procedure for sampling and analysis of selected volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in ambient,
indoor, and workplace atmospheres. The test method is based on the collection of whole air samples in stainless steel canisters with
specially treated (passivated) interior surfaces. For sample analysis, a portion of the sample is subsequently removed from the
canister and the collected VOCs are selectively concentrated by adsorption or condensation onto a trap, subsequently released by
thermal desorption, separated by gas chromatography, and measured by a low resolution mass spectrometric detector or other
detector(s). detector. This test method describes procedures for sampling into canisters to final pressures both above and below
2
atmospheric pressure (respectively referred to as pressurized and subatmospheric pressure sampling).
1.3 This test method is applicable to specific VOCs that have been determined to be stable when stored in canisters. canisters (see
Table 1). Numerous compounds, many of which are chlorinated VOCs, have been successfully tested for storage stability in
3
pressurized canisters (1-4). Documentation is also available demonstrating stability of VOCs in subatmospheric pressure canisters.
Information on storage stability is also available for many polar compounds as well (5-7). This test method has been documented
for the compounds listed in Table 1 and performance results apply only to those compounds. A laboratory may determine other
VOCs by this test method after completion of verification studies that include measurement of recovery as specified in 5.7 and that
are as extensive as required to meet the performance needs of the customer and the given application.
1.4 The procedure for collecting the sample involves the use of inlet lines, air filters, flow rate regulators for obtaining
time-integrated samples, and in the case of pressurized samples, an air pump. Typical long-term fixed location canister samplers
have been designed to automatically start and stop the sample collection process using electronically actuated valves and timers
(8-10). Temporary or short-term canister samplers may require the user to manually start and stop sample collection. A
weatherproof shelter may be required if the sampler is used outdoors. For the purposes of this test method, refer to Practice D1357
for practices and planning ambient sampling events.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D22 on Air Quality and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D22.05 on Indoor Air.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2015Aug. 15, 2021. Published June 2016September 2021. Originally approved in 1993. Last previous edition approved in 20072015 as
D5466 – 01 (2007).D5466 – 15. DOI: 10.1520/D5466-15.10.1520/D5466-21.
2
This test method is based on EPA Compendium Method TO-14, “The Determination TO-15, “Determination of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) in Ambient Air
Using SUMMA Passivated Canister Sampling and Gas Chromatographic Analysis,” May 1988.Air Collected in Specially-Prepared Canisters and Analyzed by Gas
Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry (GC/MS)” January 1999.
3
The boldface numbers in parentheses refer to the list of references at the end of the standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5466 − 21
3
1.5 The organic compounds that have been successfully measured at single-digit single-digit micrograms per cubic metre (μg/m
(or single digit parts-per-billion by volume (ppbv) levels(ppbv)) concentration with this test method are liste
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.