ASTM B916-01
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Adherence of Porcelain Enamel Coatings to Sheet Metal
Standard Test Method for Adherence of Porcelain Enamel Coatings to Sheet Metal
SCOPE
1.1 The scope of this test method is:
1.1.1 To determine quantitatively the amount of enamel remaining after the porcelain enamel coating specimen has been deformed;
1.1.2 To standardize the deformation parameters for testing adherence of porcelain enamel to sheet metal; and,
1.1.3 To provide a quantitative adherence rating scale for comparison to reference standards.
1.2 This adherence test method is applicable to porcelain enamel coatings on substrates from 18 to 24 gage (0.0478 to 0.025 in. or from 1.214 to 0.654 mm).
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: B 916 – 01
Standard Test Method for
Adherence of Porcelain Enamel Coatings to Sheet Metal
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B 916; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3.3 A satisfactory degree of deformation and damage are
obtained if the conditions in 3.2 use the following parameters:
1.1 The scope of this test method is:
0.50-in. (12.7-mm) diameter hemispherical indenter, 0.75-in.
1.1.1 To determine quantitatively the amount of enamel
(19.1-mm) diameter bottomless die (lower plunger guide in
remaining after the porcelain enamel coating specimen has
Fig. 1) with sharp edge, and 80–in./lb (9.03–J) energy at
been deformed;
impact.
1.1.2 To standardize the deformation parameters for testing
3.4 Deformation Devices, of other designs may be used
adherence of porcelain enamel to sheet metal; and,
provided that the parameters in 3.3 are used.
1.1.3 To provide a quantitative adherence rating scale for
3.5 Adherence Reference Standards, see 7.1.
comparison to reference standards.
1.2 This adherence test method is applicable to porcelain
4. Test Specimens
enamel coatings on substrates from 18 to 24 gage (0.0478 to
4.1 The test specimens shall be flat enameled panels not less
0.025 in. or from 1.214 to 0.654 mm).
2 2
in size than 4 in. (101.6 mm ). Larger sizes and shapes may be
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
used provided that a flat surface can be held firmly against and
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
parallel to the lower plunger guide during deformation.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
5. Safety Precautions
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
5.1 During the procedure in 6.1, fine enameled chips may be
2. Significance and Use released with some force from the steel surface; therefore, it is
recommended that personnel in the immediate vicinity of the
2.1 The measurement of adherence in porcelain enamel
test wear safety goggles.
systems, such as ground coat, ground coat/cover coat, and
direct-on cover-coat enamels, is an important procedure for
6. Procedure
monitoring process variables in metal preparation, enamel
6.1 Specimen Deformation—The hammer weight of the
application thickness, steel selection, and enamel selection, as
suggested drop weight device is 5 lb (2268 g), which requires
well as assuring the ultimate quality of the finished product.
a 16-in. (406.4-mm) drop distance to yield the specified
3. Apparatus 80-in./lb (9.03-J) energy at impact. The hammer weight of the
2 drop weight device may range from 2 to 8 lb (907 to 3629 g).
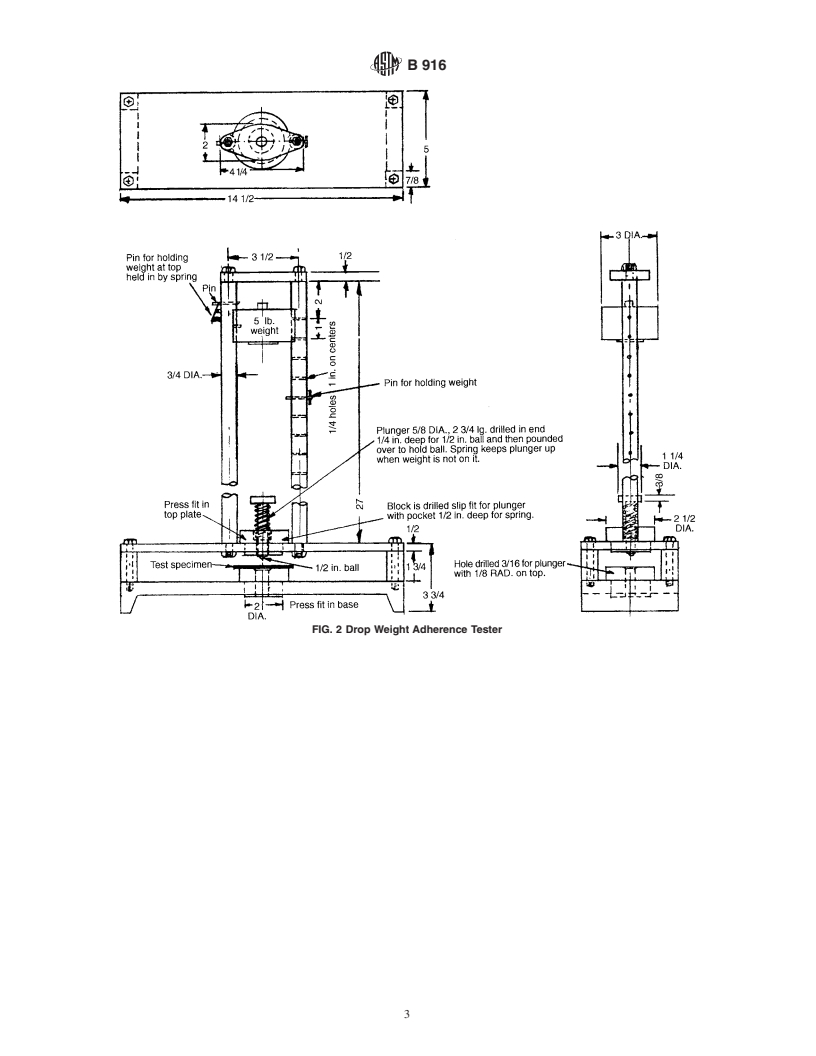
3.1 Drop Weight Deformation Device , see Figs. 1 and 2.
If the hammer weight is within this range, but not 5 lb,
3.2 The drop weight deformation device as shown in Fig. 1
calculate the drop distance to yield 80 in./lbf of energy at
shall impart a single impact blow from a hemispherical
impact. The center of the area to be deformed shall be at least
indenter to a coated specimen supported over a sharp-edged
1 ⁄2 in. (38.1 mm) from the edge of the specimen. If two or
bottomless die. The area of the deformation and the concomi-
more deformations are made on a single specimen, place them
cant damage to the coating is largely influenced by the size of
at least 3 in. (76.2 mm) between centers and average and treat
the hemispherical indenter; the die opening size and edge
the measurements on them as a single measurement. Raise and
sharpness; and, the energy of the blow at impact.
secure the hammer to obtain the required drop distance. Hold
the specimen firmly against and parallel to the top surface of
the die with the enam
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.