ASTM D8019-15
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Determining the Full Section Flexural Modulus and Bending Strength of Fiber Reinforced Polymer Crossarms Assembled with Center Mount Brackets
Standard Test Methods for Determining the Full Section Flexural Modulus and Bending Strength of Fiber Reinforced Polymer Crossarms Assembled with Center Mount Brackets
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Determination of the flexural modulus, beam bending strength and full assembly strength, by this test method is especially useful for product validation, design and specification purposes.
5.2 Calculated values for flexural modulus, bending strength and full assembly strength will vary with specimen depth, span length, hole configurations, loading rate, and ambient test temperature. A minimum span to depth ratio of 16:1 is required for establishing the flexural modulus.
5.3 Validity—Stress at failure, σ, is only valid for crossarm failures due to local compression buckling. Other controlling modes of failure will dictate the ultimate phase loading capacities. For example, in-plane shear, fastener pin bearing, position hardware, center mount failures and fastener pull out will dictate the failure mode and ultimately the crossarm capacity.
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover the determination of the flexural modulus and bending strength of both tangent and deadend arms bent about their minor and major axes. One method covers testing of assembled tangent crossarms including the tangent bracket and relative hardware. The other method covers testing of assembled deadend crossarms with a deadend bracket and relative phase loading hardware. The failure modes and associated stresses can be used for predicting the phase load capacities of pultruded crossarms specific to certain conductor loading scenarios.
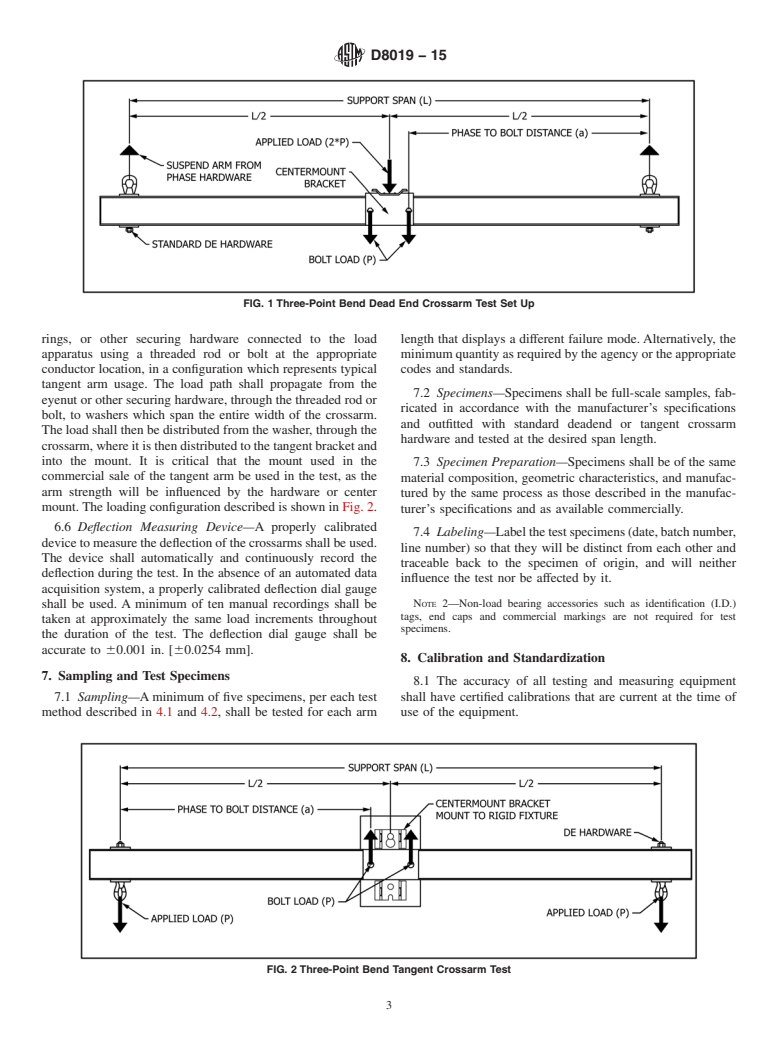
1.2 The test methods described in this standard can be used for predicting the vertical and horizontal component loads of deadend and tangent arms. Both deadend and tangent crossarms shall be tested in the two configurations described in Figures 1 and 2. This will permit the manufactures to publish both vertical and horizontal design capacities for deadend crossarm configurations so that two way bending stresses, caused by catenary effects, can be considered when developing the capacity of the deadend crossarms by utility design engineers and manufacturers.
