ASTM A1022-01
(Specification)Standard Specification for Deformed and Plain Stainless Steel Wire and Welded Wire for Concrete Reinforcement
Standard Specification for Deformed and Plain Stainless Steel Wire and Welded Wire for Concrete Reinforcement
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers stainless steel wire and welded wire reinforcement produced from hot-rolled stainless steel rod. The stainless steel wire is cold-worked, drawn or rolled, plain (non-deformed) or deformed or a combination of deformed and plain. It is used as concrete reinforcement for applications requiring resistance to corrosion and/or controlled magnetic permeability. Common wire sizes and dimensions are found in this specification. Actual wire sizes are not restricted to those shown in the tables.
1.2 Supplement S1 describes high strength wire, which shall be furnished when specifically ordered. It shall be permissible to furnish high strength wire in place of regular wire if mutually agreed to by the purchaser and supplier.
1.2.1 A supplementary requirement (S2) of an optional nature is provided. It shall apply only when specified by the purchaser. In order to obtain a corrosion tested or controlled magnetic permeability product, steel conforming to Supplementary Requirement S2 should be ordered.
1.3 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units are to be regarded as standard. Within the text the inch-pound units are shown in parentheses. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system must be used independently of the other. Combining values may result in nonconformance with the specification.
1.4 The chemical composition of the steel (stainless grade) shall be selected for suitability to the application involved by agreement between the manufacturer and the purchaser. Use Specification A 276 for chemical requirements. The UNS designations are to be included with the type number and noted in brackets, i.e. austenitic stainless steels as Type 304 [S30400], 304L [S30403], 316 [S31600], 316L [S31603], 316N [S31651], 316LN [S31653] and duplex stainless steels, Types 2205 [S32205] and 329 [S32900].Note 1—Only austenitic and duplex stainless steels are usually recommended for use as reinforcement in concrete because of their high corrosion resistance. Austenitic stainless steels have good general corrosion resistance, strength characteristics which can be improved by cold working, good toughness and ductility properties at low temperatures, and low magnetic permeability. Duplex stainless steels have generally a corrosion resistance greater than that of most austenitic steels and are magnetic. Other stainless steels with different chemical compositions than the series and types mentioned above, may be used for less restrictive applications.
1.5 Wire for welded wire reinforcement is generally manufactured at 520 MPa (75 ksi) yield strength level. Other strength levels shall be by agreement between the purchaser and manufacturer. Note 2—The term used to refer to yield strength levels are the same as those in ASTM Standards for welded wire reinforcement.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn. Contact ASTM
International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: A 1022 – 01
Standard Specification for
Deformed and Plain Stainless Steel Wire and Welded Wire
for Concrete Reinforcement
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A 1022; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
working, good toughness and ductility properties at low temperatures, and
1. Scope
low magnetic permeability. Duplex stainless steels have generally a
1.1 This specification covers stainless steel wire and welded
corrosion resistance greater than that of most austenitic steels and are
wire reinforcement produced from hot-rolled stainless steel
magnetic. Other stainless steels with different chemical compositions than
rod. The stainless steel wire is cold-worked, drawn or rolled,
the series and types mentioned above, may be used for less restrictive
plain (non-deformed) or deformed or a combination of de- applications.
formed and plain. It is used as concrete reinforcement for
1.5 Wire for welded wire reinforcement is generally manu-
applications requiring resistance to corrosion and/or controlled
factured at 520 MPa (75 ksi) yield strength level. Other
magnetic permeability. Common wire sizes and dimensions are
strength levels shall be by agreement between the purchaser
found in this specification. Actual wire sizes are not restricted
and manufacturer.
to those shown in the tables.
