ASTM E1571-06
(Practice)Standard Practice for Electromagnetic Examination of Ferromagnetic Steel Wire Rope
Standard Practice for Electromagnetic Examination of Ferromagnetic Steel Wire Rope
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
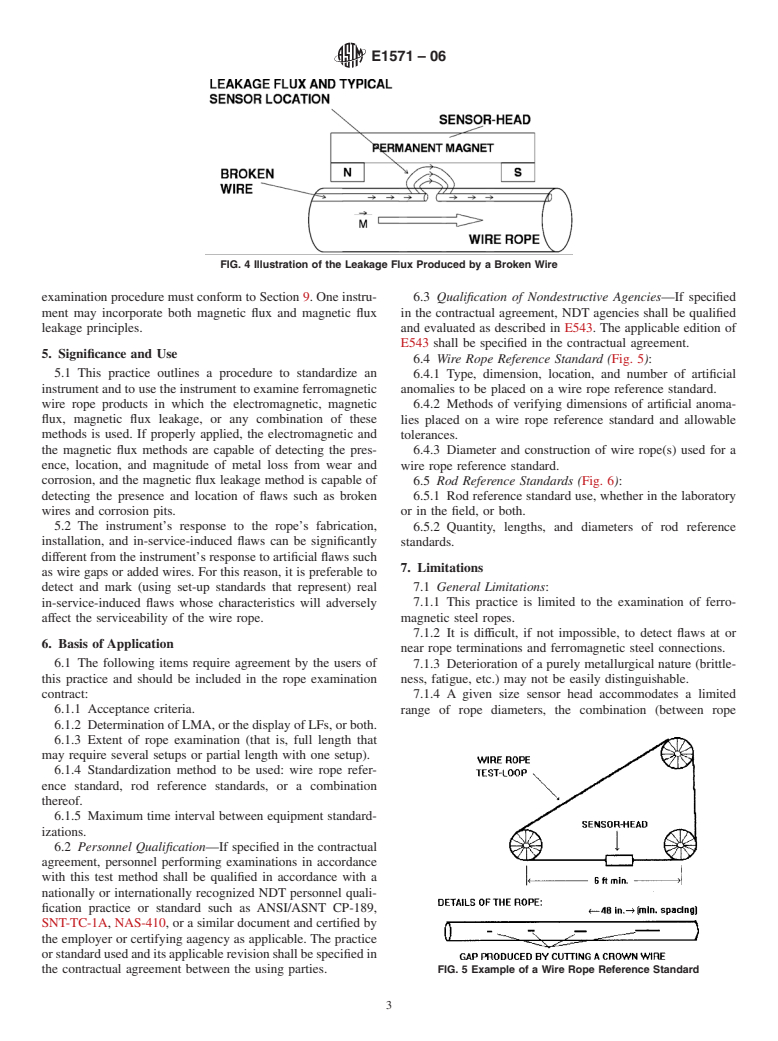
This practice outlines a procedure to standardize an instrument and to use the instrument to examine ferromagnetic wire rope products in which the electromagnetic, magnetic flux, magnetic flux leakage, or any combination of these methods is used. If properly applied, the electromagnetic and the magnetic flux methods are capable of detecting the presence, location, and magnitude of metal loss from wear and corrosion, and the magnetic flux leakage method is capable of detecting the presence and location of flaws such as broken wires and corrosion pits.
The instrument’response to the rope’fabrication, installation, and in-service-induced flaws can be significantly different from the instrument’response to artificial flaws such as wire gaps or added wires. For this reason, it is preferable to detect and mark (using set-up standards that represent) real in-service-induced flaws whose characteristics will adversely affect the serviceability of the wire rope.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice covers the application and standardization of instruments that use the electromagnetic, the magnetic flux, and the magnetic flux leakage examination method to detect flaws and changes in metallic cross-sectional areas in ferromagnetic wire rope products.
