ASTM E2574/E2574M-17(2021)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Fire Testing of School Bus Seat Assemblies
Standard Test Method for Fire Testing of School Bus Seat Assemblies
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 In this test method fire test response characteristics of a school bus seat assembly are assessed following ignition by a square gas burner.
5.2 This test method is similar in concept to a fire test currently used, and which has been in such use for many years, as the industry standard for flammability testing of school bus seats (see Appendix X1). However, in this test method the paper bag has been replaced by a gas burner as the ignition source.
5.3 The US federal government has issued a flammability test applicable to interior materials in road vehicles, FMVSS 302. FMVSS 302 remains the only regulatory test for assessing fire-test-response characteristics of school bus seats.
5.4 ASTM has issued Test Method D5132 in order to provide a more standardized way of conducting FMVSS 302.
5.5 The test method described in this document provides a significantly higher challenge to school bus seats than the FMVSS 302 federal regulatory test. Therefore, any seat assembly that performs acceptably in this test is likely to meet the requirements of FMVSS 302.
5.6 It is clear that those seat assemblies that exhibit little or no flame spread, short times to flame extinction and little mass loss in this test are likely to exhibit improved performance in an actual fire situation compared to seat assemblies that burn vigorously and have high mass loss.
5.7 This test is primarily useful to distinguish products that, when exposed to these fire conditions, will become fully involved in fire from other products that will not.
SCOPE
1.1 This is a fire-test-response standard.
1.2 This test method assesses the burning behavior of upholstered seating used in school buses by measuring specific fire-test responses when a school bus seat specimen is subjected to a specified flaming ignition source under normally ventilated conditions.
1.3 The ignition source is a gas burner.
1.4 This fire test is primarily useful to distinguish products that, when exposed to an ignition source, will become fully involved in fire from other products that will not.
1.5 Data are obtained describing the burning behavior of the seat assemblies from a specific ignition source until all burning has ceased.
1.6 This test method does not provide information on the fire performance of upholstered seating in fire conditions other than those conditions specified.
1.7 The burning behavior is visually documented by photographic or video recordings, whenever possible.
1.8 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.9 This standard is used to measure and describe the response of materials, products, or assemblies to heat and flame under controlled conditions, but does not by itself incorporate all factors required for fire hazard or fire risk assessment of the materials, products or assemblies under actual fire conditions.
1.10 Fire testing is inherently hazardous. Adequate safeguards for personnel and property shall be employed in conducting these tests.
1.11 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.12 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: E2574/E2574M − 17 (Reapproved 2021) An American National Standard
Standard Test Method for
Fire Testing of School Bus Seat Assemblies
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationE2574/E2574M;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyear
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 1.11 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
1.1 This is a fire-test-response standard.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
1.2 This test method assesses the burning behavior of
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
upholstered seating used in school buses by measuring specific
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
fire-test responses when a school bus seat specimen is sub-
1.12 This international standard was developed in accor-
jected to a specified flaming ignition source under normally
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
ventilated conditions.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
1.3 The ignition source is a gas burner. Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
1.4 This fire test is primarily useful to distinguish products
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
that, when exposed to an ignition source, will become fully
involved in fire from other products that will not.
2. Referenced Documents
1.5 Dataareobtaineddescribingtheburningbehaviorofthe 2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
seat assemblies from a specific ignition source until all burning
D5132 Test Method for Horizontal Burning Rate of Poly-
has ceased.
meric Materials Used in Occupant Compartments of
Motor Vehicles
1.6 This test method does not provide information on the
fire performance of upholstered seating in fire conditions other E176 Terminology of Fire Standards
E1537 Test Method for Fire Testing of Upholstered Furni-
than those conditions specified.
ture
1.7 The burning behavior is visually documented by photo-
E1590 Test Method for Fire Testing of Mattresses
graphic or video recordings, whenever possible.
E2061 Guide for Fire Hazard Assessment of Rail Transpor-
1.8 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
tation Vehicles
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
E2067 Practice for Full-Scale Oxygen Consumption Calo-
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
rimetry Fire Tests
system shall be used independently of the other. Combining
E2257 Test Method for Room Fire Test of Wall and Ceiling
values from the two systems may result in non-conformance
Materials and Assemblies
with the standard.
F1550 TestMethodforDeterminationofFire-Test-Response
Characteristics of Components or Composites of Mat-
1.9 This standard is used to measure and describe the
response of materials, products, or assemblies to heat and tresses or Furniture for Use in Correctional Facilities after
Exposure to Vandalism, by Employing a Bench Scale
flame under controlled conditions, but does not by itself
Oxygen Consumption Calorimeter
incorporate all factors required for fire hazard or fire risk
IEEE/ASTM SI 10 American National Standard for Metric
assessment of the materials, products or assemblies under
Practice
actual fire conditions.