NOTE 2—The term used to refer to yield strength levels are the same as
1.2 SupplementS1describeshighstrengthwire,whichshall
those in ASTM Standards for welded wire reinforcement.
be furnished when specifically ordered. It shall be permissible
to furnish high strength wire in place of regular wire if
2. Referenced Documents
mutually agreed to by the purchaser and supplier.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.2.1 A supplementary requirement (S2) of an optional
A82 Specification for Steel Wire, Plain, for Concrete Re-
nature is provided. It shall apply only when specified by the
inforcement
purchaser. In order to obtain a corrosion tested or controlled
A 185 Specification for Steel Welded Wire, Plain for Con-
magnetic permeability product, steel conforming to Supple-
crete Reinforcement
mentary Requirement S2 should be ordered.
A 262 Practices for detecting Susceptibility to Intergranular
1.3 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units
Attack in Austenitic Stainless Steels
are to be regarded as standard. Within the text the inch-pound
A 276 Specification for Stainless Steel Bars and Shapes
units are shown in parentheses. The values stated in each
A 314 Specification for Stainless Steel Billets and Bars for
system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system must
Forging
be used independently of the other. Combining values may
A 342 Test Methods for Permeability of Feebly Magnetic
result in nonconformance with the specification.
Materials
1.4 The chemical composition of the steel (stainless grade)
A 370 Test Methods and Definitions for MechanicalTesting
shall be selected for suitability to the application involved by
of Steel Products
agreement between the manufacturer and the purchaser. Use
A 496 Specification for Steel Wire, Deformed, for Concrete
Specification A 276 for chemical requirements. The UNS
Reinforcement
designations are to be included with the type number and noted
A 497 Specification for Steel Welded Wire, Deformed, for
in brackets, i.e. austenitic stainless steels as Type 304
Concrete Reinforcement
[S30400], 304L [S30403], 316 [S31600], 316L [S31603],
A 700 PracticesforPackaging,MarkingandLoadingMeth-
316N [S31651], 316LN [S31653] and duplex stainless steels,
ods for Steel Products for Domestic Shipment
Types 2205 [S32205] and 329 [S32900].
A 704 SpecificationforWeldedSteelPlainBarorRodMats
NOTE 1—Only austenitic and duplex stainless steels are usually recom-
for Concrete Reinforcement
mended for use as reinforcement in concrete because of their high
A 955 Deformed and Plain Stainless Steel Bars for concrete
corrosion resistance. Austenitic stainless steels have good general corro- 2
Reinforcement (Metric)
sion resistance, strength characteristics which can be improved by cold
1 2
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel, Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.04
Stainless Steel, and RelatedAlloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.03
A01.05 on Steel Reinforcement. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.04
Current edition approved Dec. 10, 2001. Published February 2002. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.05
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn. Contact ASTM
International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
A1022–01
E83 Practice for Verification and Classification of Exten- 4.1.10 Heat treatment condition.
someters 4.1.11 Supplementary requirements (if desired).
2.2 Military Standards:
NOTE 3—Atypical ordering description is as follows: For metric units:
MIL-STD-129 Marking for Shipment and Storage
10,000 square meters of welded wire for concrete reinforcement,
MIL-STD-163 Steel Mill Products Preparation for Ship-
3053305-MW653MW65, in flat sheets 2438 mm wide by 4.6 mm long
ment and Storage in secured bundles for crane or forklift truck lifts. For in-lbs units:
(100,000 square feet of welded wire for concrete reinforcement, 12312-
2.3 Federal Standard:
W103W10 in flat sheets 96 in. wide by 15 ft long) in secured bundles for
Fed. Std. No. 123 Marking for Shipments (CivilAgencies)
crane or forklift truck lifts. Testing shall be in accordance with Test
2.4 Other Standard:
Methods A 370.
ACI 318 Building Code Requirements for Structural Con-
NOTE 4—Longitudinal wires can be variably spaced. (Ex: 3053305-
crete
MW653MW65,12312-W103W10 or V3305-MD653MD65 or V312-
D103D10). See the Tables 1 and 2 for wire sizes.
