ASTM D3628-01
(Practice)Standard Practice for Selection and Use of Emulsified Asphalts
Standard Practice for Selection and Use of Emulsified Asphalts
SCOPE
1.1 This practice covers the selection of emulsified asphalts for various paving and allied uses.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
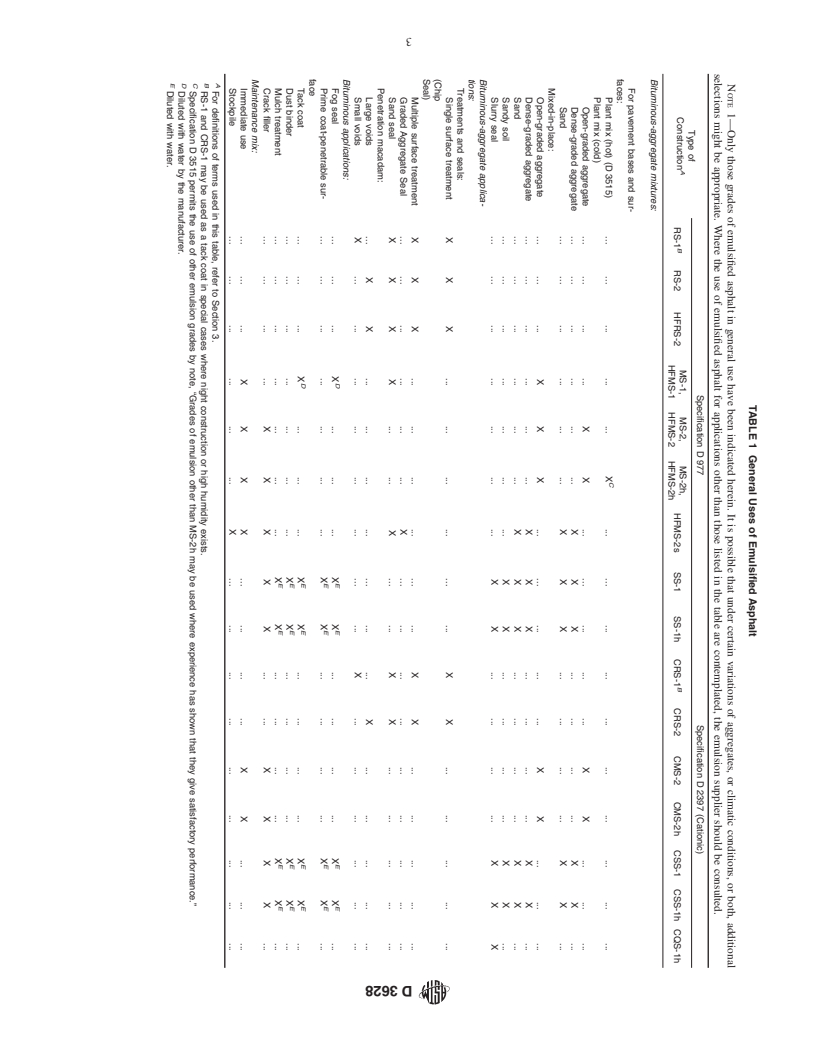
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D 3628 – 01
Standard Practice for
1
Selection and Use of Emulsified Asphalts
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 3628; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3.1.6 dust binder—a light application of bituminous mate-
rial for the express purpose of laying and bonding loose dust.
1.1 This practice covers the selection of emulsified asphalts
3.1.7 fog seal—a light spray application of asphalt to an
for various paving and allied uses.
existing pavement as a seal to inhibit raveling, or seal the
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
surface, or both.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.1.8 graded aggregate seal, n—a single surface treatment
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
in which the aggregate is graded with little or no mineral filler,
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
typically with a nominal maximum size of about 19 mm, and
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
containing sufficient sand that the bituminous material will be
2. Referenced Documents required to penetrate upward into the aggregate cover; the
nominal maximum aggregate size may vary depending on the
2.1 ASTM Standards:
course thickness desired and aggregate availability. It is an
D 8 Terminology Relating to Materials for Roads and Pave-
2
application method used in lieu of a chip seal to provide a
ments
2
lower cost road.
D 977 Specification for Emulsified Asphalt
2
3.1.8.1 Discussion—In this case, nominal maximum size
D 2397 Specification for Cationic Emulsified Asphalt
refers to the definition in Terminology D 8.
D 3515 Specification for Hot-Mixed, Hot-Laid Bituminous
2
3.1.9 maintenance mix—a mixture of bituminous material
Paving Mixtures
and mineral aggregate applied at ambient temperature for use
3. Terminology
in patching holes, depressions, and distress areas in existing
pavements, using appropriate hand or mechanical methods in
3.1 Definitions:
placing and compacting the mix.These mixes may be designed
3.1.1 bituminous-aggregate applications—applications of
for immediate use or for use out of a stockpile at a later date
bituminous material to a prepared aggregate base or pavement
without further processing.
surface followed by the application of aggregate.
3.1.10 mixed-in-place—the procedures by which the bitu-
3.1.2 bituminous-aggregate mixtures—a combination of bi-
minous material and mineral aggregrate are mixed on the job
tuminous material and aggregate that is physically mixed by
site by means of travel plants, blade mixing, or other special
mechanical means, spread on the job site, and compacted.
road-mixing equipment.
3.1.3 bituminous applications—the application of sprayed
3.1.11 mulch treatment—a spray application of bituminous
bituminous coatings not involving the use of aggregates.
material used to temporarily stabilize a recently seeded area.
3.1.4 crack filler—the bituminous material used to fill and
The bituminous material can be applied to the soil or to a straw
seal cracks in existing pavements.
or hay mulch as a tie-down.
3.1.5 dense-graded aggregate—aggregate that is graded
3.1.12 multiple surface treatment—two or more single sur-
from the maximum size, down to and including filler, with the
face treatments placed one on the other. The maximum
object of obtaining a bituminous mix with a controlled void
aggregate size of each successive treatment is usually one half
content and high stability.
that of the previous one, and the total thickness is about the
same as the nominal maximum size aggregate particles of the
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D04 on Road and
first course.
Paving Materials and is the direct responsibility of Subcommitee D04.41 on
3.1.13 open-graded aggregate—aggregate containing little
Emulsified Asphalt Specifications.
or no mineral filler and in which the void spaces in the
Current edition approved Dec. 10, 2001. Published January 2002. Originally
published as D 3628 – 78. Last previous edition D 3628 – 97. compacted aggregate are relatively large.
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.03.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D 3628
3.1.14 pavement bases and surfaces—the lower or underly- 3.1.23 slurry seal—a uniform application of a mixture of
ing pavement course atop the subbase or subgrade and the top emulsified asphalt, fine aggregate, mineral filler, and water to
or wearing course
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.