2.2 National Safety Council Standard:
1.10 Fire testing is inherently hazardous. Adequate safe-
School bus seat upholstery fire block test, approved by the
guards for personnel and property shall be employed in
National Conference on School Transportation as part of
conducting these tests.
the National Standards for School Buses and National
1 2
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E05 on Fire For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Standards and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E05.17 on Transporta- contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
tion. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved April 1, 2021. Published April 2021. Originally the ASTM website.
approved in 2011. Last previous edition approved in 2017 as E2574/E2574M–17. Available from National Safety Council (NSC), 1121 Spring Lake Dr., Itasca,
DOI: 10.1520/E2574_E2574M-17R21. IL 60143-3201, http://www.nsc.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
E2574/E2574M − 17 (2021)
Standards for School Bus Operations 5.2 This test method is similar in concept to a fire test
currently used, and which has been in such use for many years,
2.3 Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards:
as the industry standard for flammability testing of school bus
FMVSS 222 School Bus Passenger Seating and Crash
seats (see Appendix X1). However, in this test method the
Protection, U.S. Code of Federal Regulations, Title 49,
paper bag has been replaced by a gas burner as the ignition
Transportation,SubtitleB,ChapterV,Part571,SubpartB.
source.
FMVSS302 FlammabilityofInteriorMaterial,U.S.Codeof
Federal Regulations, Title 49, Transportation, Subtitle B,
5.3 The US federal government has issued a flammability
Chapter V, Part 571, Subpart B
test applicable to interior materials in road vehicles, FM-
2.4 NFPA Standard:
VSS 302. FMVSS 302 remains the only regulatory test for
NFPA 286 Standard Method of Tests for Evaluating Contri-
assessing fire-test-response characteristics of school bus seats.
bution of Wall and Ceiling Interior Finish to Room Fire
5.4 ASTM has issued Test Method D5132 in order to
Growth
provide a more standardized way of conducting FMVSS 302.
3. Terminology
5.5 The test method described in this document provides a
3.1 For definitions of terms used in this test method asso-
significantly higher challenge to school bus seats than the
ciated with fire issues, refer to the terminology contained in FMVSS 302 federal regulatory test.Therefore, any seat assem-
Terminology E176.
bly that performs acceptably in this test is likely to meet the
requirements of FMVSS 302.
3.2 Definitions:
3.2.1 screening test, n—as related to fire,afire-responsetest
5.6 It is clear that those seat assemblies that exhibit little or
performed to determine whether a material, product, or assem-
no flame spread, short times to flame extinction and little mass
bly (a) exhibits any unusual fire-related characteristics, (b) has
loss in this test are likely to exhibit improved performance in
certain expected fire-related characteristics, or (c) is capable of
an actual fire situation compared to seat assemblies that burn
being preliminarily categorized according to the fire character-
vigorously and have high mass loss.
istic in question.
5.7 This test is primarily useful to distinguish products that,
3.3 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
when exposed to these fire conditions, will become fully
3.3.1 newspaper, n—as related to this test method, standard
involved in fire from other products that will not.
size double sheets of newsprint, with black print and no
colored ink or surface treatment.
