ASTM D6587-12
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Yarn Number Using Automatic Tester
Standard Test Method for Yarn Number Using Automatic Tester
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method for yarn number is satisfactory for acceptance of commercial shipments and is used in the trade.
In case of a dispute arising from differences in reported test results when using this Test Method for acceptance testing of commercial shipments, the purchaser and the supplier should either use the referee Test Method D1907 for yarn number or conduct comparative tests to determine if there is a statistical bias between their laboratories. Competent statistical assistance is recommended for the investigation of bias. As a minimum, the two parties should take a group of test specimens that are as homogeneous as possible and that are from a lot of material of the type in question. The test specimens should then be randomly assigned in equal numbers to each laboratory for testing. The average results from the two laboratories should be compared using appropriate statistical analysis and a probability level chosen by the two parties before the testing is begun. If a bias is found, either its cause must be found and corrected or the purchaser and the supplier must agree to interpret future test results with consideration to the known bias.
This test method is also used for the quality control for both filament and spun yarns.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of yarn number of filament and spun yarns using automated testers. Some of the instruments are stand-alone and others are optional modules for instruments that perform additional tests.
1.1.1 The instruments are capable of measuring yarn numbers up to 4000 dtex (3600 denier).
Note 1—For determination of yarn number by use of reel and balance, refer to Test Method D1907.
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D6587 − 12
StandardTest Method for
1
Yarn Number Using Automatic Tester
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6587; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3.1.1 The following terms are relevant to this standard:
cotton count, denier, linear density, tex, yarn number, yarn
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of yarn
numbering system.
number of filament and spun yarns using automated testers.
Someoftheinstrumentsarestand-aloneandothersareoptional
3.2 For all other textile terms used in this test method, see
modules for instruments that perform additional tests.
Terminology D123.
1.1.1 The instruments are capable of measuring yarn num-
bers up to 4000 dtex (3600 denier).
4. Summary of Test Method
NOTE 1—For determination of yarn number by use of reel and balance,
4.1 A specified length of yarn (specimen) is automatically
refer to Test Method D1907.
stripped directly from the package, cut, and weighed. The yarn
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
number is calculated by an interfaced computer, displayed on a
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
monitor, and may be printed. The yarn number can be reported
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
in tex, denier, or cotton count units.
system shall be used independently of the other. Combining
values from the two systems may result in non-conformance
5. Significance and Use
with the standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
5.1 This test method for yarn number is satisfactory for
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the acceptance of commercial shipments and is used in the trade.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
5.1.1 In case of a dispute arising from differences in
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
reported test results when using this Test Method for accep-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
tance testing of commercial shipments, the purchaser and the
supplier should either use the referee Test Method D1907 for
2. Referenced Documents
yarn number or conduct comparative tests to determine if there
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
is a statistical bias between their laboratories. Competent
D123 Terminology Relating to Textiles
statistical assistance is recommended for the investigation of
D1776 Practice for Conditioning and Testing Textiles
bias.As a minimum, the two parties should take a group of test
D1907 Test Method for Linear Density of Yarn (Yarn Num-
specimens that are as homogeneous as possible and that are
ber) by the Skein Method
from a lot of material of the type in question. The test
D2258 Practice for Sampling Yarn for Testing
specimens should then be randomly assigned in equal numbers
D4849 Terminology Related to Yarns and Fibers
to each laboratory for testing.The average results from the two
laboratories should be compared using appropriate statistical
3. Terminology
analysis and a probability level chosen by the two parties
3.1 For all terminology relating to D13.58, Yarns and
before the testing is begun. If a bias is found, either its cause
Fibers, refer to Terminology D4849.
must be found and corrected or the purchaser and the supplier
must agree to interpret future test results with consideration to
the known bias.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D13 on Textiles
5.2 This test method is also used for the quality control for
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D13.58 on Yarns and Fibers.
Current edition approved July 1, 2012. Published October 2012. Originally
both filament and spun yarns.
ε1
approved in 2000. Last previous edition approved in 2006 as D6587–00(2006) .
DOI: 10.1520/D6587-12.