3. Terminology
5. Materials
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
5.1 Stainless steel wire for welded wire reinforcement shall
3.1.1 stainless steel plain wire and welded plain wire
be cold worked, either drawn or rolled from steel rod, which is
reinforcement—as used within the scope and intent of this
rolled from properly identified heats of mold or strand cast
specification, designates a material composed of cold-worked
steel.
stainless steel wire, as cold-drawn or cold-rolled from stainless
5.2 Cold worked wire or rod used in the manufacture of
steel hot-rolled rod. The welded intersections provide the bond
stainless steel welded reinforcement shall follow the chemical
strength for shear resistance.
and physical requirements of Specification A 276.
3.1.2 stainless steel deformed wire and welded deformed
wire reinforcement—as used within the scope and intent of this
6. Manufacture
specification, designates a material composed of cold- worked
deformedstainlesssteelwireascold-drawnorcold-rolledfrom
6.1 The wire or rod shall be assembled by automatic
stainless steel hot-rolled rod. Deformations may be indented or
machines or by other suitable mechanical means which will
raised rib (protrusion) types. As with plain stainless steel
assure accurate spacing and alignment of all wires of the
welded wire, the welded intersections provide bond strength
finished welded wire reinforcement. The finished welded wire
for shear resistance and the deformations add to the bond
reinforcementshallbefurnishedinflatorbentsheetsorinrolls
strength.
as specified by the purchaser.
3.1.3 convoluted wire—when wire for welded wire rein-
6.2 Longitudinal and transverse wires shall be securely
forcement is formed into a sinusoidal wave shape, it is
connected at every intersection by a process of electrical-
commonly referred to as convoluted wire. The wire is used in
resistance welding which employs the principle of fusion
the manufacture of cages for certain applications of concrete
combined with pressure.
pipe reinforcement. Only plain wire is normally subject to
convolution.
TABLE 1 Dimensional Requirements for Plain Wire—SI Units
4. Ordering Information
Size Nominal Diameter, Nominal Area,
A 2
Number mm mm
4.1 It shall be the responsibility of the purchaser to specify
MW 5 2.50 5
all requirements that are necessary for material ordered to this
MW 10 3.60 10
specification. Such requirement shall include but are not
MW 15 4.40 15
limited to the following:
MW 20 5.00 20
MW 25 5.60 25
4.1.1 Quantity–mass (weight) or square area.
MW 30 6.20 30
4.1.2 Name of material (Ex: stainless steel welded wire for
MW 35 6.70 35
concrete reinforcement).
MW 40 7.10 40
MW 45 7.60 45
4.1.3 Wire spacing and wire sizes.
MW 50 8.00 50
4.1.4 Exclusion of over-steeling or using a larger area of
MW 55 8.40 55
steel than specified.
MW 60 8.70 60
MW 65 9.10 65
4.1.5 Length and width of sheets or rolls.
MW 70 9.40 70
4.1.6 ASTM designation and year of issue.
MW 80 10.10 80
4.1.7 Application (corrosion resistance or magnetic perme- MW 90 10.70 90
MW 100 11.30 100
ability).
MW 120 12.40 120
4.1.8 Grade (strength level).
MW 130 12.90 130
4.1.9 Chemical composition (stainless steel grade). MW 200 15.95 200
MW 290 19.22 290
A
This table represents a hard metrication of the most readily available sizes in
the welded wire reinforcement industry. Table 1 shall be used in projects that are
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.01
designed using SI units: Table 2 shall be used on projects designed using
Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, Bldg. 4, Section D,
inch-pound units.Areas of wire shall be checked with the most efficient and readily
700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111–5094.
