ISO 3303:1979
(Main)Rubber- or plastics-coated fabrics — Determination of bursting strength
Rubber- or plastics-coated fabrics — Determination of bursting strength
Supports textiles revêtus de caoutchouc ou de plastique — Détermination de la résistance à l'éclatement
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
International Standard 3303
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDlZA~lONOMff~YHAPO~HAR OPrAHl43AUMFl Il0 CTAHJlAFTl43Al(WlWRGANlSATlON INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
Rubber- or plastics-coated fabrics - Determination of
a bursting strength
Supports textiles revêtus de caoutchouc ou de plastique - Détermination de la résistance à l'éclatement
First edition - 1979-12-15
- UDC 678.066 : 677.017.464 Ref. No. IS0 3303-1979 (E)
Q)
Descriptors : coated fabrics, fabrics coated with plastics, fabrics coated with rubber, tests, burst tests, test equipment
E
s
Price based on 3 pages
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
Foreword
IS0 (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide federation of
national standards institutes (IS0 member bodies). The work of developing Inter-
national Standards is carried out through IS0 technical committees. Every member
body interested in a subject for which a technical committee has been set up has the
right to be represented on that committee. International organizations, governmental
O
ISO, also take part in the work.
and non-governmental, in liaison with
Draft International Standards adopted by the technical committees are circulated to
the member bodies for approval before their acceptance as International Standards by
the IS0 Council.
International Standard IS0 3303 was developped by Technical Committee ISO/TC 45,
Rubber and rubber products, and was circulated to the member bodies in September
1977.
It has been approved by the member bodies of the following countries :
Austria Ireland Sweden
Belgium Korea, Rep. of Switzerland
Canada Mexico Thailand
Czechoslovakia Netherlands Turkey
France Poland United Kingdom
Greece Romania USA
Hungary South Africa, Rep. of USSR
India Spain
No member body expressed disapproval of the document.
O International Organization for Standardization, 1979 0
Printed in Switzerland
---------------------- Page: 2 ----------------------
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
IS0 3303-1979 (E)
Rubber- or plastics-coated fabrics - Determination of
bursting strength
1 Scope and field of application
3 Apparatus
This International Standard specifies two methods for the
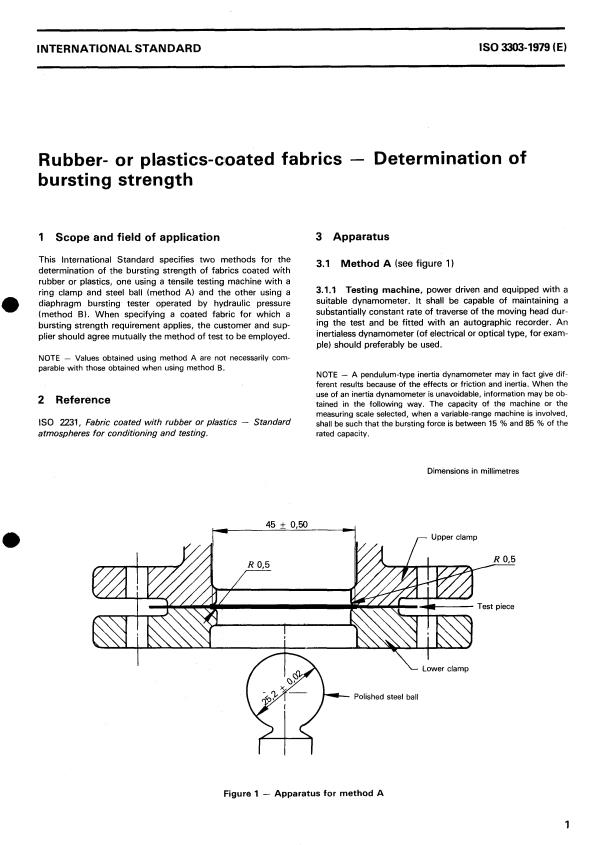
3.1 Method A (see figure 1)
determination of the bursting strength of fabrics coated with
rubber or plastics, one using a tensile testing machine with a
3.1.1 Testing machine, power driven and equipped with a
ring clamp and steel ball (method A) and the other using a
It shall be capable of maintaining a
suitable dynamometer.
diaphragm bursting tester operated by hydraulic pressure
0
substantially constant rate of traverse of the moving head dur-
B). When specifying a coated fabric for which a
(method
ing the test and be fitted with an autographic recorder. An
bursting strength requirement applies, the customer and sup-
inertialess dynamometer (of electrical or optical type, for exam-
plier should agree mutually the method of test to be employed.
ple) should preferably be used.
