ASTM E2074-00
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Fire Tests of Door Assemblies, Including Positive Pressure Testing of Side-Hinged and Pivoted Swinging Door Assemblies
Standard Test Method for Fire Tests of Door Assemblies, Including Positive Pressure Testing of Side-Hinged and Pivoted Swinging Door Assemblies
SCOPE
1.1 This fire-test-response standard is applicable to door assemblies for use in walls to retard the passage of fire (see .).
1.2 This fire-test-response standard determines the ability of door assemblies to function as a fire-resistive barrier during a standard fire endurance test. Such a test meth shall not be construed as determining the suitability of door assemblies for continued use after their exposure to fire.
1.3 This fire-test-response standard is intended to evaluate the ability of a door assembly to remain in an opening during a predetermined test exposure, which when required by is then followed by the application of a hose stream (see ).
1.4 The hose stream test used in this test method is not designed to be representative of an actual hose stream used by a fire department during fire suppression efforts.
1.5 The fire exposure is not representative of all fire conditions, which vary with changes in the amount, nature, and distribution of the fire loading, ventilation, compartment size and configuration, and heat characteristics of the compartment. It does, however, provide a relative measure of fire endurance of door assemblies under specified fire exposure conditions.
1.6 Any variation from the tested construction or test conditions will possibly change the performance characteristics of door assembly.
1.7 This fire-test-response standard does not provide the following:
1.7.1 The fire endurance of door assemblies constructed of materials other than those tested.
1.7.2 A temperature limit on the unexposed surface of the door assembly, although the temperatures are measured and recorded.
1.7.3 A limit on the number of openings allowed in glazed areas or of the number and size of lateral openings between the door and frame.
1.7.4 A measurement of smoke or products of combustion that pass through the door assembly.
1.7.5 A measurement of smoke, toxic gases, or other products of combustion generated by the door assembly.Note 1
The information in and may be important in determining the fire hazard or fire risk of door assemblies under actual fire conditions. This information may be determined by other suitable fire test methods. For example, flame spread and smoke development may be determined by Test Method E 84.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.8 This standard is intended to measure and describe the response of materials, products, or assemblies to heat and flame under controlled conditions and is not intended to describe or appraise the fire hazard or fire risk of materials, products, or assemblies under actual fire conditions. However, results of the test are permitted to be used as elements of a fire-hazard assessment or a fire-risk assessment which takes into account all of the factors which are pertinent to an assessment of the fire hazard or fire risk of a particular end use.
1.9 This test method references notes and footnotes which provide explanatory material. These notes and footnotes (excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered as requirements of this test method.
1.10 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the standard.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
Designation: E 2074 – 00
Standard Test Method for
Fire Tests of Door Assemblies, Including Positive Pressure
Testing of Side-Hinged and Pivoted Swinging Door
Assemblies
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E 2074; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
This fire-test-response standard replaces E 152, Standard Methods of Fire Tests of Door Assemblies,
which was formerly under the jurisdiction of Committee E-5 on Fire Standards. The E 152 standard
was withdrawn on January 1, 1995 in accordance with Section 10.5.3.1 of the Regulations Governing
ASTM Technical Committee, which requires that standards shall be updated by the end of the eighth
year since last approval date.
1. Scope 1.7 This fire-test-response standard does not provide the
following:
1.1 This fire-test-response standard is applicable to door
1.7.1 The fire endurance of door assemblies constructed of
assemblies for use in walls to retard the passage of fire (see
materials other than those tested.
X1.1-X1.3.).
1.7.2 A temperature limit on the unexposed surface of the
1.2 This fire-test-response standard determines the ability of
door assembly, although the temperatures are measured and
door assemblies to function as a fire-resistive barrier during a
recorded.
standard fire endurance test. Such a test meth shall not be
1.7.3 A limit on the number of openings allowed in glazed
construed as determining the suitability of door assemblies for
areas or of the number and size of lateral openings between the
continued use after their exposure to fire.
door and frame.
1.3 This fire-test-response standard is intended to evaluate
1.7.4 A measurement of smoke or products of combustion
the ability of a door assembly to remain in an opening during
that pass through the door assembly.
a predetermined test exposure, which when required by 12.10
1.7.5 A measurement of smoke, toxic gases, or other prod-
is then followed by the application of a hose stream (see X1.4
ucts of combustion generated by the door assembly.
and X1.5).
