ASTM D7294-06
(Guide)Standard Guide for Collecting Treatment Process Design Data at a Contaminated Site-A Site Contaminated With Chemicals of Interest
Standard Guide for Collecting Treatment Process Design Data at a Contaminated Site-A Site Contaminated With Chemicals of Interest
SCOPE
1.1 This guide lists the physical and chemical treatment processes design data needed to evaluate, select, and design treatment processes for remediation of contaminated sites. This data is listed in . Much of these data can be obtained and analyzed at the site with instruments and test kits.
1.2 It is recommended that this guide be used in conducting environmental site assessments and Remedial Investigations/Feasibility Studies (RI/FS) and selections of remedy in U.S. Code of Federal Regulations 40 CFR 300.430.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D7294 − 06
StandardGuide for
Collecting Treatment Process Design Data at a
Contaminated Site—A Site Contaminated With Chemicals of
Interest
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7294; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D3152 Test Method for Capillary-Moisture Relationships
for Fine-Textured Soils by Pressure-MembraneApparatus
1.1 This guide lists the physical and chemical treatment
(Withdrawn 2007)
processes design data needed to evaluate, select, and design
D3590 Test Methods for Total Kjeldahl Nitrogen in Water
treatmentprocessesforremediationofcontaminatedsites.This
D3921 Test Method for Oil and Grease and Petroleum
data is listed in Tables 1 and 2. Much of these data can be
Hydrocarbons in Water
obtained and analyzed at the site with instruments and test kits.
D4327 Test Method for Anions in Water by Suppressed Ion
1.2 It is recommended that this guide be used in conducting
Chromatography
environmental site assessments and Remedial Investigations/
D4564 Test Method for Density and Unit Weight of Soil in
Feasibility Studies (RI/FS) and selections of remedy in U.S.
Place by the Sleeve Method
Code of Federal Regulations 40 CFR 300.430.
D4611 Test Method for Specific Heat of Rock and Soil
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the D4943 Test Method for Shrinkage Factors of Soils by the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
Wax Method
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- D4972 Test Method for pH of Soils
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
D5084 Test Methods for Measurement of Hydraulic Con-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. ductivity of Saturated Porous Materials Using a Flexible
Wall Permeameter
2. Referenced Documents
D5334 Test Method for Determination of Thermal Conduc-
tivity of Soil and Soft Rock by Thermal Needle Probe
2.1 ASTM Standards:
Procedure
D422 Test Method for Particle-Size Analysis of Soils
D5463 Guide for Use of Test Kits to Measure Inorganic
D1067 Test Methods for Acidity or Alkalinity of Water
Constituents in Water
D1293 Test Methods for pH of Water
D5730 Guide for Site Characterization for Environmental
D1498 Test Method for Oxidation-Reduction Potential of
Purposes With Emphasis on Soil, Rock, the Vadose Zone
Water
and Groundwater
D2216 Test Methods for Laboratory Determination of Water
D6836 Test Methods for Determination of the Soil Water
(Moisture) Content of Soil and Rock by Mass
Characteristic Curve for Desorption Using Hanging
D2325 Test Method for Capillary-Moisture Relationships
Column, Pressure Extractor, Chilled Mirror Hygrometer,
for Coarse- and Medium-Textured Soils by Porous-Plate
or Centrifuge
Apparatus (Withdrawn 2007)
E953 Test Method for Fusibility of Refuse-Derived Fuel
D2434 Test Method for Permeability of Granular Soils
(RDF) Ash
(Constant Head)
2.2 Other Documents:
Remediation Technologies Screening Matrix and Reference
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D34 on Waste 4
Guide
Management and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D34.01.01 on
U.S. Code of Federal Regulations 40 CFR 300.430
Planning for Sampling.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2006. Published November 2006. DOI:
10.1520/D7294-06. 3. Terminology
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
3.1 Definitions:
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
3 4
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on Available at http://www.frtr.gov
www.astm.org. Available at http://www.gpoaccess.gov/cfr/index.html
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D7294 − 06
A
TABLE 1 Water Parameters
B
Technology
IN SITU TREATMENT
H
Phytoremediation XX X X X O O X O O O X
Permeable Reactive Barriers X X O X O X X O O X X O X X O X X O O X
Monitored Natural Attenuation X X X O O O XXXX X O X O O X XX O X
Enhanced Bioremediation X X X OOOO X X X X O X O O X X X O X
Air Sparging X X X O X X X O O X X O O X O O O X
Hot Water or Steam Flush/Strip See Soil, Sediment & Sludge Parameters—thermally enhanced SVE
Slurry Walls See Soil, Sediment & Sludge Parameters
I
Bioslurping XX X X X X X X
J
Dual (multiphase) Phase Extraction XX X X X
Chemical oxidation X X X O O X X O X O O O X O O X
In Well Air Stripping Same parameters as air sparging
Free Product Recovery See Dual (multiphase) Phase Extraction
EX SITU TREATMENT
Advanced Oxidation (UV) X X O X O X X X O X O O X X X O X O O
Bioreactor X X O X O X X X O X O O O X O O O O O O
Air Stripping X X X X X O X O X X O X
Ion Exchange X X O X X X O X X O O O X O O O
Adsorption (carbon) X X O X O X X O X O O O X O O O
Precipitation/Coagulation/Flocculation X X O X X X O X O X O O O O
Constructed Wetlands X X O X O X X O O O X O O X O O O O O
A
This table was developed jointly by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Hazardous, Toxic, and Radioactive Waste Center of Expertise and the U.S. Environmental Project—Engineering Forum.