NOTE - Values obtained using method A are not necessarily com-
parable with those obtained when using method B.
NOTE - A pendulum-type inertia dynamometer may in fact give dif-
ferent results because of the effects or friction and inertia. When the
use of an inertia dynamometer is unavoidable, information may be ob-
2 Reference
tained in the following way. The capacity of the machine or the
measuring scale selected, when a variable-range machine is involved,
IS0 2231, Fabric coated with rubber or plastics - Standard
shall be such that the bursting force is between 15 % and 85 % of the
atmospheres for conditioning and testing.
rated capacity.
Dimensions in millimetres
I Lower clamp
Polished steel ball
Figure 1 - Apparatus for method A
1
---------------------- Page: 3 ----------------------
IS0 3303-1979 (E)
The accuracy of the machine shall be such that the error in the edge of the aperture and shall be rounded to a radius of not
force measurement as shown and recorded does not exceed
greater than 0,4 mm. The bottom inner edge of the upper
2 YO of the force or 0,5 YO of the maximum of the scale, clamp shall be rounded to a radius of 0,5 mm. The lower clamp
whichever is the greater. shall be integral with the chamber in which liquid is introduced
at a uniform rate of approximately 1,6 ml/s in the case of the
31 mm aperture and 2,5 ml/s in the case of the 35,7 mm aper-
3.1.2 Bursting attachment, such that the test piece is held
ture. The chamber shall be covered with a rubber diaphragm
securely by a ring mechanism of internal diameter
fitted to expand through the aperture and exerting pressure on
45 f 0,W mm, with the centre of the test piece pressed against
the coated fabric between clamps.
a polished steel ball of diameter 25,2 I 0,02 mm until the test
piece ruptures. The direction of motion of the ring-clamp or
NOTE - Results from a testing machine having an aperture of
steel ball shall be at right angles to the plane of the fabric.
diameter 31 ,O 0,2 mm will not necessarily give the same results as a
testing machine having an aperture of diameter of 35,7 i 0,2 mm.
3.1.3 The clamping surfaces of the upper and lower clamps
shall be grooved concentrically such that the crowns of the
3.2.3 Pressure gauge, of the maximum reading type, of ap-
grooves of one plate fit the grooves of the other. The grooves
propriate capacity and graduated in kilopascals. It shall
mm apart and not less than 0,15 mm
shall be not less than 0,8
preferably be used within the range from 25 % to 75 % and in
deep. The grooves shall start no further than 3 mm from the
no case outside the range from 15 % to 85 YO of the maxi
...
Norme internationale 3303
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATlON.ME~YHAPOAHAfl OPTAHM3AUMfl no CTAH~APTM3A~M~~RGANlSATlON INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
Supports textiles revêtus de caoutchouc ou de plastique
- Détermination de la résistance à l'éclatement
Rubber- or plastics-coated fabrics - Determination of bursting strength
Première édition - 1979-12-15
CDü 678.066 : 677.017.464 Réf. no : IS0 3303-1979 (FI
Descripteurs : support textile revêtu, étoffe revêtue de plastique, étoffe revêtue de caoutchouc, essai, essai d'éclatement, matériel d'essai
Prix basé sur 3 pages
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
Avant-propos
L’ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération mondiale
d’organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de I’ISO). L‘élaboration
des Normes internationales est confiée aux comités techniques de I’ISO. Chaque
comité membre intéressé par une étude a le droit de faire partie du comité technique
correspondant. Les organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non gouverne-
mentales, en liaison avec I‘ISO, participent également aux travaux.
Les projets de Normes internationalef adoptés par les comités techniques sont soumis
aux comités membres pour approbation, avant leur acceptation comme Normes inter-
nationales par le Conseil de I’ISO.