1.4 The hose stream test used in this test method is not
NOTE 1—The information in 1.7.4 and 1.7.5 may be important in
designed to be representative of an actual hose stream used by
determining the fire hazard or fire risk of door assemblies under actual fire
conditions. This information may be determined by other suitable fire test
a fire department during fire suppression efforts.
methods. For example, flame spread and smoke development may be
1.5 The fire exposure is not representative of all fire
determined by Test Method E 84.
conditions, which vary with changes in the amount, nature, and
distribution of the fire loading, ventilation, compartment size 1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the
and configuration, and heat characteristics of the compartment. safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
It does, however, provide a relative measure of fire endurance
of door assemblies under specified fire exposure conditions. priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 Any variation from the tested construction or test
conditions will possibly change the performance characteristics 1.9 This standard is intended to measure and describe the
response of materials, products, or assemblies to heat and
of door assembly.
flame under controlled conditions and is not intended to
describe or appraise the fire hazard or fire risk of materials,
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E-5 on Fire
products, or assemblies under actual fire conditions. However,
Standards and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E05.11 on Fire
results of the test are permitted to be used as elements of a
Endurance.
Current edition approved March 10, 2000. Published May 2000. fire-hazard assessment or a fire-risk assessment which takes
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
E2074–00
into account all of the factors which are pertinent to an 5. Significance and Use
assessment of the fire hazard or fire risk of a particular end use.
5.1 In this fire-test-response standard, the test specimens are
1.10 This test method references notes and footnotes which
subjected to one or more specific sets of laboratory test
provide explanatory material. These notes and footnotes (ex-
conditions. When different test conditions are substituted or the
cluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered as
end-use conditions are changed, it is not always possible by, or
requirements of this test method.
from, this test method to predict changes to the characteristics
1.11 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units
measured. Therefore, the results are valid only for the exposure
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
conditions described in this test method.
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
5.2 This fire-test-response standard measures and records
system shall be used independently of the other. Combining
the temperatures on the unexposed side of a door assembly.
values from the two systems may result in nonconformance
This data is intended to assist and enable regulatory bodies to
with the standard.
determine the suitability of door assemblies for use in locations
where fire resistance of a specified duration is required.
2. Referenced Documents
5.3 The data is not intended to be used to describe or
2.1 ASTM Standards:
appraise the fire hazard or fire risk of materials, products, or
E 84 Test Method for Surface Burning Characteristics of
assemblies under actual fire conditions.
Building Materials
5.4 This fire-test-response standard requires that observa-
E 119 Tests Methods for Fire Tests of Building Construction
tions be made and recorded relevant to the passage of flame.
and Materials
5.5 This fire-test-response standard uses a cotton wool pad
E 152 Methods of Fire Tests of Door Assemblies
test to assess the integrity of the door assembly relevant to the
E 176 Terminology of Fire Standards
passage of hot gases.
E 631 Terminology of Building Constructions
5.6 This fire-test-response standard uses a hose stream test
2.2 Other Documents:
to assess the durability of the door assembly relevant to the
UL 385 Standard for Play Pipes for Water Supply Testing in
passage of a stream of water.
Fire-Protection Service, 1993
6. Apparatus
3. Terminology
6.1 Furnace and Test Frame:
3.1 For the purpose of this test method, the definitions given
6.1.1 The furnace construction shall be suitable to meet the
in Terminologies E 176 and E 631, together with the following,
requirements of the fire test protocol. An example of the
shall apply:
furnace and test frame is illustrated in Fig. 1 (see X1.6).
3.1.1 integrity, n—the ability of a test assembly, when
6.1.2 The height and width of the furnace opening shall be
exposed to fire from one side, to prevent the passage of flame
greater than the test assembly’s corresponding dimension.
and hot gases through it or the occurrence of flames on its
6.1.3 The furnace shall be heated with burners that are fired
unexposed side.
using either natural gas or liquefied petroleum gases. The
3.1.2 through-opening, n—an uninterrupted hole in the test
burners shall have a controllable heat output (see X1.8) and be
assembly that is seen from the unexposed side when viewing
able to expose the test assembly to the uniform heating of the
the suspected hole from a position perpendicular to the plane of
standard time-temperature curve.
the test assembly.
6.2 Copper Disk Thermocouples:
6.2.1 The copper disk thermocouples shall be covered by
4. Summary of Test Method
pads as specified in 6.2.4, reference Fig. 2, and shall have a
4.1 This fire-test-response standard describes the following
test sequence and procedure.
4.1.1 A door assembly is exposed to a standard fire expo-
sure, controlled to achieve specified temperatures and pres-
sures throughout a specified time period.
4.1.2 The integrity of the door assembly is evaluated using
a cotton wool pad test when the average unexposed surface
temperature of a door assembly is less than 650°F (361°C)
above ambient and openings are created by the fire exposure.
4.1.3 After the fire endurance test the door assembly is
subjected to a hose stream test when required by 12.10.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.07.
This standard was withdrawn on Jan. 1, 1995, in accordance with Section
10.5.3.1 of the Regulations Governing ASTM Technical Committees which requires
that standards be updated at least every eight years.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.11.