1.1.1 This practice includes rope diameters up to 2.5 in. (63.5 mm). Larger diameters may be included, subject to agreement by the users of this practice.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:E1571–06
Standard Practice for
Electromagnetic Examination of Ferromagnetic Steel Wire
1
Rope
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E1571; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 dual-function instrument—a wire rope NDT instru-
1.1 This practice covers the application and standardization
ment designed to detect and display changes of metallic
of instruments that use the electromagnetic, the magnetic flux,
cross-sectional area on one channel and local flaws on another
and the magnetic flux leakage examination method to detect
channel of a dual-channel strip chart recorder or another
flaws and changes in metallic cross-sectional areas in ferro-
appropriate device.
magnetic wire rope products.
3.2.2 local flaw (LF)—a discontinuity in a rope, such as a
1.1.1 This practice includes rope diameters up to 2.5 in.
broken or damaged wire, a corrosion pit on a wire, a groove
(63.5 mm). Larger diameters may be included, subject to
worn into a wire, or any other physical condition that degrades
agreement by the users of this practice.
the integrity of the rope in a localized manner.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.2.3 loss of metallic cross-sectional area (LMA)—a rela-
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
tive measure of the amount of material (mass) missing from a
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
location along the wire rope and is measured by comparing a
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
point with a reference point on the rope that represents
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
maximum metallic cross-sectional area, as measured with an
2. Referenced Documents instrument.
2
3.2.4 single-function instrument—a wire rope NDT instru-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
ment designed to detect and display either changes in metallic
E543 Specification for Agencies Performing Nondestruc-
cross-sectional area or local flaws, but not both, on a strip chart
tive Testing
recorder or another appropriate device.
E1316 Terminology for Nondestructive Examinations
2.2 Other Documents:
4. Summary of Practice
ANSI/ASNT-CP-189 ASNT Standard for Qualification and
3
4.1 The principle of operation of a wire rope nondestructive
Certification in Nondestructive Testing Personnel
examination instrument is as follows:
SNT-TC-1A Recommended Practice for Personnel Qualifi-
3
4.1.1 AC Electromagnetic Instrument—An electromagnetic
cation and Certification in Nondestructive Testing
wire rope examination instrument works on the transformer
NAS-410 Certification and Qualification of Nondestructive
4
principle with primary and secondary coils wound around the
Personnel (Quality Assurance Committee)
rope (Fig. 1). The rope acts as the transformer core. The
3. Terminology
primary (exciter) coil is energized with a low frequency
alternating current (ac), typically in the 10 to 30 Hz range. The
3.1 Definitions—See Terminology E1316 for general termi-
secondary (search) coil measures the magnetic characteristics
nology applicable to this practice.
of the rope. Any significant change in the magnetic character-
istics in the core (wire rope) will be reflected as voltage
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E07 on Nonde-
changes (amplitude and phase) in the secondary coil. Electro-
structive Testing and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E07.07 on
Electromagnetic Method. magnetic instruments operate at relatively low magnetic field
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2006. Published January 2007. Originally
strengths; therefore, it is necessary to completely demagnetize
published as E1571 – 93. Last previous edition E1571 – 01. DOI: 10.1520/E1571-
the rope before the start of an examination. This type of
06.
2
instrument is designed to detect changes in metallic cross-
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
sectional area.
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
4.1.2 Direct Current and Permanent Magnet (Magnetic
the ASTM website.
3 Flux) Instruments—Direct current (dc) and permanent magnet
AvailablefromAmericanSocietyforNondestructiveTesting(ASNT),P.O.Box
instruments (Figs. 2 and 3) supply a constant flux that
28518, 1711 Arlingate Ln., Columbus, OH 43228-0518, http://www.asnt.org.
4
Available fromAerospace IndustriesAssociation ofAmerica, Inc. (AIA), 1000
magnetizesalengthofropeasitpassesthroug
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.