B
See Treatment Technology Profiles in www.frtr.gov for a description of the technology.
C
Quality of sampling indicators.
D
If these cations are to be analyzed in an offsite laboratory, evaluate analyzing all metal as the cost may be the same.
E
Conductivity is a good indicator of Total Dissolved Solids (TDS).
F +2 +2
Analyze for Fe in the field or total iron in the laboratory and estimate Fe from turbidity, etc.
G
Estimate of soil hydraulic properties in the aquifer where the samples were taken. This information may already be available.
H
See soil parameaters for vadose zone.
I
Easily converted to conventional bio venting system or SVE after free product is removed to complete the remediation. Include bio/SVE parameters.
J
Dual (multiphase) extraction is generally combined with technologies such as bioremediation, air sparging, bioventing and soil vapor extraction. Include parameters for these technologies if they are being considered
NOTE 1—“X” parameters are recommended during early site investigations before any treatment is being considered or has been selected.
NOTE 2—“O” parameters are recommended in addition to “X” if the technology is being considered or has been selected.
DO (field)
Temperature (field)
Total Suspended Solids (TSS)
C
Turbidity
CO
H S
Dissolved H
Methane, Ethane and Ethene
pH (field)
ORP (field)
Chloride (Cl-)
Fluoride (Fl-)
+2 +2 +2 + +D
Ca ,Mg ,Mn ,Na ,K
TOC
COD
DOC
Total Dissolved Solids (TDS)
- -2
Alkalinity HCO , CO3
E
Conductivity (field)
Volatile Fatty Acids
Biological Oxygen Demand (5-day BOD)
Oil/Grease
Ammonia (NH )
Phosphorous (total)
+2F
Ferrous Iron Fe
+2 +3D
Total Iron Fe +Fe
Sulfate/sulfite (SO =/SO =)
4 3
Nitrate/nitrite (NO -/NO -)
3 2
Kjeldahl Nitrogen
G
Sieve Analysis
D7294 − 06
A
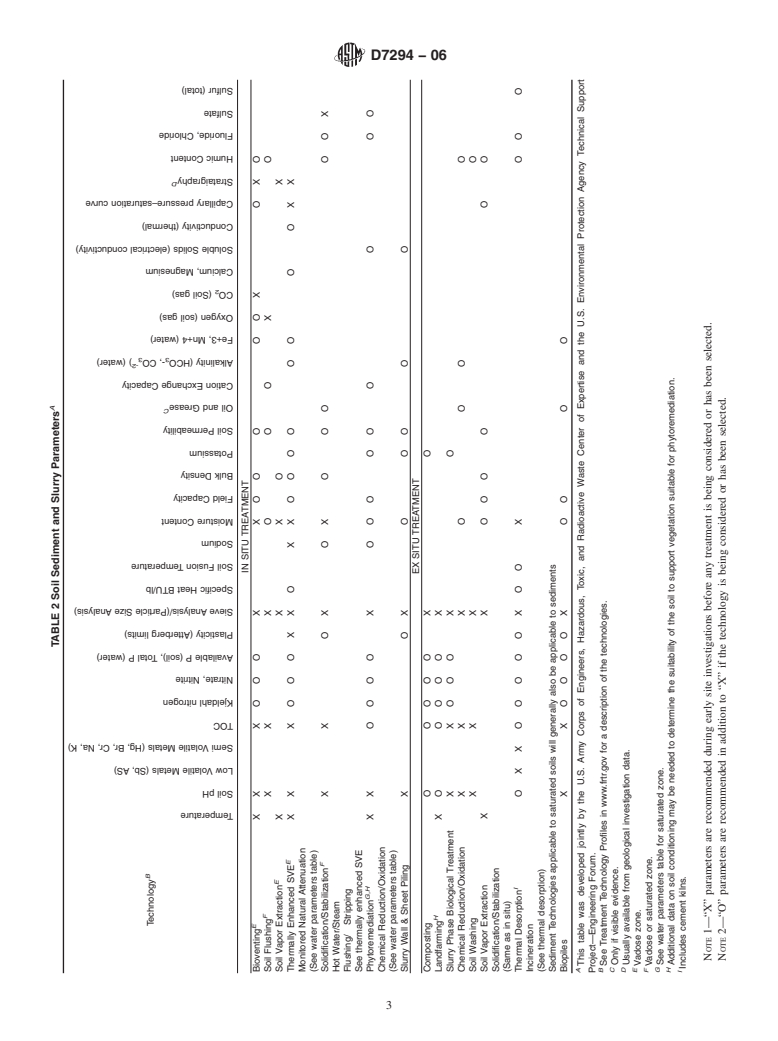
TABLE 2 Soil Sediment and Slurry Parameters
B
Technology
IN SITU TREATMENT
E
Bioventing X X X OOO X X OO O O O X O X O
F
Soil Flushing XX X O O O X O
E
Soil Vapor ExtractionXXXO X
E
Thermally Enhanced SVE X X X OOO X X O X X OOOO OO O O X X
Monitored Natural Attenuation
(See water parameters table)
F
Solidification/Stabilization X X OX OX O O O O OX
Hot Water/Steam
Flushing/ Stripping
See thermally enhanced SVE
G,H
Phytoremediation X X OOOO X OOO OO O O OO
Chemical Reduction/Oxidation
(See water parameters table)
Slurry Wall & Sheet Piling X O X O O O O O
EX SITU TREATMENT
Composting O OOOO X O
H
Landfarming X O OOOO X
Slurry Phase Biological Treatment X X O O O X O
Chemical Reduction/Oxidation X X X O O O O
Soil Washing X X X O
Soil Vapor Extraction X X O O O O O O
Solidification/Stabilization
(Same as in situ)
I
Thermal Desorption O X X OOOOO X O O X OO O
Incineration
(See thermal desorption)
Sediment Technologies applicable to saturated soils will generally also be applicable to sediments
