ASTM A503/A503M-15
(Specification)Standard Specification for Ultrasonic Examination of Forged Crankshafts
Standard Specification for Ultrasonic Examination of Forged Crankshafts
ABSTRACT
This test method deals with the acceptance specifications for the ultrasonic examination of forged steel crankshafts. This practice is applicable to both solid (slab) forged and continuous grain flow crankshafts. Specimens shall be divided into three volumetric zones, namely: the major critical sections (Zone 1), which includes the heavily loaded areas of the crankpins, webs, and main bearings; the minor critical sections (Zone 2), which includes the balance of the surface areas of the main bearing and crankpin journals and adjacent fillets, flanges, and gear fit areas; and Zone 3, which includes the balance of the crankshaft, and the remaining sections of the webs. The crankshafts shall be examined after heat treatment, but before machining geometric features such as chamfers and oil holes. Acceptance zones and criteria for both types of crankshafts are discussed briefly.
SCOPE
1.1 This is an acceptance specification for the ultrasonic inspection of forged steel crankshafts having main bearing journals or crankpins 4 in. [100 mm] or larger in diameter.
1.2 This specification covers the testing equipment required and the test procedure to be followed, and it defines the critical and noncritical areas and limits of acceptance.
1.3 This specification is intended to cover both continuous grain flow (CGF) crankshafts for medium and high speed diesel engines as well as solid (slab) forged crankshafts for other applications.
1.4 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI (metric) units are to be regarded separately as the standard. Within the text and tables, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the specification.
1.5 Unless the order specifies the applicable “M” specification designation, the inch-pound units shall be used.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: A503/A503M −15
Standard Specification for
1
Ultrasonic Examination of Forged Crankshafts
This standard is issued under the fixed designationA503/A503M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* than Aluminum, Reference Blocks Used in Ultrasonic
Testing
1.1 This is an acceptance specification for the ultrasonic
3
2.2 American National Standard:
inspection of forged steel crankshafts having main bearing
ANSI B46.1, Surface Texture
journals or crankpins 4 in. [100 mm] or larger in diameter.
1.2 This specification covers the testing equipment required
3. Terminology
and the test procedure to be followed, and it defines the critical
3.1 Definitions:
and noncritical areas and limits of acceptance.
3.1.1 continuous grain flow crankshafts—produced by a
1.3 This specification is intended to cover both continuous
process in which the solidification centerline of the original
grain flow (CGF) crankshafts for medium and high speed
ingot or starting stock is maintained through the main bearings,
diesel engines as well as solid (slab) forged crankshafts for
webs, crankpins, and flanges of the finished crankshaft, usually
other applications.
by means of closed die forging.
1.4 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI
3.1.2 solid (slab) forged crankshafts—made from open die
(metric) units are to be regarded separately as the standard.
forgings such that the grain flow in the webs is essentially
Within the text and tables, the SI units are shown in brackets.
parallel to the major axis of the forging and the crankpins are
Thevaluesstatedineachsystemshallbeusedindependentlyof
offset from the forging centerline by machining. They may be
the other. Combining values from the two systems may result
set in the correct orientation by a hot twisting operation.
in nonconformance with the specification.
4. Ordering Information
1.5 Unless the order specifies the applicable “M” specifica-
tion designation, the inch-pound units shall be used. 4.1 It is necessary that the crankshaft be identified as being
either continuous grain flow or solid (slab) forged.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
4.2 Unless otherwise specified by means of supplementary
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
ordering information, the test methods and acceptance criteria
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
for the appropriate crankshaft type shall be used.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
5. Apparatus and Personnel Requirements
2. Referenced Documents
5.1 The apparatus and personnel requirements shall be in
2
2.1 ASTM Standards: accordance with Practice A388/A388M. For standardization
A388/A388M Practice for Ultrasonic Examination of Steel purposes, it is recommended that final acceptance be based on
Forgings the use of 2–5 MHz transducers.
A788/A788M Specification for Steel Forgings, General Re-
6. Critical Sections
quirements
E428 Practice for Fabrication and Control of Metal, Other
6.1 Thedivisionofacrankshaftintothreevolumetriczones,
as shown in Fig. 1 and Fig. 2, for the purpose of ultrasonic
examination evaluation is applicable to both solid (slab) forged
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel,
and continuous grain flow crankshafts.
Stainless Steel and Related Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
A01.06 on Steel Forgings and Billets. 6.2 The major critical sections shown as Zone 1 in Fig. 1
Current edition approved May 1, 2015. Published May 2015. Originally
include the heavily loaded areas of the crankpins, webs, and
approved in 1964. Last previous edition approved in 2011 as A503/
main bearings.
