ASTM A453/A453M-17(2024)
(Specification)Standard Specification for High-Temperature Bolting, with Expansion Coefficients Comparable to Austenitic Stainless Steels
Standard Specification for High-Temperature Bolting, with Expansion Coefficients Comparable to Austenitic Stainless Steels
ABSTRACT
This specification covers standards for Grade 660 (Class A, B, C, and D) , Grade 651 (Class A and B), Grade 662 (Class A and B), and Grade 665 (Class A and B) of bolting materials for use in high-temperature service such as fasteners, for pressure vessels and valve flanges. Bolting materials in this specification covers rolled, forged, or hot-extruded bars, and also bolts, nuts, screws, washers, studs, and stud bolts. Materials shall adhere to specified contents of carbon, manganese, phosphorus, sulfur, silicon, nickel, chromium, molybdenum, tungsten, titanium, columbium, aluminum, vanadium, boron, and copper. Materials shall be subjected to tension, stress-rupture, and hardness tests. Materials shall conform to yield strength, tensile strength, elongation, reduction of area, Brinell hardness, and Rockwell hardness requirements. Hardening and solution treatment requirements for each material class are also given.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification2 covers five grades of bolting materials with twelve classes of yield strength ranging from 50 to 120 ksi [345 to 827 MPa] for use in high-temperature service for bolting components, such as bolts, screws, nuts, or studs, for pressure vessel and valve flanges. See Specification A962/A962M for the definition of bolting. The material requires special processing and is not intended for general purpose applications.
1.2 The following referenced general requirements are indispensable for application of this specification: Specification A962/A962M.
1.3 Supplementary Requirements are provided for use at the option of the purchaser. The Supplementary Requirements shall only apply when specified individually by the purchaser in the purchase order or contract.
1.4 This specification is expressed in both inch-pound units and in SI units; however, unless the purchase order or contract specifies the applicable “M” specification designation (SI units), the inch-pound units shall apply.
1.5 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: A453/A453M − 17 (Reapproved 2024)
Standard Specification for
High-Temperature Bolting, with Expansion Coefficients
Comparable to Austenitic Stainless Steels
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A453/A453M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
2 Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
1.1 This specification covers five grades of bolting mate-
rials with twelve classes of yield strength ranging from 50 to
2. Referenced Documents
120 ksi [345 to 827 MPa] for use in high-temperature service
2.1 ASTM Standards:
for bolting components, such as bolts, screws, nuts, or studs,
A193/A193M Specification for Alloy-Steel and Stainless
for pressure vessel and valve flanges. See Specification A962/
Steel Bolting for High Temperature or High Pressure
A962M for the definition of bolting. The material requires
Service and Other Special Purpose Applications
special processing and is not intended for general purpose
A962/A962M Specification for Common Requirements for
applications.
Bolting Intended for Use at Any Temperature from Cryo-
1.2 The following referenced general requirements are in-
genic to the Creep Range
dispensable for application of this specification: Specification
E139 Test Methods for Conducting Creep, Creep-Rupture,
A962/A962M.
and Stress-Rupture Tests of Metallic Materials
1.3 Supplementary Requirements are provided for use at the
E292 Test Methods for Conducting Time-for-Rupture Notch
option of the purchaser. The Supplementary Requirements
Tension Tests of Materials
shall only apply when specified individually by the purchaser
3. Terminology
in the purchase order or contract.
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
1.4 This specification is expressed in both inch-pound units
3.1.1 heat-treatment charge—one heat of material heat
and in SI units; however, unless the purchase order or contract
treated in one batch. If a continuous operation is used, the
specifies the applicable “M” specification designation (SI
weight processed as a heat-treatment charge shall not exceed
units), the inch-pound units shall apply.
the weights in Table 1.
1.5 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
3.1.2 lot—a lot shall consist of the quantities shown in Table
are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the
2.
SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each
system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system
4. Ordering Information
shall be used independently of the other. Combining values
4.1 The inquiry and order shall indicate the following:
from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the
4.1.1 Quantity (weight or number of pieces),
standard.
4.1.2 Description of item (bars, bolts, nuts, etc.),
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
4.1.3 Grade and class (see Table 3),
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
4.1.4 Method of finishing (see 6.1),
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
4.1.5 Type of thread desired (see 6.1.1),
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
4.1.6 Alternative test method option (see 8.2.4.3),
4.1.7 Bolt shape option, if any,
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel,
4.1.8 Thread option, if any,
Stainless Steel and Related Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
4.1.9 Test method for surface quality, if any,
A01.22 on Steel Forgings and Wrought Fittings for Piping Applications and Bolting
Materials for Piping and Special Purpose Applications.