6. Apparatus
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
6.1 Automatic Yarn Numbering Instrument, with interfaced
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. computer.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6587 − 12
3
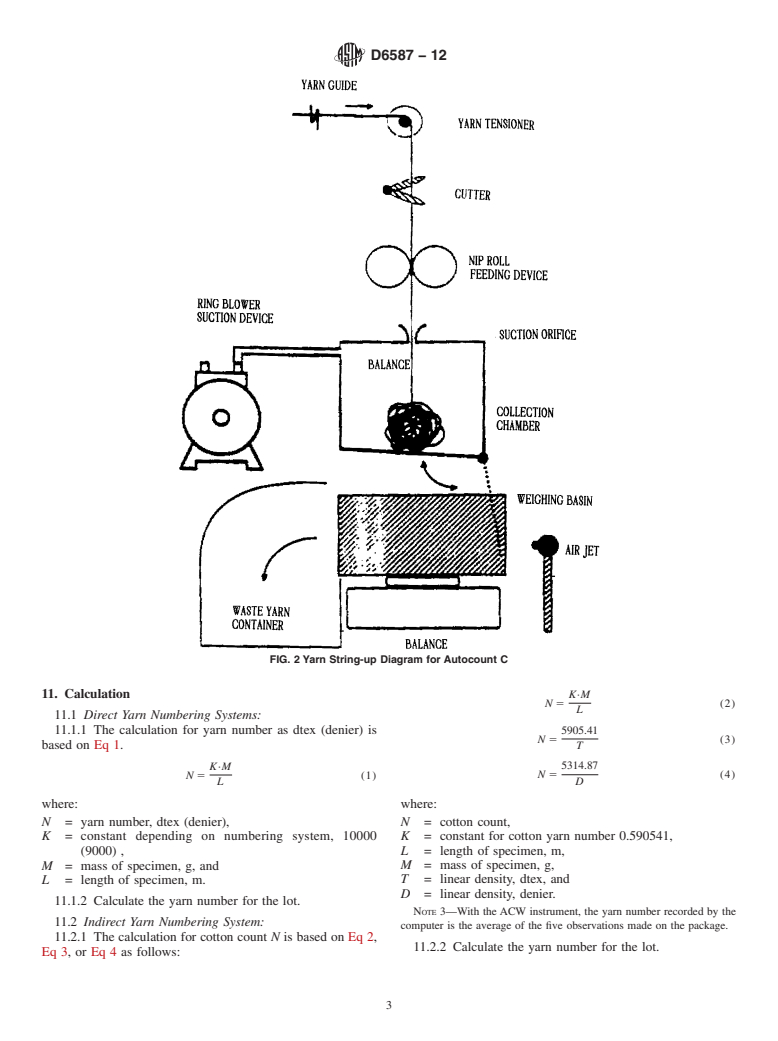
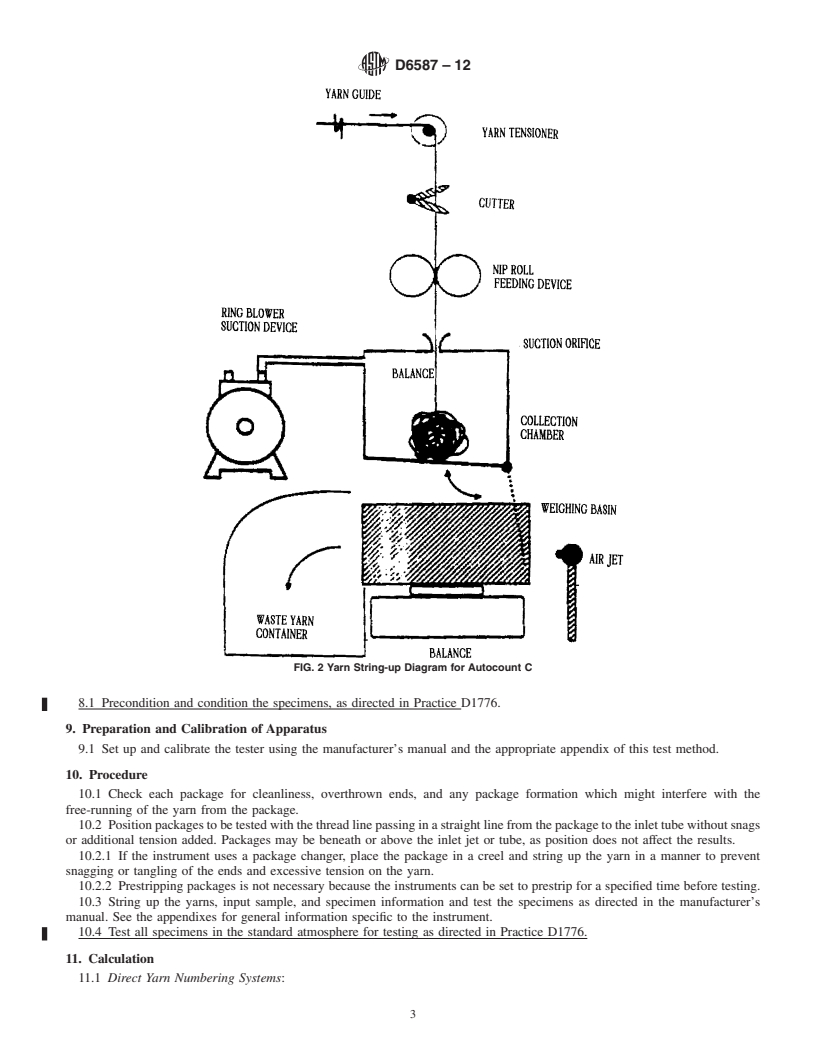
6.1.1 ACW(AutomaticCutandWeigh)YarnTester, SeriesT lot sample, determine at random which shipping units are to
for textile yarns, Series BCF for bulked continuous filament have each number of packages drawn.
