ASTM D235-02(2007)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Mineral Spirits (Petroleum Spirits) (Hydrocarbon Dry Cleaning Solvent)
Standard Specification for Mineral Spirits (Petroleum Spirits) (Hydrocarbon Dry Cleaning Solvent)
ABSTRACT
This specification covers hydrocarbon solvents, normally petroleum distillates, used in coatings and dry-cleaning industries. These solvents are also known as mineral spirits and as Stoddard solvents when used in dry cleaning. The following are the types of mineral spirits: Type I, Type II, Type III, Type IV, Class A, Class B, and Class C. The physical and chemical properties of mineral spirits shall conform to the requirements specified for: aromatic content, commercial reference, appearance, flash point, color, kauri-butanol value, bromine number, odor, doctor test, distillation, residue for distillation, copper corrosion, and apparent specific gravity. These properties shall be tested with the specified test methods.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers four types of hydrocarbon solvents, normally petroleum distillates, used primarily in the coatings and dry-cleaning industries. “Mineral spirits” is the most common name for these solvents. They are also called “Stoddard Solvents” when used for dry cleaning.
1.2 For specific hazard information and guidance, see the supplier's Material Safety Data Sheet for materials listed in this specification.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 The following applies to all specified limits in this standard; for purposes of determining conformance with this standard, an observed value or a calculated value shall be rounded off “to the nearest unit” in the last right-hand digit used in expressing the specification limit, in accordance with the rounding-off method of Practice E 29.
1.5 The following hazard caveat pertains only to the test method portion, 6.1.10, of this specification. This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D235 −02(Reapproved2007)
Standard Specification for
Mineral Spirits (Petroleum Spirits) (Hydrocarbon Dry
Cleaning Solvent)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D235; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope* Atmospheric Pressure
D130 Test Method for Corrosiveness to Copper from Petro-
1.1 This specification covers four types of hydrocarbon
leum Products by Copper Strip Test
solvents, normally petroleum distillates, used primarily in the
D156 Test Method for Saybolt Color of Petroleum Products
coatings and dry-cleaning industries. “Mineral spirits” is the
(Saybolt Chromometer Method)
most common name for these solvents. They are also called
D268 Guide for Sampling and Testing Volatile Solvents and
“Stoddard Solvents” when used for dry cleaning.
Chemical Intermediates for Use in Paint and Related
1.2 For specific hazard information and guidance, see the
Coatings and Material
supplier’sMaterialSafetyDataSheetformaterialslistedinthis
D1133 Test Method for Kauri-Butanol Value of Hydrocar-
specification.
bon Solvents
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as D1159 Test Method for Bromine Numbers of Petroleum
Distillates and Commercial Aliphatic Olefins by Electro-
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
only. metric Titration
D1209 Test Method for Color of Clear Liquids (Platinum-
1.4 The following applies to all specified limits in this
Cobalt Scale)
standard; for purposes of determining conformance with this
D1296 Test Method for Odor of Volatile Solvents and
standard, an observed value or a calculated value shall be
Diluents
rounded off “to the nearest unit” in the last right-hand digit
D2710 Test Method for Bromine Index of Petroleum Hydro-
used in expressing the specification limit, in accordance with
carbons by Electrometric Titration
the rounding-off method of Practice E29.
D3227 Test Method for (Thiol Mercaptan) Sulfur in
1.5 The following hazard caveat pertains only to the test
Gasoline, Kerosine,Aviation Turbine, and Distillate Fuels
method portion, 6.1.10, of this specification.This standard does
(Potentiometric Method)
not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any,
D3257 Test Methods for Aromatics in Mineral Spirits by
associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this
Gas Chromatography
standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices
D3278 Test Methods for Flash Point of Liquids by Small
and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior
Scale Closed-Cup Apparatus
to use.