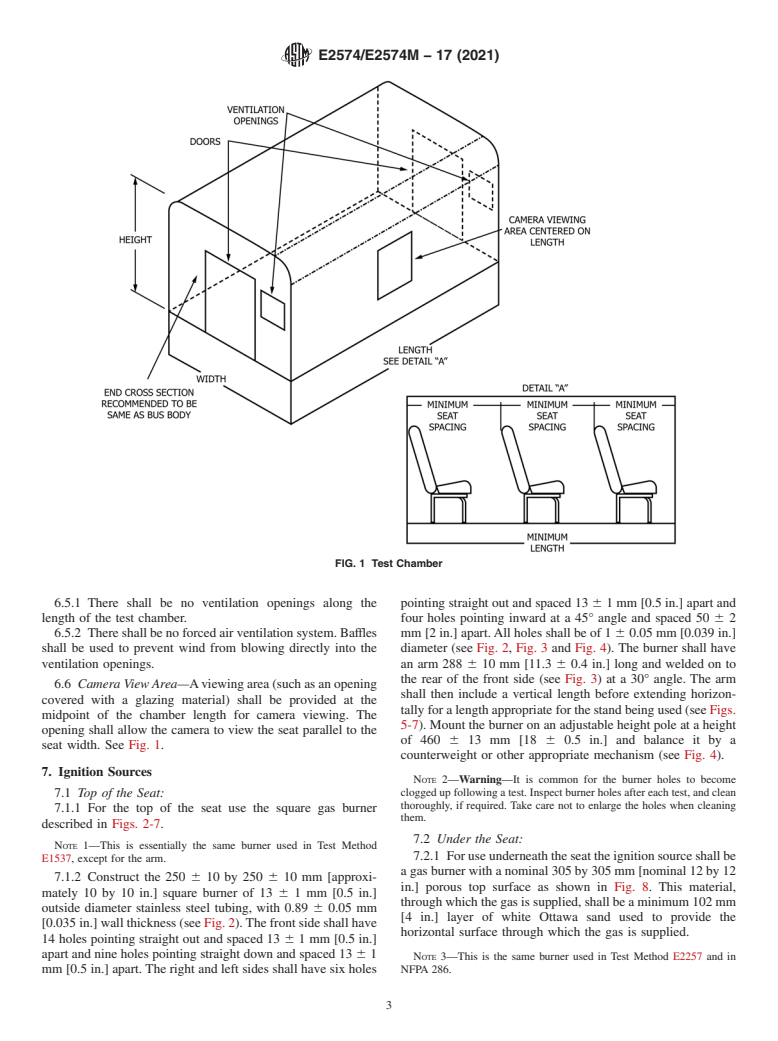
6. Apparatus: Test Chamber
3.3.2 paper bag, n—as related to this test method, a bag
6.1 General—The test chamber shall be either an actual
constructed of unbleached (brown, #30) kraft paper having
section of a school bus or it shall comply with the cross section
four sides and a bottom, with an open top, and held together
requirements of 6.2.2. Fig. 1 describes the test chamber.
with adhesive.
6.2 Cross Section:
4. Summary of Test Method
6.2.1 Use a test chamber that has the same cross section as
the body of an actual school bus, in which the seats are
4.1 A mock-up of a school bus is constructed with three
intended to be used, with a rear section on each end.
rows of actual seats.
6.2.2 Thetestchambercrosssectionshallbe2300 630mm
4.2 A gas burner ignition source is used.
[91 6 1 in.] in width by 1900 6 80 mm [75 6 3 in.] in height.
4.3 Each test consists of two trials. In each trial a gas burner
6.3 The test chamber shall have a door, which is not
ignition source is placed at a specified location to ignite the
intended for use to provide ventilation, in the center of each
middle row of seats and is ignited.
end of the test chamber. The door shall be 970 6 80 mm [38
4.4 Adifferent gas burner is used for the top of the seat and
6 3 in.] in width by 1270 6 80 mm [53 6 3 in.] in height and
for the bottom of the seat.
it shall include a latch to keep the door closed during the test.
4.5 Once flame extinction has occurred, the time to flame
See Fig. 1.
extinction, the extent of fire spread (within the seat and to the
6.4 Length—The length of the test chamber shall be such as
other seats if applicable) and the mass loss of the seat are
to allow three rows of seats at the minimum spacing recom-
assessed.
mendedbytheinstallerorasrequiredbyFMVSS222.SeeFig.
1, Detail A.
5. Significance and Use
6.4.1 In order for different types of seats to be able to be
5.1 In this test method fire test response characteristics of a
testedinthesamechamber,alengthtoleranceofplus1140mm
school bus seat assembly are assessed following ignition by a
[45 in.] shall be allowed.
square gas burner.
6.5 Ventilation—There shall be two ventilation openings in
the test chamber, one at each end. Each opening shall have an
Available from Superintendent of Documents, U.S. Government Printing 2 2
opening area of 0.210 6 0.016 m [325 6 25 in. ].The bottom
Office, Washington, DC 20402.
of the opening shall be 760 6 80 mm [30 6 3 in.] above the
Available from National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), 1 Batterymarch
Park, Quincy, MA 02169-7471, http://www.nfpa.org. chamber floor.
