ASTM D2732-14(2020)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Unrestrained Linear Thermal Shrinkage of Plastic Film and Sheeting
Standard Test Method for Unrestrained Linear Thermal Shrinkage of Plastic Film<brk/> and Sheeting
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 As a result of the manufacturing process, internal stresses may be locked into the film which can be released by heating. The temperature at which shrinkage will occur is related to the processing techniques employed to manufacture the film and may also be related to a phase transition in the base resin. The magnitude of the shrinkage will vary with the temperature of the film.
4.2 Shrinkage of a particular material produced by a particular process may be characterized by this test method by making measurements at several temperatures through the shrinkage range of the material.
4.3 Following a characterization in a particular case, it is usually sufficient thereafter to measure shrinkage at only one selected temperature for purposes of process or quality control, or both.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers determination of the degree of unrestrained linear thermal shrinkage at given specimen temperatures of plastic film and sheeting of 0.76 mm (0.030 in.) thickness or less. This test method does not cover shrinkage from loss of solvent in some materials.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to inch-pound units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Note 1: This standard and ISO 11501 address the same subject matter, but differ in technical content.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D2732 − 14 (Reapproved 2020)
Standard Test Method for
Unrestrained Linear Thermal Shrinkage of Plastic Film
and Sheeting
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2732; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope E2251 Specification for Liquid-in-Glass ASTM Thermom-
eters with Low-Hazard Precision Liquids
1.1 This test method covers determination of the degree of
2.2 ISO Standard:
unrestrained linear thermal shrinkage at given specimen tem-
ISO 11501 Determination of Dimensional Change on Heat-
peratures of plastic film and sheeting of 0.76 mm (0.030 in.)
ing
thickness or less. This test method does not cover shrinkage
from loss of solvent in some materials.
3. Terminology
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
3.1 Definitions:
standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
3.1.1 unrestrained linear thermal shrinkage (free shrink or
conversions to inch-pound units that are provided for informa-
shrinkage)—the irreversible and rapid reduction in linear
tion only and are not considered standard.
dimension in a specified direction occurring in film subjected
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the to elevated temperatures under conditions where nil or negli-
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the gible restraint to inhibit shrinkage is present. It is normally
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- expressed as a percentage of the original dimension.
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
4. Significance and Use
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
4.1 As a result of the manufacturing process, internal
NOTE 1—This standard and ISO 11501 address the same subject matter,
stresses may be locked into the film which can be released by
but differ in technical content.
heating. The temperature at which shrinkage will occur is
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
related to the processing techniques employed to manufacture
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
thefilmandmayalsoberelatedtoaphasetransitioninthebase
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
resin. The magnitude of the shrinkage will vary with the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
temperature of the film.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
4.2 Shrinkage of a particular material produced by a par-
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
ticular process may be characterized by this test method by
2. Referenced Documents
making measurements at several temperatures through the
shrinkage range of the material.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
4.3 Following a characterization in a particular case, it is
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
usually sufficient thereafter to measure shrinkage at only one
D1204 Test Method for Linear Dimensional Changes of
selected temperature for purposes of process or quality control,
Nonrigid Thermoplastic Sheeting or Film at Elevated
or both.
Temperature
5. Apparatus
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D20 on Plastics
5.1 Constant-Temperature Liquid Bath, capable of control-
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.19 on Film, Sheeting, and
ling accurately to 60.5°C.
Molded Products.
5.1.1 The liquid for the bath should not plasticize or react
Current edition approved April 1, 2020. Published April 2020. Originally
with the specimens. Poly(ethylene glycol), glycerin, and water
approved in 1968. Last previous edition approved in 2014 as D2732 – 14. DOI:
10.1520/D2732-14R20.
have been found to have wide applicability.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
the ASTM website. 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D2732 − 14 (2020)
5.2 Thermometer—ASTM Thermometer S5C-11 conform- 6.2 Aminimum of two specimens is necessary for each test
ing to the requirements as prescribed in Specification E2251. temperature.
5.3 Square Metal Stamp, 100 by 100 mm, with engraved
7. Conditioning
arrow indicating machine direction of film and stamp pad and
7.1 Conditioning—Condition the test specimens in accor-
ink. (The ink should not be soluble in the bath liquid.)
dance with Procedure A of Practice D618 unless otherwise
NOTE 2—Ametal die or template (100 by 100 mm) can be used instead
specified by agreement or the relevant ASTM material speci-
of the square metal stamp.
fication.Incasesofdisagreement,thetolerancesshallbe 61°C
5.4 Free Shrink Holder—A holder designed for test of a
(61.8°F) and 65 % relative humidity
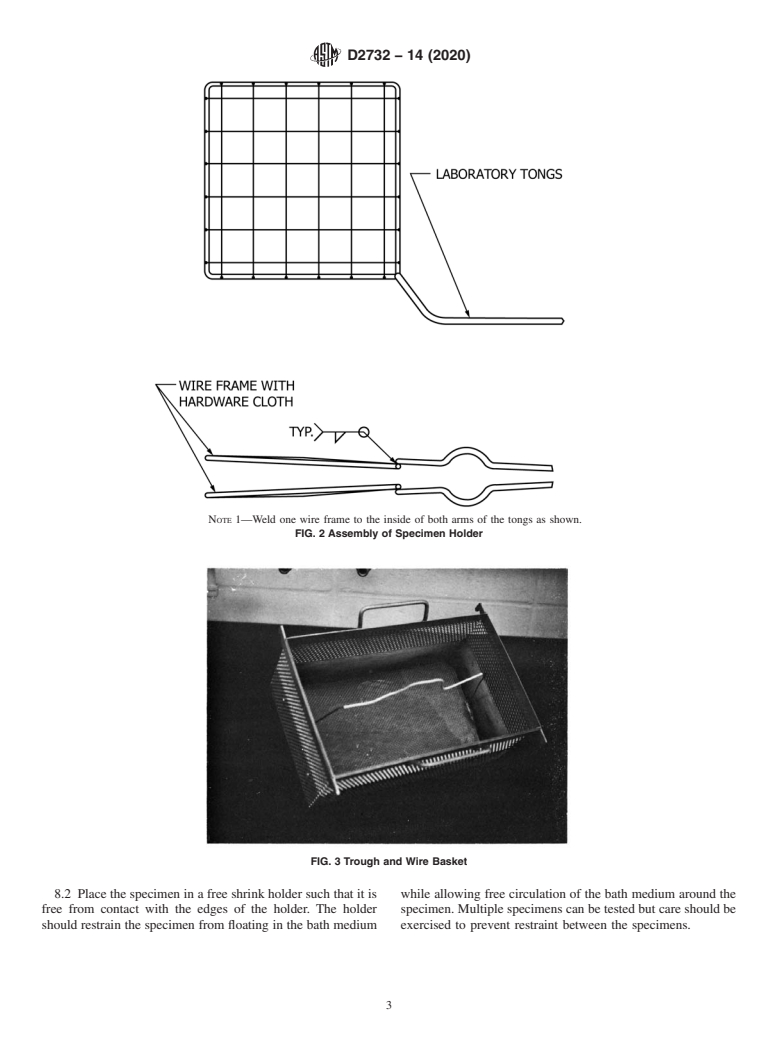
single specimen, such as that shown in Fig. 1 and Fig. 2.
7.2 Test Conditions—Set the liq
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.