ASTM F734-95(2011)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Shear Strength of Fusion Bonded Polycarbonate Aerospace Glazing Material
Standard Test Method for Shear Strength of Fusion Bonded Polycarbonate Aerospace Glazing Material
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
At this writing, aerospace quality extruded transparent polycarbonate material is not available in thicknesses greater than 0.5 in. (12.7 mm). When a requirement exists for sheets thicker than 0.5 in. (12.7 mm), two or more sheets are fusion bonded together to form a single sheet of the desired thickness.
The structural integrity of the completed transparency depends on the integrity of the fusion bond. This test applies torsional shear loads to measure the structural integrity of the fusion bond. This test method is considered more reliable and more reproducible than shear tests in tension or compression.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method determines the shear yield strength Fsy and shear ultimate strength Fsu of fusion bonds in polycarbonate by applying torsional shear loads to the fusion-bond line.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: F734 − 95 (Reapproved 2011)
Standard Test Method for
Shear Strength of Fusion Bonded Polycarbonate Aerospace
Glazing Material
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationF734;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginal
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope required to fracture the fusion bond is transformed into the
torsional shear strength of the fusion bond.
1.1 This test method determines the shear yield strength F
sy
and shear ultimate strength F of fusion bonds in polycarbon-
su
ate by applying torsional shear loads to the fusion-bond line.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 At this writing, aerospace quality extruded transparent
2. Referenced Documents
polycarbonate material is not available in thicknesses greater
2.1 ASTM Standards:
than 0.5 in. (12.7 mm). When a requirement exists for sheets
D618Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
thicker than 0.5 in. (12.7 mm), two or more sheets are fusion
bondedtogethertoformasinglesheetofthedesiredthickness.
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard: 5.2 The structural integrity of the completed transparency
depends on the integrity of the fusion bond. This test applies
3.1.1 fusion bond, n—thebondingoftwopiecesofthesame
material using heat and pressure. torsional shear loads to measure the structural integrity of the
fusion bond. This test method is considered more reliable and
3.1.2 shear, n—internal force tangential to the section on
more reproducible than shear tests in tension or compression.
which it acts.
3.1.3 shear strength, n—the maximum allowable stress in a
6. Apparatus
bodyresultingfromforceswhichtendtocausetwocontiguous
NOTE 1—A standard torsional test machine may be substituted for the
parts of the body to slide relative to each other in a direction
apparatus described in this section. The machine shall have variable
parallel to their plane of contact.
angular displacement rates from 8 to 800°/min. (0.14 to 14 rad/min.). If a
torsional test machine is used, the calibration and standardization in
3.1.4 torsional shear fixture, n—a device used to apply a
Section 8 should be disregarded.
shear force in the circular section of the test specimen to
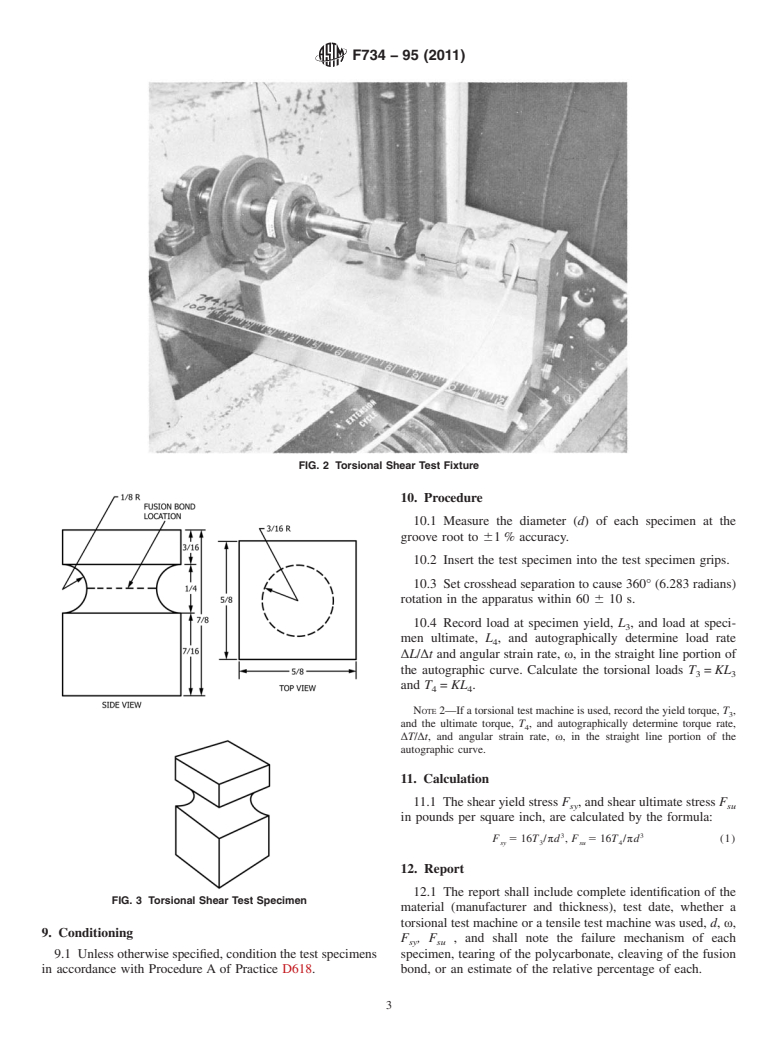
produce a peripherally uniform stress distribution. 6.1 Torsional Shear Fixture—Illustrations of the fixture are
shown in Figs. 1 and 2.
4. Summary of Test Method
6.2 Calibration Load Arm—A lever arm with a load pan
4.1 Test specimens are prepared with a fusion bond at the
shallbeprovidedforpurposesofcalibratingthetorsionalshear
center of a polycarbonate laminate joined to two metal test
apparatus.
blocks. A twisting action is applied to one block and the load
6.3 Universal Testing Machine—Anautographicallyrecord-
ing universal tensile testing machine shall be used to apply a
This practice is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F07 on Aerospace
constant rate of rotation to the torsional shear fixture by means
andAircraft and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F07.08 on Transparent
Enclosures and Materials. of the loading cable. The machine shall have variable cross-
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2011. Published April 2012. Originally
head rates (from 0.2 in./min [5.08 mm/min] to 20 in./min [508
approved in 1981. Last previous edition approved in 2006 as F734–95(2006).
mm/min.]), and a calibrated load measurement mechanism
DOI: 10.1520/F0734-95R11.
usable in a range from 0 to 200 lb (0 to 90 kg) in tension.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
6.4 Calibrated Spring Scales, 0 to 10 lb (4.54 kg) 61%,
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. are required for calibration purposes.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
F734 − 95 (2011)
FIG. 1 Torsional Shear Test Fixture (All Dimensions in Inches)
7. Test Specimens and Sample 8.3 Determine the equivalent weight of the calibrating arm
attheloadpanwithnotorsionalresistanceintheapparatusand
7.1 Machine test specimens to the geometry shown in Fig.
with the load arm level. This load is L .
3. Machine specimens at less than 1-m (3.28-ft)/s surface
velocity to avoid heat buildup during machining. Po
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.