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
Determine Conformance with Specifications
2. Referenced Documents
E300 Practice for Sampling Industrial Chemicals
2.1 ASTM Standards:
2.2 U.S. Federal Specification:
D56 Test Method for Flash Point by Tag Closed Cup Tester
PPP-C-2020 Chemical, Liquid, Dry, and Paste: Packaging of
D86 Test Method for Distillation of Petroleum Products at
3. Classification
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint
and Related Coatings, Materials, andApplications and is the direct responsibility of 3.1 Mineral spirits shall be of the following types as
Subcommittee D01.35 on Solvents, Plasticizers, and Chemical Intermediates.
specified:
Current edition approved June 1, 2007. Published April 2008. Originally
3.1.1 Type I—Full Range.
approved in 1926. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as D235 – 02. DOI:
10.1520/D0235-02R07.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, DODSSP, Bldg. 4,
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Section D, 700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5098, http://
the ASTM website. www.dodssp.daps.mil.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D235−02(2007)
3.1.2 Type II—High Flash Point. 4. Properties
3.1.3 Type III—Odorless.
4.1 The physical and chemical properties of the different
3.1.4 Type IV—Low Dry Point.
types and classes of mineral spirits shall conform to the
3.2 Mineral spirits types may be further differentiated based requirements specified in Table 1.
on aromatics content as follows:
5. Sampling
3.2.1 Class A—8 to 22 vol % aromatics.
3.2.2 Class B—2 to 8 max vol % aromatics. 5.1 The material shall be sampled in accordance with
3.2.3 Class C—less than 2 vol % aromatics. Practice E300.
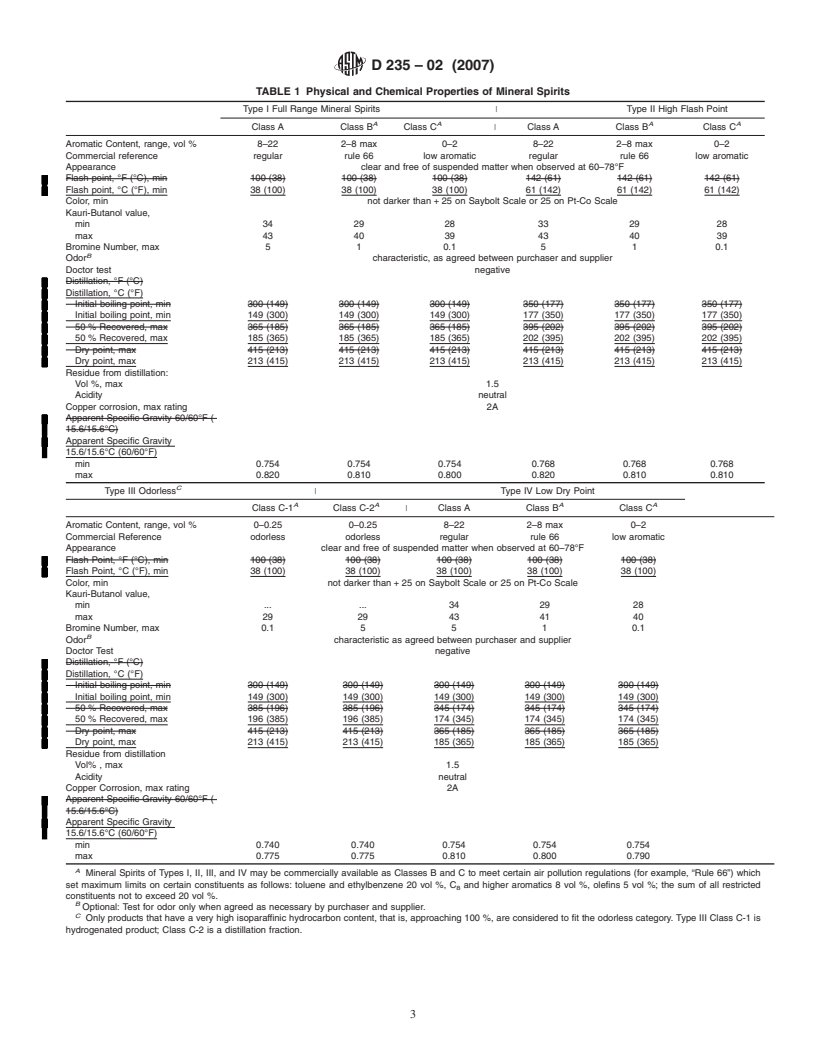
TABLE 1 Physical and Chemical Properties of Mineral Spirits
Type I Full Range Mineral Spirits Type II High Flash Point
A A A A
Class A Class B Class C Class A Class B Class C
Aromatic Content, range, vol % 8–22 2–8 max 0–2 8–22 2–8 max 0–2
Commercial reference regular rule 66 low aromatic regular rule 66 low aromatic
Appearance clear and free of suspended matter when observed at 60–78°F
Flash point, °C (°F), min 38 (100) 38 (100) 38 (100) 61 (142) 61 (142) 61 (142)
Color, min not darker than + 25 on Saybolt Scale or 25 on Pt-Co Scale
Kauri-Butanol value,
min 34 29 28 33 29 28
max 43 40 39 43 40 39
Bromine Number, max 5 1 0.1 5 1 0.1
B
Odor characteristic, as agreed between purchaser and supplier
Doctor test negative
Distillation, °C (°F)
Initial boiling point, min 149 (300) 149 (300) 149 (300) 177 (350) 177 (350) 177 (350)
50 % Recovered, max 185 (365) 185 (365) 185 (365) 202 (395) 202 (395) 202 (395)
Dry point, max 213 (415) 213 (415) 213 (415) 213 (415) 213 (415) 213 (415)
Residue from distillation:
Vol%,max 1.5
Acidity neutral
Copper corrosion, max rating 2A
Apparent Specific Gravity
15.6/15.6°C (60/60°F)
min 0.754 0.754 0.754 0.768 0.768 0.768
max 0.820 0.810 0.800 0.820 0.810 0.810
C
Type III Odorless Type IV Low Dry Point
|
A A A
A