(BCF) carpet yarns, and Series I for industrial yarns. See Fig.
7.3 Test Specime
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation:D6587–00 (Reapproved 2006) Designation:D6587–12
Standard Test Method for
1
Yarn Number Using Automatic Tester
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6587; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
´ NOTE—Section 3 was updated editorially in August 2006.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of yarn number of filament and spun yarns using automated testers. Some of the
instruments are stand-alone and others are optional modules for instruments that perform additional tests.
1.1.1 The instruments are capable of measuring yarn numbers up to 4000 dtex (3600 denier).
NOTE 1—For determination of yarn number by use of reel and balance, refer to Test Method D1907.
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the
inch-poundunitsareinparentheses.Thevaluesstatedineachsystemaremaynotbeexactequivalents;therefore,eachsystemshall
beusedindependentlyoftheother.Combiningvaluesfromthetwosystemsmayresultininaccuraciesofresults.non-conformance
with the standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D123 Terminology Relating to Textiles
D1776 Practice for Conditioning and Testing Textiles
D1907 Test Method for Linear Density of Yarn (Yarn Number) by the Skein Method
D2258 Practice for Sampling Yarn for Testing
D4849 Terminology Related to Yarns and Fibers
3. Terminology
3.1 For all terminology relating to D13.58, Yarns and Fibers, refer to Terminology D4849.
3.1.1 The following terms are relevant to this standard: cotton count, denier, linear density, tex, yarn number, yarn numbering
system.
3.2 For all other textile terms used in this test method, see Terminology D123.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 A specified length of yarn (specimen) is automatically stripped directly from the package, cut, and weighed. The yarn
number is calculated by an interfaced computer, displayed on a monitor, and may be printed. The yarn number can be reported
in tex, denier, or cotton count units.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 This test method for yarn number is satisfactory for acceptance of commercial shipments and is used in the trade.
5.1.1 In case of a dispute arising from differences in reported test results when using this Test Method for acceptance testing
of commercial shipments, the purchaser and the supplier should either use the referee Test Method D1907 for yarn number or
conduct comparative tests to determine if there is a statistical bias between their laboratories. Competent statistical assistance is
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D13 on Textiles and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D13.58 on Yarns and Fibers.
Current edition approved June 1, 2006. Published August 2006. Originally approved in 2000. Last previous edition approved in 2000 as D6587–00. DOI:
10.1520/D6587-00R06E01.
´1
Current edition approved July 1, 2012. Published October 2012. Originally approved in 2000. Last previous edition approved in 2006 as D6587–00(2006) . DOI:
10.1520/D6587-12.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book ofASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6587–12
recommended for the investigation of bias. As a minimum, the two parties should take a group of test specimens that are as
homogeneous as possible and that are from a lot of material of the type in question. The test specimens should then be randomly
assigned in equal numbers to each laboratory for testing. The average results from the two laboratories should be compared using
appropriatestatisticalanalysisandaprobabilitylevelchosenbythetwopartiesbeforethetestingisbegun.Ifabiasisfound,either
itscausemustbefoundandcorrectedorthepurcha
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.