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the standard.
1.4 This standard will not address all factors that affect the phase loading capacity.
1.5 This standard does not address the use of core materials that are added to increase the structural capacity of the crossarms. Core material shall not be considered in the calculations provided in this standard.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Note 1: There is no known ISO equivalent to this standard.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D8019 − 15
Standard Test Methods for
Determining the Full Section Flexural Modulus and Bending
Strength of Fiber Reinforced Polymer Crossarms
1
Assembled with Center Mount Brackets
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D8019; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
1.1 These test methods cover the determination of the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
flexural modulus and bending strength of both tangent and
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
deadend arms bent about their minor and major axes. One
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
method covers testing of assembled tangent crossarms includ-
ing the tangent bracket and relative hardware. The other NOTE 1—There is no known ISO equivalent to this standard.
method covers testing of assembled deadend crossarms with a
2. Referenced Documents
deadend bracket and relative phase loading hardware. The
2
failuremodesandassociatedstressescanbeusedforpredicting 2.1 ASTM Standards:
the phase load capacities of pultruded crossarms specific to D4968 Practice for Annual Review of Test Methods and
certain conductor loading scenarios. Specifications for Plastics
E4 Practices for Force Verification of Testing Machines
1.2 The test methods described in this standard can be used
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
for predicting the vertical and horizontal component loads of
ASTM Test Methods
deadend and tangent arms. Both deadend and tangent cros-
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
sarms shall be tested in the two configurations described in
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
Figures 1 and 2. This will permit the manufactures to publish
both vertical and horizontal design capacities for deadend
3. Terminology
crossarm configurations so that two way bending stresses,
3.1 Definitions of variables used in the calculations as
caused by catenary effects, can be considered when developing
shown in Section 11 are as follows:
the capacity of the deadend crossarms by utility design
engineers and manufacturers.
a = distance from phase hardware to the center mount
bolt through the crossarm, in. (m),
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
2 2
A = area of the webs in shear in. [m ],
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
w
E = flexural modulus, psi (Pa),
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
I = moment of inertia about the neutral axis of the
system shall be used independently of the other. Combining
4 4
crossarm, in. [m ],
values from the two systems may result in nonconformance
L = support span, in. [m],
with the standard.
M = moment at failure, lbf-in [N•m],
1.4 This standard will not address all factors that affect the
P = ultimate or failure load acting through a single center
phase loading capacity.
mount bolt, lbf [N],
S = section modulus about the neutral axis of the
x
1.5 This standard does not address the use of core materials
3 3
crossarm, in. [m ],
that are added to increase the structural capacity of the
V = in-plane shear force, lbf [N],
crossarms. Core material shall not be considered in the
σ = bending stress at failure, psi [Pa],
calculations provided in this standard.
δ = deflection relative to the applied load, in. [m],
τ = maximum transverse shear stress, psi [Pa],
max
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D20 on Plastics
2
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.18 on Reinforced Thermoset- For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
ting Plastics. contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2015. Published January 2016. DOI: 10.1520/ Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
D8019-15. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D8019 − 15
3 3
position hardware, center mount failures and fastener pull out
Q = static moment of area in. [m ],
will dictate the failure mode and ultimately the crossarm
t = thickness of region or regions under consideration in.
capacity.
[
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.