ASTM D6142-97
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Analysis of Phenol by Capillary Gas Chromatography
Standard Test Method for Analysis of Phenol by Capillary Gas Chromatography
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of known impurities in phenol by gas chromatography (GC). It is generally meant for the analysis of phenol of 99.9% or greater purity.
1.2 The following applies to all specified limits in this test method: for purposes of determining conformance with this test method, an observed value or calculated value shall be rounded off "to the nearest unit" in the last right-hand digit used in expressing the specification limit in accordance with the rounding-off method of Practice E 29. Precision data is based on impurity concentrations of 15 to 70 mg/kg. Users of this test method believe it is linear over a wider range.
1.3 This Test Method does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements, see Section 9.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: D 6142 – 97
Standard Test Method for
Analysis of Phenol by Capillary Gas Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 6142; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope OSHA Regulations, 29 CFR, paragraphs 1910.1000 and
1910.1200
1.1 This test method covers the determination of known
impurities in phenol by gas chromatography (GC). It is
3. Terminology
generally meant for the analysis of phenol of 99.9 % or greater
3.1 See Terminology D 4790 for definition of terms used in
purity.
this method.
1.2 The following applies to all specified limits in this test
method: for purposes of determining conformance with this
4. Summary of Test Method
test method, an observed value or calculated value shall be
4.1 A known amount of an internal standard is added to a
rounded off “to the nearest unit” in the last right-hand digit
sample of phenol. The prepared sample is mixed and analyzed
used in expressing the specification limit in accordance with
by a gas chromatograph equipped with a flame ionization
the rounding-off method of Practice E 29. Precision data is
detector (FID). The peak area of each impurity and the internal
based on impurity concentrations of 15 to 70 mg/kg. Users of
standard is measured. The amount of each impurity is calcu-
this test method believe it is linear over a wider range.
lated from the ratio of the peak area of the internal standard
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
versus the peak area of the impurity. Results are reported in
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
milligrams per kilogram.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
5. Significance and Use
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard
5.1 This test method is suitable for setting specifications on
statements, see Section 9.
phenol and for use as an internal quality control tool where
phenol is produced or is used in a manufacturing process. It
2. Referenced Documents
may also be used in development or research work involving
2.1 ASTM Standards:
phenol. It is generally applied to determining those commonly
D 3852 Practice for Sampling and handling Phenol and
2 occurring impurities such as mesityl oxide, cumene, hydroxy-
Cresylic Acid
acetone, acetone, alpha-methylstyrene, 2-methylbenzofuran,
D 4790 Terminology of Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Re-
2 and acetophenone.
lated Chemicals
5.2 Purity is commonly reported by subtracting the deter-
E 29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
3 mined expected impurities from 100.00. However, a gas
Determine Conformance with Specific Specifications
chromatographic analysis cannot determine absolute purity if
E 355 Practice for Gas Chromatography Terms and Rela-
3 unknown components are contained within the material being
tionships
examined.
E 691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
6. Interferences
E 1510 Practice for Installing Fused Silica Open Tubular
6.1 The internal standard chosen must be sufficiently re-
Columns in Gas Chromatographs
solved from any impurity and the phenol peak.
2.2 Other Document:
6.2 Any solvent used must also be sufficiently resolved from
any impurity, the internal standard, and the phenol peak.
7. Apparatus
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D16 on
Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Related Chemicals and is the direct responsibility of
7.1 Gas Chromatograph—Any chromatograph having a
Subcommittee D16.02 on Oxygenated Aromatics.
flame ionization detector that can be operated at the conditions
Current edition approved June 10, 1997. Published August 1997.
2 given in Table 1. The system should have sufficient sensitivity
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 06.04.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02.