Current edition approved March 1, 2024. Published March 2024. Originally
approved in 1961. Last previous edition approved in 2017 as A453/A453M – 17. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
DOI: 10.1520/A0453_A0453M-17R24. contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code Applications see related Specifi- Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
cation SA-453 in Section II of that Code. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
A453/A453M − 17 (2024)
TABLE 1 Continuous Heat-Treatment Charge Sizes
8.1.2 Number of Specimens:
Diameter, in. [mm] Weight, lb [kg] 8.1.2.1 Heat-Treated Bars—When not more than two sizes
To 1 ⁄4 [44] 3000 [1400] of bars are heat treated in the same load, one tension test shall
3 1
Over 1 ⁄4 [44] to 2 ⁄2 [63] 6000 [2700]
be made from each size in each heat of material in the
Over 2 ⁄2 [63] 12000 [5400]
heat-treatment charge (see 3.1.1). When more than two sizes of
bars are treated in the same charge, one tension test shall be
made from one bar of each of the two largest diameters from
TABLE 2 Lot Sizes
each heat of material in the heat-treating charge.
Diameter, in. [mm] Maximum Lot Size, lb [kg]
8.1.2.2 Finished Bolting Components—One tension test
1 ⁄2 [38] and under 200 [90]
1 3 shall be made if the lot consists of parts of the same nominal
Over 1 ⁄2 [38] to 1 ⁄4 [44], incl 300 [140]
3 1
Over 1 ⁄4 [44] to 2 ⁄2 [63], incl 600 [270]
diameter. If the lot consists of components of more than one
Over 2 ⁄2 [63] 20 pieces
nominal diameter, one tension test shall be made from each
nominal diameter of each heat involved in the lot (see Section
3).
4.1.10 Test location option, if any,
8.2 Stress-Rupture Test:
4.1.11 Rejection option, if any, and
8.2.1 Requirements—Bolting material shall conform to the
4.1.12 If stress-rupture testing is not required, except for
stress-rupture requirements prescribed in Table 6 for design
Grade 660 Class D and Grade 668 (see 8.2.1).
temperatures above 800 °F [427 °C]. Bolting material not
stress-rupture tested shall be permanently stamped NR. Grade
5. Common Requirements
660 Class D and Grade 668 do not require stress-rupture and
5.1 Bolting materials and bolting components supplied to
shall be stamped NR.
this specification shall conform to the requirements of Speci-
8.2.2 The number of specimens shall be the same as the
fication A962/A962M. These requirements include test
required number of tension test specimens.
methods, finish, thread dimensions, marking, certification,
8.2.3 The test location and orientation shall be the same as
optional supplementary requirements, and others. Failure to
that required for the tension test specimens.
comply with the requirements of Specification A962/A962M
8.2.4 Test Method:
constitutes nonconformance with this specification. In case of
8.2.4.1 The rupture test shall be performed in accordance
conflict between the requirements of this specification and
with Practice E139.
Specification A962/A962M, this specification shall prevail.
NOTE 1—Fig. 1 is taken from Test Method E292. This is to facilitate
detection of notch sensitivity. The specimen found in Practice E139 does
6. Materials and Manufacture
not include a notch. The specimen in Fig. 1 is to be used only to determine
6.1 Finishing Process:
if the material is notch sensitive. Actual testing is to Practice E139, not
Test Method E292, so the additional test data required by Test Method
6.1.1 Threads may be formed by machining or rolling.
E292 is not to be determined or reported.
Threads may be formed after precipitation heat treatment or
after solution anneal but prior to precipitation heat treatment.
8.2.4.2 A combination smooth and notched test specimen,
Type designations are as follows:
machined to the dimensions prescribed in Fig. 1 and Table 7,
Type M1—threads formed by machining after precipitation
shall be tested in accordance with the stress-rupture require-
heat treatment.
ments prescribed in Table 6. The test shall be continued to
Type M2—threads formed by machining after solution
rupture. The rupture shall occur in the smooth section of the
anneal but prior to precipitation heat treatment.
bar.