E2574/E2574M − 17 (2021)
FIG. 1 Test Chamber
6.5.1 There shall be no ventilation openings along the pointing straight out and spaced 13 6 1 mm [0.5 in.] apart and
length of the test chamber. four holes pointing inward at a 45° angle and spaced 50 6 2
6.5.2 Thereshallbenoforcedairventilationsystem.Baffles mm [2 in.] apart.All holes shall be of 1 6 0.05 mm [0.039 in.]
shall be used to prevent wind from blowing directly into the diameter (see Fig. 2, Fig. 3 and Fig. 4). The burner shall have
ventilation openings. an arm 288 6 10 mm [11.3 6 0.4 in.] long and welded on to
the rear of the front side (see Fig. 3) at a 30° angle. The arm
6.6 Camera ViewArea—Aviewingarea(suchasanopening
shall then include a vertical length before extending horizon-
covered with a glazing material) shall be provided at the
tallyforalengthappropriateforthestandbeingused(seeFigs.
midpoint of the chamber length for camera viewing. The
5-7). Mount the burner on an adjustable height pole at a height
opening shall allow the camera to view the seat parallel to the
of 460 6 13 mm [18 6 0.5 in.] and balance it by a
seat width. See Fig. 1.
counterweight or other appropriate mechanism (see Fig. 4).
7. Ignition Sources
NOTE 2—Warning—It is common for the burner holes to become
clogged up following a test. Inspect burner holes after each test, and clean
7.1 Top of the Seat:
thoroughly, if required. Take care not to enlarge the holes when cleaning
7.1.1 For the top of the seat use the square gas burner
them.
described in Figs. 2-7.
7.2 Under the Seat:
NOTE 1—This is essentially the same burner used in Test Method
7.2.1 Foruseunderneaththeseattheignitionsourceshallbe
E1537, except for the arm.
a gas burner with a nominal 305 by 305 mm [nominal 12 by 12
7.1.2 Construct the 250 6 10 by 250 6 10 mm [approxi-
in.] porous top surface as shown in Fig. 8. This material,
mately 10 by 10 in.] square burner of 13 6 1 mm [0.5 in.]
throughwhichthegasissupplied,shallbeaminimum102mm
outside diameter stainless steel tubing, with 0.89 6 0.05 mm
[4 in.] layer of white Ottawa sand used to provide the
[0.035 in.] wall thickness (see Fig. 2).The front side shall have
horizontal surface through which the gas is supplied.
14 holes pointing straight out and spaced 13 6 1 mm [0.5 in.]
apart and nine holes pointing straight down and spaced 13 6 1
NOTE 3—This is the same burner used in Test Method E2257 and in
mm [0.5 in.] apart. The right and left sides shall have six holes NFPA 286.
E2574/E2574M − 17 (2021)
FIG. 4 Cross-sectional View of Each Side of Square Gas Burner
FIG. 5 Top Burner Placement – Side View
NOTE 1—All tubing 13 mm outside diameter, stainless steel, 0.89 mm
wall thickness.
NOTE 2—All holes 1 mm in diameter.
7.2.2 The top surface of the burner through which the gas is
NOTE 3—All units are mm unless otherwise noted.
appliedshallbelocatedhorizontally300 650mm[12 62in.]
NOTE 4—See text for tolerances.
above the floor.
FIG. 2 Plan View of Square Gas Burner
7.3 Forbothignitionsourcesusepropanegas,withaknown
net heat of combustion of 2050 6 50 kJ/mol, as a fuel for this
ignition source. Meter the flow rate of propane and keep it
constant throughout the test.
7.4 For both ignition sources, use the gas burner at a flow
rate of 19.5 6 0.25 L/min for a total of 120 s. Measure the gas
flow rate at a pressure of 101 6 5 kPa (standard atmospheric
pressure,measuredattheflowgage)andatemperatureof20 6
5°C.
8. Mass Measurements
8.1 Use a balance that is capable of assessing the mass of
the test specimen and of the individual test specimen compo-
nents with a precision of 6150 g.
8.2 Calibrate the balance regularly to ensure its accuracy.
9. Test Specimens
9.1 The test specimen shall be a fully-assembled seat.
9.2 Measure the weight of all padding and upholstery prior
to assembly.
9.3 Measure the weight of the non-combustible components
FIG. 3 Side View of Square Gas Burner
of the seat (steel frame, etc.). Record this weight.
E2574/E2574M − 17 (2021)
FIG. 6 Top Burner Placement – Rear View
FIG. 7 Top Burner Placement – Front View
assembly or (b) weighing each component separately and
calculating the total weight by summing the weight of each of
the combustible and non-combustible components.
10. Preparation of Apparatus
10.1 Prior to running each trial, ensure that the test chamber
is clean and free of debris.
11. Conditioning
11.1 Condition specimens to equilibrium (constant weight)
at an ambient temperature of 23 6 3°C [73 6 5°F] and a
relative humidi
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.