La Norme internationale IS0 3303 a été élaborée par le comité technique ISO/TC 45,
Elastomères et produits à base d’élastomères, et a été soumise aux comités membres
en septembre 1977.
Les comités membres des pays suivants l’ont approuvée :
Afrique du Sud, Rép. d‘ Hongrie
Suède
Autriche Inde Suisse
Belgique Irlande Tchécoslovaquie
Corée, Rép. de ‘ Mexique Thaïlande
Canada Pays-Bas Turquie
Espagne Pologne USA
France Roumanie URSS
Royaume-Uni
Grèce
Aucun comité membre ne l’a désapprouvée.
0 Organisation internationale de normalisation, 1979 O
Imprimé en Suisse
---------------------- Page: 2 ----------------------
NORME INTERNATIONALE IS0 3303-1979 (FI
Supports textiles revêtus de caoutchouc ou de
plastique - Détermination de la résistance à
I 'éclate ment
1 Objet et domaine d'application 3 Appareillage
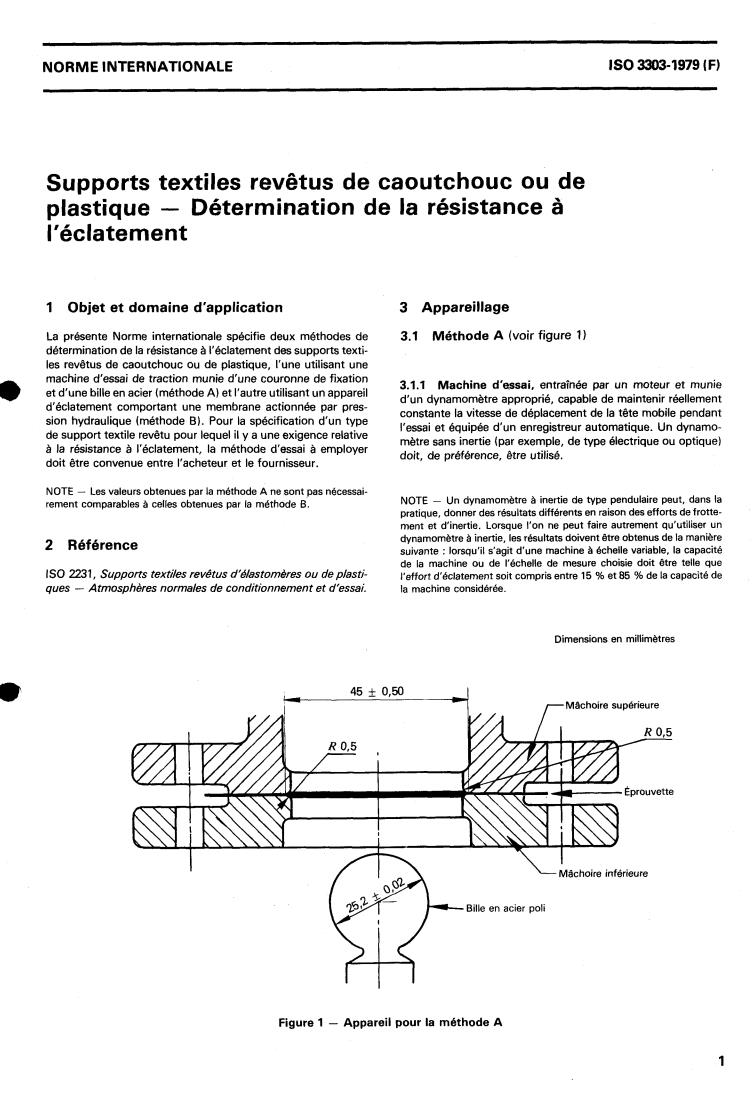
Méthode A (voir figure 1)
La présente Norme internationale spécifie deux méthodes de 3.1
détermination de la résistance à l'éclatement des supports texti-
les revêtus de caoutchouc ou de plastique, l'une utilisant une
machine d'essai de traction munie d'une couronne de fixation
3.1.1 Machine d'assai, entraînée par un moteur et munie
et d'une bille en acier (méthode A) et l'autre utilisant un appareil
d'un dynamomètre approprié, capable de maintenir réellement
d'éclatement comportant une membrane actionnée par pres-
constante la vitesse de déplacement de la tête mobile pendant
sion hydraulique (méthode 6). Pour la spécification d'un type
l'essai et équipée d'un enregistreur automatique. Un dynamo-
de support textile revêtu pour lequel il y a une exigence relative
mètre sans inertie (par exemple, de type électrique ou optique)
à la résistance à l'éclatement, la méthode d'essai à employer
doit, de préférence, être utilisé.
doit être convenue entre l'acheteur et le fournisseur.