available material from producers. Other wire sizes are available and many
8 2
Available from ACI International, PO Box 9094, Farmington Hills, MI 48333. manufacturers can produce them in 1-mm increments.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn. Contact ASTM
International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
A1022–01
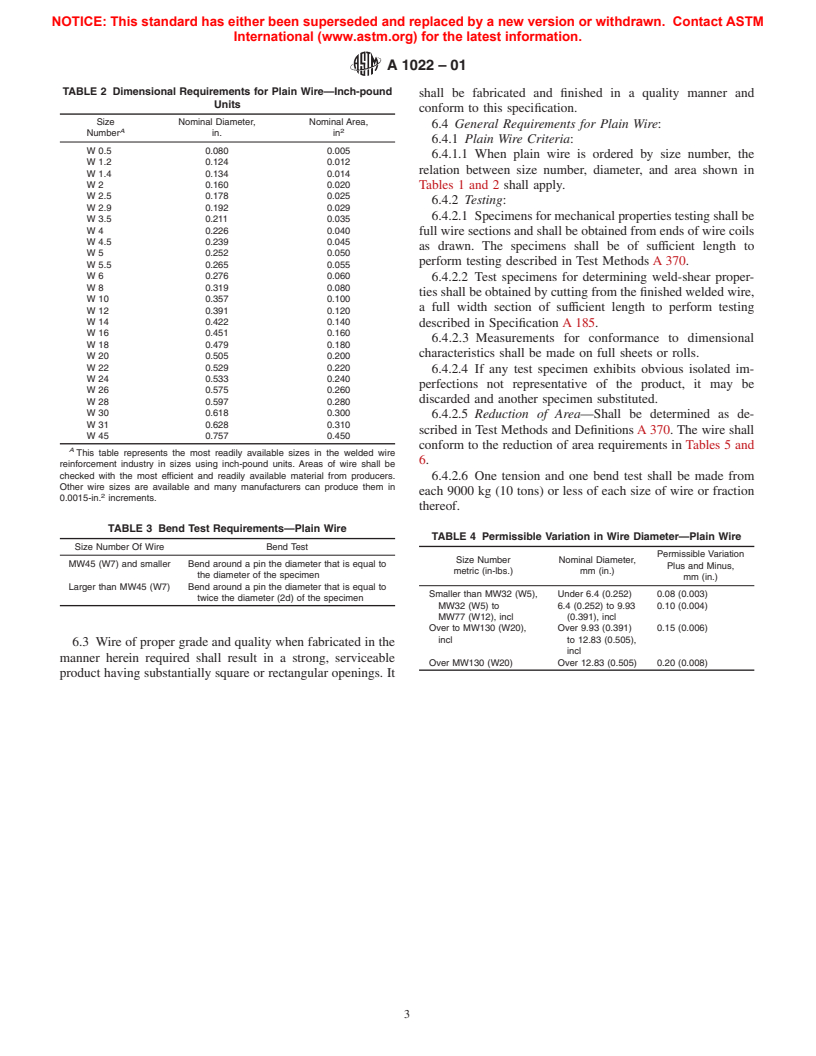
TABLE 2 Dimensional Requirements for Plain Wire—Inch-pound
shall be fabricated and finished in a quality manner and
Units
conform to this specification.
Size Nominal Diameter, Nominal Area,
6.4 General Requirements for Plain Wire:
A 2
Number in. in
6.4.1 Plain Wire Criteria:
W 0.5 0.080 0.005
6.4.1.1 When plain wire is ordered by size number, the
W 1.2 0.124 0.012
relation between size number, diameter, and area shown in
W 1.4 0.134 0.014
W 2 0.160 0.020 Tables 1 and 2 shall apply.
W 2.5 0.178 0.025
6.4.2 Testing:
W 2.9 0.192 0.029
6.4.2.1 Specimens for mechanical properties testing shall be
W 3.5 0.211 0.035
W 4 0.226 0.040
full wire sections and shall be obtained from ends of wire coils
W 4.5 0.239 0.045
as drawn. The specimens shall be of sufficient length to
W 5 0.252 0.050
perform testing described in Test Methods A 370.