Available from Underwriters Laboratories, 333 Pfingsten Road, Northbrook, IL
60062. FIG. 1 Furnace and Test Frame
E2074–00
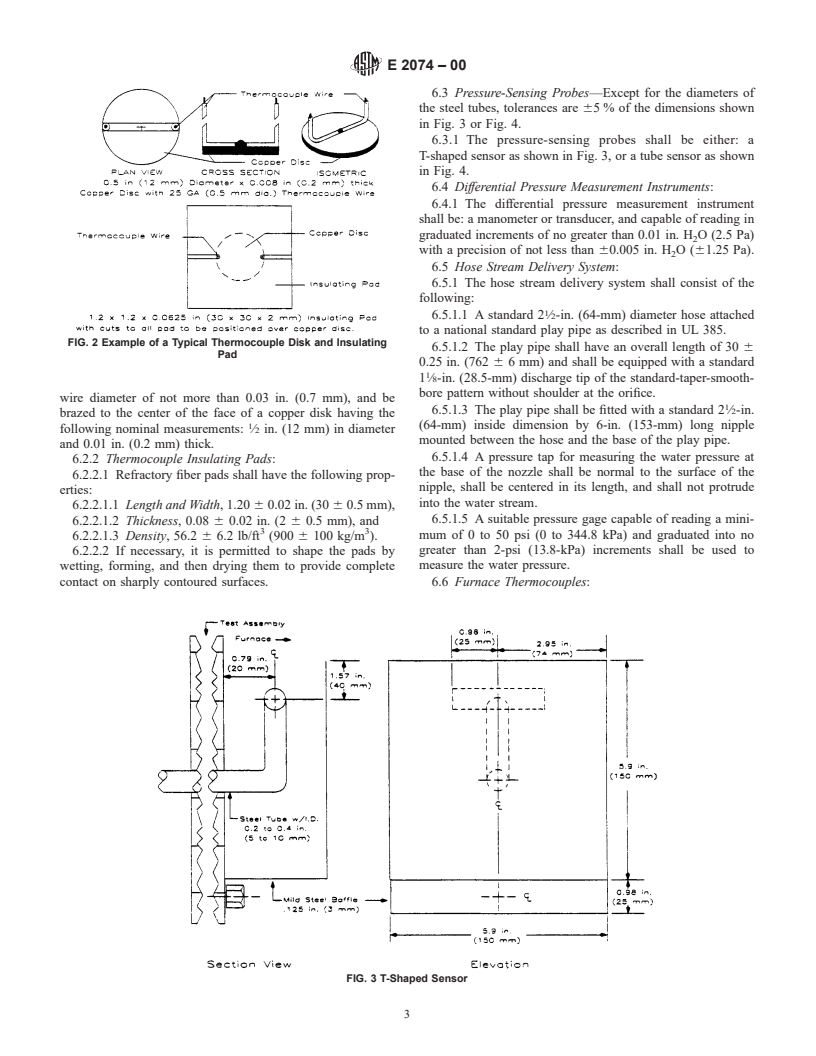
6.3 Pressure-Sensing Probes—Except for the diameters of
the steel tubes, tolerances are 65 % of the dimensions shown
in Fig. 3 or Fig. 4.
6.3.1 The pressure-sensing probes shall be either: a
T-shaped sensor as shown in Fig. 3, or a tube sensor as shown
in Fig. 4.
6.4 Differential Pressure Measurement Instruments:
6.4.1 The differential pressure measurement instrument
shall be: a manometer or transducer, and capable of reading in
graduated increments of no greater than 0.01 in. H O (2.5 Pa)
with a precision of not less than 60.005 in. H O(61.25 Pa).
6.5 Hose Stream Delivery System:
6.5.1 The hose stream delivery system shall consist of the
following:
6.5.1.1 A standard 2 ⁄2-in. (64-mm) diameter hose attached
to a national standard play pipe as described in UL 385.
FIG. 2 Example of a Typical Thermocouple Disk and Insulating
6.5.1.2 The play pipe shall have an overall length of 30 6
Pad
0.25 in. (762 6 6 mm) and shall be equipped with a standard
1 ⁄8-in. (28.5-mm) discharge tip of the standard-taper-smooth-
bore pattern without shoulder at the orifice.
wire diameter of not more than 0.03 in. (0.7 mm), and be
6.5.1.3 The play pipe shall be fitted with a standard 2 ⁄2-in.
brazed to the center of the face of a copper disk having the
1 (64-mm) inside dimension by 6-in. (153-mm) long nipple
following nominal measurements: ⁄2 in. (12 mm) in diameter
mounted between the hose and the base of the play pipe.
and 0.01 in. (0.2 mm) thick.