Class C-1 Class A Class B Class C
Class C-2
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D235–02 Designation: D 235 – 02 (Reapproved 2007)
Standard Specification for
Mineral Spirits (Petroleum Spirits) (Hydrocarbon Dry
Cleaning Solvent)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 235; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification covers four types of hydrocarbon solvents, normally petroleum distillates, used primarily in the coatings
and dry-cleaning industries. “Mineral spirits” is the most common name for these solvents. They are also called “Stoddard
Solvents” when used for dry cleaning.
1.2 For specific hazard information and guidance, see the supplier’s Material Safety Data Sheet for materials listed in this
specification.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 The following applies to all specified limits in this standard; for purposes of determining conformance with this standard,
an observed value or a calculated value shall be rounded off “to the nearest unit” in the last right-hand digit used in expressing
the specification limit, in accordance with the rounding-off method of Practice E 29.
1.41.5 The following hazard caveat pertains only to the test method portion, 6.1.10, of this specification. This standard does not
purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to
establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 56 Test Method for Flash Point by Tag Closed Cup Tester
D 86 Test Method for Distillation of Petroleum Products at Atmospheric Pressure
D 130Test Method for Detection of Copper Corrosion from Petroleum Products by the Copper StripTarnishTest Test Method
for Corrosiveness to Copper from Petroleum Products by Copper Strip Test
D 156 Test Method for Saybolt Color of Petroleum Products (Saybolt Chromometer Method)
D 268 Guide for Sampling andTestingVolatile Solvents and Chemical Intermediates for Use in Paint and Related Coatings and
Materials Material
D 1133 Test Method for Kauri-Butanol Value of Hydrocarbon Solvents
D 1159 Test Method for Bromine Numbers of Petroleum Distillates and Commercial Aliphatic Olefins by Electrometric
Titration
D 1209 Test Method for Color of Clear Liquids (Platinum-Cobalt Scale)
D 1296 Test Method for Odor of Volatile Solvents and Diluents
D 2710 Test Method for Bromine Index of Petroleum Hydrocarbons by Electrometric Titration
D 3227 Test Method for (Thiol Mercaptan) Sulfur in Gasoline, Kerosine,AviationTurbine, and Distillate Fuels (Potentiometric
Method)
D 3257 Test Methods for Aromatics in Mineral Spirits by Gas Chromatography
D 3278 Test Methods for Flash Point of Liquids by Small Scale Closed-Cup Apparatus
E 29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to Determine Conformance with Specifications
E 300 Practice for Sampling Industrial Chemicals
2.2 U.S. Federal Specification:
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on PaintsPaint and Related Coatings, Materials, and Applications and is the direct responsibility
of Subcommittee D01.35 on Solvents, Plasticizers, and Chemical Intermediates .