Biopiles X X OOOO X O O O O
A
This table was developed jointly by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Hazardous, Toxic, and Radioactive Waste Center of Expertise and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Technical Support
Project—Engineering Forum.
B
See Treatment Technology Profiles in www.frtr.gov for a description of the technologies.
C
Only if visible evidence.
D
Usually available from geological investigation data.
E
Vadose zone.
F
Vadose or saturated zone.
G
See water parameters table for saturated zone.
H
Additional data on soil conditioning may be needed to determine the suitability of the soil to support vegetation suitable for phytoremediation.
I
Includes cement kilns.
NOTE 1—“X” parameters are recommended during early site investigations before any treatment is being considered or has been selected.
NOTE 2—“O” parameters are recommended in addition to “X” if the technology is being considered or has been selected.
Temperature
Soil pH
Low Volatile Metals (Sb, AS)
Semi Volatile Metals (Hg, Br, Cr, Na, K)
TOC
Kjeldahl nitrogen
Nitrate, Nitrite
Available P (soil), Total P (water)
Plasticity (Atterberg limits)
Sieve Analysis/(Particle Size Analysis)
Specific Heat BTU/lb
Soil Fusion Temperature
Sodium
Moisture Content
Field Capacity
Bulk Density
Potassium
Soil Permeability
C
Oil and Grease
Cation Exchange Capacity
-2
Alkalinity (HCO -, CO ) (water)
3 3
Fe+3, Mn+4 (water)
Oxygen (soil gas)
CO (Soil gas)
Calcium, Magnesium
Soluble Solids (electrical conductivity)
Conductivity (thermal)
Capillary pressure–saturation curve
D
Strataigraphy
Humic Content
Fluoride, Chloride
Sulfate
Sulfur (total)
D7294 − 06
3.1.1 remedial treatment process, n— as used in this guide, 4.6 This guide does not address sampling for contaminants
physical, chemical and biological technologies used to destroy, and sampling locations. See EM 200-1-2 Technical Project
contain or remove contaminants of concern at contaminated
Planning (TPP) under Engineering Manuals for information
sites.
on sampling contaminants of concern. It is recommended that
the treatment process design sampling be coordinated with the
3.1.2 treatment process design data, n—as used in this
sampling for chemicals of concern to minimize duplicate
guide, physical and chemical data that are needed, in addition
to data on contaminants of concern, characterization of the sampling and trips to the site.
subsurface, and major factors affecting the surface and subsur-
4.7 This guide does not address physical and chemical
face environment that are addressed in Guide D5730 to
propertiesrelatedtocontaminanttransport.Thisisaddressedin
evaluate and design treatment processes for remediation of
Guide D5730.