W 5.5 0.265 0.055
W 6 0.276 0.060
6.4.2.2 Test specimens for determining weld-shear proper-
W 8 0.319 0.080
ties shall be obtained by cutting from the finished welded wire,
W 10 0.357 0.100
a full width section of sufficient length to perform testing
W 12 0.391 0.120
W 14 0.422 0.140
described in Specification A 185.
W 16 0.451 0.160
6.4.2.3 Measurements for conformance to dimensional
W 18 0.479 0.180
characteristics shall be made on full sheets or rolls.
W 20 0.505 0.200
W 22 0.529 0.220
6.4.2.4 If any test specimen exhibits obvious isolated im-
W 24 0.533 0.240
perfections not representative of the product, it may be
W 26 0.575 0.260
discarded and another specimen substituted.
W 28 0.597 0.280
W 30 0.618 0.300
6.4.2.5 Reduction of Area—Shall be determined as de-
W 31 0.628 0.310
scribed in Test Methods and Definitions A 370. The wire shall
W 45 0.757 0.450
conform to the reduction of area requirements in Tables 5 and
A
This table represents the most readily available sizes in the welded wire
6.
reinforcement industry in sizes using inch-pound units. Areas of wire shall be
checked with the most efficient and readily available material from producers. 6.4.2.6 One tension and one bend test shall be made from
Other wire sizes are available and many manufacturers can produce them in
each 9000 kg (10 tons) or less of each size of wire or fraction
0.0015-in. increments.
thereof.
TABLE 3 Bend Test Requirements—Plain Wire
TABLE 4 Permissible Variation in Wire Diameter—Plain Wire
Size Number Of Wire Bend Test
Permissible Variation
Size Number Nominal Diameter,
MW45 (W7) and smaller Bend around a pin the diameter that is equal to
Plus and Minus,
metric (in-lbs.) mm (in.)
the diameter of the specimen
mm (in.)
Larger than MW45 (W7) Bend around a pin the diameter that is equal to
Smaller than MW32 (W5), Under 6.4 (0.252) 0.08 (0.003)
twice the diameter (2d) of the specimen
MW32 (W5) to 6.4 (0.252) to 9.93 0.10 (0.004)
MW77 (W12), incl (0.391), incl
Over to MW130 (W20), Over 9.93 (0.391) 0.15 (0.006)
incl to 12.83 (0.505),
6.3 Wire of proper grade and quality when fabricated in the
incl
manner herein required shall result in a strong, serviceable
Over MW130 (W20) Over 12.83 (0.505) 0.20 (0.008)
product having substantially square or rectangular openings. It
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn. Contact ASTM
International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
A1022–01
TABLE 5 Tension Test Requirement—Plain Wire
6.5.1.4 The minimum average height of the center of typical
deformations based on the nominal wire diameters shown in
Tables 7 and 8 shall be as follows:
Tensile strength, min, MPa (ksi) 550 (80)
Yield strength, min, MPa (ksi) 485 (70)
Wire Sizes Minimum Average Height of Deformations,
A
Reduction of area, min. % 30
Percent of Nominal Wire Diameter
A
MD 19 (D 3) and finer 4
For material testing over 100 ksi (690 MPa) tensile strength, the reduction of
Coarser than MD 19 (D 3) through 4 ⁄2
area shall be not less than 25%.
MD 65 (D 10)
Coarser than MD 65 (D 10) 5
TABLE 6 Tension Test Requirement Plain Wire (Material for
6.5.1.5 The deformations shall be placed with respect to the
Welded Wire)
axis of the wire so that the included angle is not less than 45º;
Size MW8 (W1.2) Smaller than
and Larger Size MW8(W1.2) or if deformations are curvilinear, the angle formed by the
transverseaxisofthedeformationandthewireaxisshallbenot
Tensile strength, min, MPa (ksi) 515 (75) 485 (70)
Yield strength, min, MPa (ksi) 450 (65) 385 (56)
less
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.