6.5.1.4 A pressure tap for measuring the water pressure at
6.2.2 Thermocouple Insulating Pads:
the base of the nozzle shall be normal to the surface of the
6.2.2.1 Refractory fiber pads shall have the following prop-
nipple, shall be centered in its length, and shall not protrude
erties:
into the water stream.
6.2.2.1.1 Length and Width, 1.20 6 0.02 in. (30 6 0.5 mm),
6.5.1.5 A suitable pressure gage capable of reading a mini-
6.2.2.1.2 Thickness, 0.08 6 0.02 in. (2 6 0.5 mm), and
3 3
mum of 0 to 50 psi (0 to 344.8 kPa) and graduated into no
6.2.2.1.3 Density, 56.2 6 6.2 lb/ft (900 6 100 kg/m ).
greater than 2-psi (13.8-kPa) increments shall be used to
6.2.2.2 If necessary, it is permitted to shape the pads by
measure the water pressure.
wetting, forming, and then drying them to provide complete
contact on sharply contoured surfaces. 6.6 Furnace Thermocouples:
FIG. 3 T-Shaped Sensor
E2074–00
FIG. 4 Tube Sensor
6.6.1 The furnace thermocouples shall: 6.7.1.4 Be attached using wire clips to a wire frame. The
6.6.1.1 Be protected by sealed porcelain tubes having a frame used to hold the cotton wool pad is to be formed of steel
3 1
nominal ⁄4-in. (19-mm) outside diameter and ⁄8-in. (3-mm) wire (typically No. 15 AWG (1.5 mm)) and is to be provided
wall thickness, or, as an alternative, in the case of base metal with a handle long enough to reach all points of the test
thermocouples, protected by a standard ⁄2-in. (13-mm) diam- assembly. See Fig. 5.
eter wrought steel or wrought iron pipe of standard weight, and 6.7.1.5 The cotton wool pads are to be conditioned prior to
6.6.1.2 Have a time constant in the range from 6.0 to 7.2 use by drying in an oven at 212 6 9°F (100 6 5°C) for at least
min while encased in the tubes described in 6.6.1.1. 30 min. After drying, the cotton wool pads shall be stored in a
desiccator until they are used.
NOTE 2—A typical thermocouple assembly meeting these time constant
requirements may be fabricated by fusion-welding the twisted ends of No.
7. Time-Temperature Curve
18 gage Chromel-Alumel wires, mounting the leads in porcelain insula-
7.1 The fire exposure of door assemblies shall be controlled
tors, and inserting the assembly so the thermocouple bead is 0.5 in. (25
mm) from the sealed end of the standard weight nominal ⁄2-in. iron, steel,
to conform to the applicable portion of the standard time-
or Inconel pipe. The time constant for this and for several other
temperature curve shown in Fig. 6 (see X1.7). The points on
thermocouple assemblies was measured in 1976. The time constant may
the curve that determine its character are as follows:
also be calculated from knowledge of its physical and thermal properties.
6.6.2 Other types of protection tubes or pyrometers are
permitted to be used provided that under test conditions they
give the same indications as those of 6.6.1 within the limit of
accuracy that applies for furnace-temperature measurements.
6.7 Cotton Wool Pads:
6.7.1 The cotton wool pads shall:
6.7.1.1 Measure 4 6 0.125 in. (100 6 3 mm) long by 4 6
0.125 in. (100 6 3 mm) wide by 0.85 6 0.0625 in. (20 6 2
mm) thick,
6.7.1.2 Consist only of new undyed soft cotton fibers,
without any admixture of artificial fibers,
6.7.1.3 Have a mass between 3 and 4 g, and
Inconel is a registered trade name of INCO Alloys, Inc., 3800 Riverside Dr.,
Huntington, WV 25720.
Supporting data is available from ASTM Headquarters. Request RR:E05-1001. FIG. 5 Example of a Typical Cotton Wool Pad Holder
E2074–00
TABLE 1 Standard Time-Temperature Curve for Control of Fire
Tests
Area Above 68°F base Area Above 20°C base
Time, Temper- Temper-
h/min ature,° F ature, °C
°F·min °F·h °C·min °C·h
0:00 68 0 0 20 0 0
0:05 1 000 2 330 39 538 1 290 22
0:10 1 300 7 740 129 704 4 300 72
0:15 1 399 14 150 236 760 7 860 131
0:20 1 462 20 970 350 795 11 650 14
0:25 1 510 28 050 468 821 15 590 260
0:30 1 550 35 360 589 843 19 650 328
0:35 1 584 42 860 714 862 23 810 397
0:40 1 613 50 510 842 878 28 060 468
0:45 1 638 58 300 971 892 32 390 540
0:
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.