contaminated sites. Examples are cations and anions com-
monly present in water such as calcium, iron, carbonate/
4.8 This guide does not address why the data is needed to
bicarbonate, Total Organic Carbon (TOC), pH, temperature,
evaluate each treatment technology. This information is ad-
and sieve analysis. See Tables 1 and 2 for the complete list.
dressed in the Federal Remediation Technologies Roundtable
(FRTF) site at http://www.frtr.gov in the U.S. Army Corps of
4. Significance and Use
Engineers guidance documents at http://www.usace.army.mil/
4.1 This guide allows the decision maker to determine
inet/usace-docs/ and the United Facilities Guide Specifications
which remedial treatment processes are and are not applicable
(UFGS) available at http://www.ccb.org/.
to remediate an area of soil, surface water or ground water that
contains contaminants of concern.
4.9 This guide does not address QualityAssurance/ Quality
Control (QA/QC) or sampling design strategy. See U.S. Army
4.2 This guide provides the data to make cost comparisons
Corps of Engineers Engineering Regulation ER 1110-1-263
of the remedial treatment processes.
and Engineering Manual EM 200-1-3 for information on
4.3 Analysis of treatment process design data can often be
QA/QC. This needs to be addressed in the Quality Assurance
performed at the site with instruments and test kits.
Project Plan (QAPP).
4.4 Tables 1 and 2 are a guide to selecting and obtaining
physical and chemical treatment process design data. Data
5. Keywords
marked with an “X” is needed to evaluate alternatives and
5.1 analysis; environmental assessment; hazardous waste;
select a remedial treatment process. Once the remedial process
remediation; sampling; solid waste
is selected the additional data that are needed to design the
selected remedial treatment process are marked with an “O”.
4.5 Tables 3 and 4 list laboratory and field methods for
analyzing this data. More than one analytical method may be
United States Army Corps of Engineers, Technical Project Planning (TPP)
listed. The most suitable method must be chosen for each
Processes, Engineering Manual—EM 200-1-2, Publications of the Headquarters,
application. available at http://www.usace.army.mil/inet/usace-docs/
D7294 − 06
A
TABLE 3 Water Analytical Methods
Field Test Methods
B B
Parameters Laboratory Methods Detection Range Detection Range
C
Meter/Kit
D,E F +G H
pH EPA 150.1/150.2 ; SM 4500-H ; 0 - 14 pH units Meter
Test Methods D1293
D,E,I G
ORP SM 2580 ; Practice D1498 Meter
D,E F G
Temperature EPA 170.1 ; SM 2550 0 - 100°C
D,E F G
Dissolved Oxygen (DO) EPA 360.1 ; SM 4500-O 360.2 0 - 20 mg/L Spectrophotometer 1 - 10 mg/L
H
(spec)/Meter
D,E F G
Conductivity EPA 120.1 ; SM 2510 1 - 1,000 µS/cm Meter 200 mS
D,E F
Turbidity EPA 180.1 0 - 40 NTU Spec/Meter 0 - 4,400 NTU/0.1 - 100 NTU
F
Total dissolved solids EPA 160.1 10 - 20,000 mg/L Meter 0 - 200 mg/L
F H
Ammonia EPA 350.1/350.2/350.3 ; SM 4500- 0.01 - 2.0 mg/L Spec/Kit 0 - 2.5 mg/L
G
NH
F
Kjeldahl (TKN) EPA 351.1/351.2/351.3/ 351.4 ;SM 0.05 - 2.0 mg/L Spec/Kit 1 - 150 mg/L
G
4500-N
org
Anions
- F
F 0013B—electrode EPA 340.1/340.2/340.3 ; SM 4500- 0.1 - 1,000 mg/L Spec/Kit 0 - 2 mg/L/0 - 2 mg/L
G
F- 0300
- F
Cl EPA 325.1/325.2/325.3 ; SM 4500 1 - 200 mg/L Spec/Kit 0-20/5-400
G
Cl- 0300
- F G H
NO EPA 352.1 ; SM 4500-NO3- ; Test 0.1 - 2 mg/L as N Spec/Kit 0 - 30/0 - 10 mg/L
Method D4327 0300
- F G H
NO EPA 354.1 ; SM 4500-NO2- 0300 0.01 - 1.0 mg/L as N Spec/Kit 0 - 0.3/0 - 1.0 mg/L
2- F H
SO EPA 375.1/375.2/375.3/ 375.4 ;SM 3 - 400 mg/L Spec/Kit 0 - 70/50 - 200 mg/L
2-G
4500-SO ;
Test Method D4327 0300
- G J
SO SM 4500-SO3-B . EPA 377.1 Kit
- 2- F G H
Alkalinity (HCO ,CO ) EPA 310.1/310.2 ; SM 2320
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.