A503M–01 (2011). DOI: 10.1520/A0503_A0503M-15.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
the ASTM website. 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
A503/A503M − 15
FIG. 1 Crankshaft UT Acceptance Zones
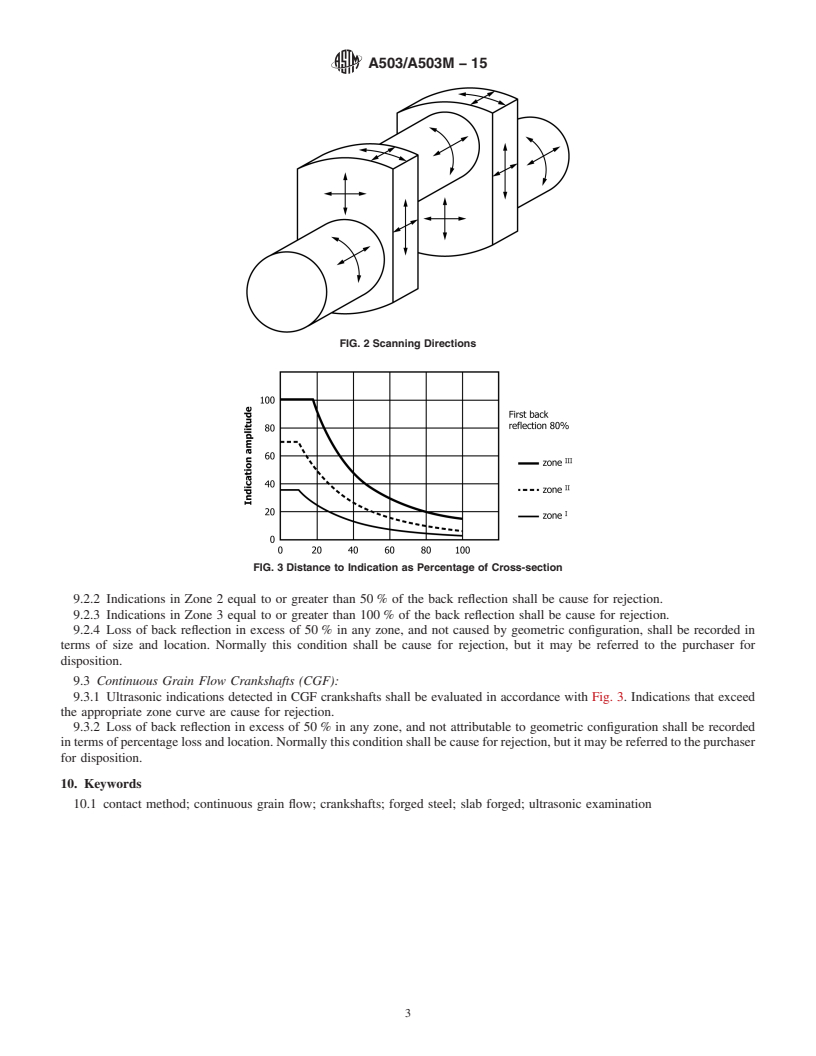
FIG. 3 Distance to Indication as Percentage of Cross-section
8. Procedure
FIG. 2 Scanning Directions
8.1 The crankshaft should b
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: A503/A503M − 01 (Reapproved 2011) A503/A503M − 15
Standard Specification for
1
Ultrasonic Examination of Forged Crankshafts
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A503/A503M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Scope*
1.1 This is an acceptance specification for the ultrasonic inspection of forged steel crankshafts having main bearing journals or
crankpins 4 in. [100 mm] or larger in diameter.
1.2 This specification covers the testing equipment required and the test procedure to be followed, and it defines the critical and
noncritical areas and limits of acceptance.
1.3 This specification is intended to cover both continuous grain flow (CGF) crankshafts for medium and high speed diesel
engines as well as solid (slab) forged crankshafts for other applications.
1.4 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI (metric) units are to be regarded separately as the standard. Within the
text and tables, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system shall be used independently of the other.
Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the specification.
1.5 Unless the order specifies the applicable “M” specification designation, the inch-pound units shall be used.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A388/A388M Practice for Ultrasonic Examination of Steel Forgings
A788/A788M Specification for Steel Forgings, General Requirements
E428 Practice for Fabrication and Control of Metal, Other than Aluminum, Reference Blocks Used in Ultrasonic Testing
3
2.2 American National Standard:
ANSI B46.1, Surface Texture
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 continuous grain flow crankshafts—produced by a process in which the solidification centerline of the original ingot or
starting stock is maintained through the main bearings, webs, crankpins, and flanges of the finished crankshaft, usually by means
of closed die forging.
3.1.2 solid (slab) forged crankshafts—made from open die forgings such that the grain flow in the webs is essentially parallel
to the major axis of the forging and the crankpins are offset from the forging centerline by machining. They may be set in the
correct orientation by a hot twisting operation.
4. Ordering Information
4.1 It is necessary that the crankshaft be identified as being either continuous grain flow or solid (slab) forged.
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel, Stainless Steel and Related Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee A01.06
on Steel Forgings and Billets.
Current edition approved April 1, 2011May 1, 2015. Published June 2011May 2015. Originally approved in 1964. Last previous edition approved in 20062011 as
A503/A503M – 01A503/A503M (2006). –01 (2011). DOI: 10.1520/A0503_A0503M-01R11.10.1520/A0503_A0503M-15.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from American National Standards Institute, 11 W. 42nd St., 13thInstitute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St., 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036.10036, http://www.ansi.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
A503/A503M − 15
4.2 Unless otherwise specified by means of supplementary ordering information, the test methods and acceptance criteria for
the appropriate crankshaft type shall be used.
5. Apparatus and Personnel Requirements
5.1 The apparatus and personnel requirements shall be in accordance with Practice A388/A388M. For standardization purposes,
it is recommended that final acceptance be based on the use of 2–5 MHz transducers.
6. Critical Sections
6.1 The division of a crankshaft into three volumetric zones, as shown in Fig. 1 a
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.