NOTE - Les valeurs obtenues par la méthode A ne sont pas nécessai-
NOTE - Un dynamomètre à inertie de type pendulaire peut, dans la
rement comparables à celles obtenues par la méthode B.
pratique, donner des résultats différents en raison des efforts de frotte-
ment et d'inertie. Lorsque l'on ne peut faire autrement qu'utiliser un
dynamomètre à inertie, les résultats doivent être obtenus de la manière
2 Référence
suivante : lorsqu'il s'agit d'une machine à échelle variable, la capacité
de la machine ou de l'échelle de mesure choisie doit être telle que
IS0 2231, Supports textiles revêtus d'élastomères ou de plasti-
l'effort d'éclatement soit compris entre 15 % et 85 % de la capacité de
ques - Atmosphères normales de conditionnement et d'essai.
la machine considérée.
Dimensions en millimètres
Mâchoire supérieure
Mâchoire inférieure
Bille en acier poli
Figure 1 - Appareil pour la méthode A
1
---------------------- Page: 3 ----------------------
IS0 3303-1979 (F)
La précision de l’appareillage doit être telle qu‘une erreur sur la
les sommets des rainures de l‘une des plaques s‘engagent dans
mesure de la force lue ou enregistrée n’excède pas 2 % de la
les rainures de l’autre. Les rainures doivent être espacées d‘au
force ou 0,5 % du maximum de la graduation, en choisissant la
moins 0,8 mm et doivent avoir au moins 0,15 mm de profon-
valeur la plus grande.
deur. Les rainures ne doivent pas être faites à moins de 3 mm
du bord de l’ouverture et doivent être arrondies selon un rayon
non supérieur à 0,4 mm. Le bord intérieur inférieur de la
3.1.2 Système de fixation pour l‘essai d’éclatement,
mâchoire supérieure doit être arrondi selon un rayon de
concu de facon que l’éprouvette soit fermement maintenue
0,5 mm. La mâchoire inférieure doit faire partis intégrante de la
entre deux mâchoires annulaires de diamètre intérieur
chambre dans laquelle le liquide est introduit à un débit cons-
45 i: 0,50 mm, le centre de l’éprouvette se trouvant pressé par
tant d’environ 1,6 ml/s pour l’ouverture de diamètre 31 mm et
une bille en acier poli de diamètre 25,2 f 0,02 mm, jusqu’à
d’environ 2,5 ml/s pour l’ouverture de diamètre de 35,7 mm.
éclatement de l’éprouvette. L‘anneau de la mâchoire ou la bille
La chambre de pression est formée par une membrane en
en acier doit se déplacer perpendiculairement au plan du sup-
caoutchouc qui se dilate à travers l‘ouverture, exercant ainsi
port textile.
une pression sur le support textile fixe entre les deux mâchoi-
res,
3.1.3 Les surfaces d‘appui des mâchoires supérieure et infé-
rieure doivent comporter des rainures concentriques telles que
NOTE - Les résultats obtenus à l‘aide d‘un appareil d‘essai à ouverture
les sommets des rainures de l‘une des plaques s‘engagent dans
de diamètre 31.0 +_ 0,2 mm ne correspondent pas nécessairement à
les rainures de l’autre. Les rainures doivent être espacées d‘au
ceux obtenus à l’aide d’un appareil d’essai à ouverture de diamètre
moins 0,8 mm et doivent avoir au moins 0,15 mm de profon-
35.7 +_ 0,2 mm.
deur. Les rainures ne doivent pas être faites à moins de 3 mm
du bord de l
...


Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.