Current edition approved Dec. 10, 2002.June 1, 2007. Published February 2003.April 2008. Originally approved in 1926. Last previous edition approved in 19992002 as
D235–99.D 235 – 02.
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
, Vol 05.01.volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D 235 – 02 (2007)
PPP-C-2020 Chemical, Liquid, Dry, and Paste: Packaging of
3. Classification
3.1 Mineral spirits shall be of the following types as specified:
3.1.1 Type I—Full Range.
3.1.2 Type II—High Flash Point.
3.1.3 Type III—Odorless.
3.1.4 Type IV—Low Dry Point.
3.2 Mineral spirits types may be further differentiated based on aromatics content as follows:
3.2.1 Class A—8 to 22 vol % aromatics.
3.2.2 Class B—2 to 8 max vol % aromatics.
3.2.3 Class C—less than 2 vol % aromatics.
4. Properties
4.1 The physical and chemical properties of the different types and classes of mineral spirits shall conform to the requirements
specified in Table 1.
5. Sampling
5.1 The material shall be sampled in accordance with Practice E 300.
6. Test Methods
6.1 The properties enumerated in this specification shall be determined in accordance with the following ASTM test methods:
6.1.1 Bromine Number—Test Method D 1159. Bromine number is expressed as g bromine reacted per 100-g sample. For
products having low olefin contents, Bromine Index (mg bromine reacted per 100-g sample) by Test Method D 2710 may be used.
6.1.2 Color—Test Method D 156 or Test Method D 1209. In case of dispute, Test Method D 156 shall be the referee method.
6.1.3 Corrosion—Test Method D 130. Perform test under the prescribed conditions for3hat 100°C.
6.1.4 Distillation—Test Method D 86.
6.1.5 Flash Point—Test Method D 56 or Test Methods D 3278. In case of dispute, Test Method D 56 shall be the referee
method.
6.1.6 Kauri-Butanol Value—Test Method D 1133.
6.1.7 Odor—Test Method D 1296. Samples of particular types of products being tested, having odor characteristics satisfactory
to consumer and producer, are to be used as reference standards for comparison.
6.1.8 Mercaptan Sulfur—Test Method D 3227.
6.1.9 Apparent Specific Gravity—Determine the apparent specific gravity by any convenient method that is accurate to the third
decimal place, the temperature of both specimen and water being 15.6°C. See Guide D 268.
6.1.10 Doctor Test:
6.1.10.1 Preparation of Doctor (Sodium Plumbite) Solution —Dissolve approximately 125 g of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) in
1 L of reagent water. Add 60 g of lead monoxide (PbO) and shake vigorously for 15 min., or let stand with occasional shakings
for at least a day.Allow to settle and decant or siphon off the clear liquid. If the solution does not settle clear, filter it through filter
paper. Keep the solution in a tightly corked bottle and refilter before use if not perfectly clear.
6.1.10.2 Procedure—Shake vigorously together in a test tube 10 mL of the solvent being tested and 5 mL of sodium plumbite
solution for about 15 s.Add a sma
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.