Type R1—threads formed by rolling after precipitation heat
8.2.4.3 As an alternative procedure and, when specifically
treatment.
approved by the purchaser, separate smooth and notched test
Type R2—threads formed by rolling after solution anneal
specimens, machined from adjacent sections of the same piece,
but prior to precipitation heat treatment.
with gage sections conforming to the respective dimensions of
When not specified by the purchaser, the type supplied shall
Table 7, may be tested under the above conditions. The notched
be the option of the manufacturer.
specimen need not be tested to rupture but shall not rupture in
less time than the companion smooth specimen.
6.2 Heat Treatment—Each grade and class shall be heat
8.2.4.4 When the minimum specified time to rupture in
treated as prescribed in Table 4.
Table 6 has been achieved, incremental loading may be used to
7. Chemical Composition accelerate the time to rupture. At intervals of 8 to 16 h,
preferably 8 to 10 h, the stress shall be increased in increments
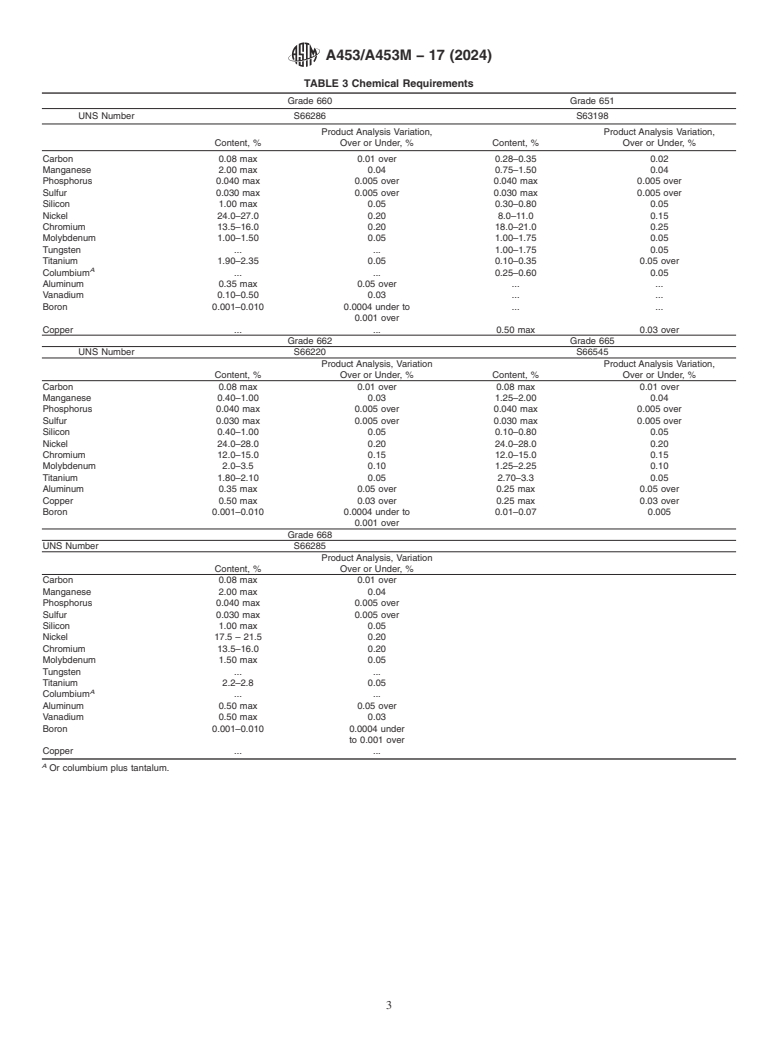
7.1 Each alloy shall conform to the chemical composition
of 5000 psi [34.5 MPa]. Rupture location, and elongation
requirements prescribed in Table 3.
requirements shall be as prescribed in Table 6, 8.2.4.2, and
8.2.4.3.
8. Mechanical Properties
8.3 Hardness Test:
8.1 Tension Test:
8.1.1 Requirements—Bolting material in each heat- 8.3.1 Requirements—Bolting material shall conform to the
room temperature hardness requirements prescribed in Table 5.
treatment charge shall conform to the room-temperature tensile
requirements in Table 5. 8.3.2 Number of Tests:
A453/A453M − 17 (2024)
TABLE 3 Chemical Requirements
Grade 660 Grade 651
UNS Number S66286 S63198
Product Analysis Va
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.