Available from the Superintendent of Documents, U.S. Government Printing
Office, Washington, DC 20402.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D 6142
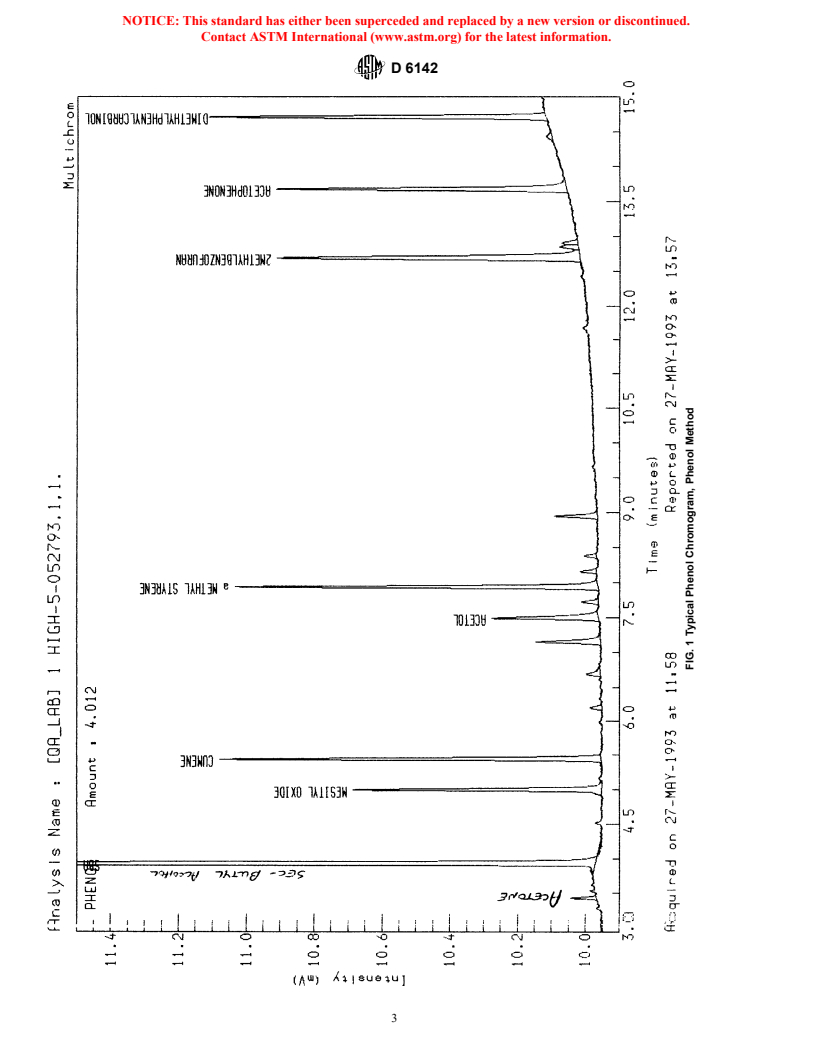
TABLE 1 Instrument Conditions for Phenol Analysis
10. Sampling
Column:
10.1 Refer to Practice D 3852 for proper sampling and
Tubing fused silica
handling of phenol analyzed by this test method.
Stationary phase polyethylene glycol-acid modified
Solid support crosslinked
11. Preparation of Apparatus
Film thickness, μ 0.5
Length, m 50
11.1 Follow manufacturer’s instructions for mounting and
Inside diameter, m 0.32
conditioning the column into the chromatograph and adjusting
Flow rate mL/min 1.3
the instrument to the conditions described in Table 1. Allow
Temperature, °C
Injector 180
sufficient time for the equipment to reach equilibrium. See
Detector 230
Practices E 355 and E 1510 for additional information on gas
Oven
chromatography practices and terminology.
Initial, °C 110 for 6 min
Rate, °C 12 per min
12. Calibration
Final, °C 210 for 90 min
Internal Standard sec-butyl alcohol
12.1 Prepare synthetic mixtures of phenol with representa-
tive impurities on a weight basis. Weigh each impurity to the
nearest 0.0001 g.
to obtain a minimum peak height response for a 2–mg/kg
NOTE 1—Phenol will freeze at room temperature. The sample and
impurity twice the height of the signal background noise.
syringe must be kept warm to prevent freezing. An alternative is to add
7.2 Columns—Different columns have been found satisfac-
about 10 % by weight of a solvent such as methanol that will not be an
tory, depending on the impurities of interest.
interference in the chromatogram.
7.2.1 The column must give satisfactory resolution of the
12.2 Using the exact weight, or alternatively exact volumes
internal standard from phenol and the impurity peaks. Table 1
and densities (see Table 2), calculate the mg/kg concentration
contains a description of one column that has been found
for each impurity in each calibration blend of 12.1.
satisfactory.
12.3 To a known weight of synthetic mixture, add a mea-
7.3 Recorder—Electronic integration is recommended.
sured weight of sec-butanol as the internal standard. Calculate
the concentration of internal standard in mg/kg (25 to 50 mg/kg
8. Reagents
is reasonable). Mix well.
8.1 Purity of Reagent—Reagent grade chemica
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.