ASTM D906-98(2004)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Strength Properties of Adhesives in Plywood Type Construction in Shear by Tension Loading
Standard Test Method for Strength Properties of Adhesives in Plywood Type Construction in Shear by Tension Loading
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The way adhesives are used in plywood makes shear strength an important performance criteria.
Shear strength measured by this test is suitable for use in adhesive development, manufacturing quality control, and in materials performance specifications.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the comparative shear strengths of adhesives in plywood-type construction, when tested on a standard specimen and under specified conditions of preparation, conditioning, and testing. This test method is intended to be applied only to adhesives used in bonding wood to wood.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are provided for information purposes only.
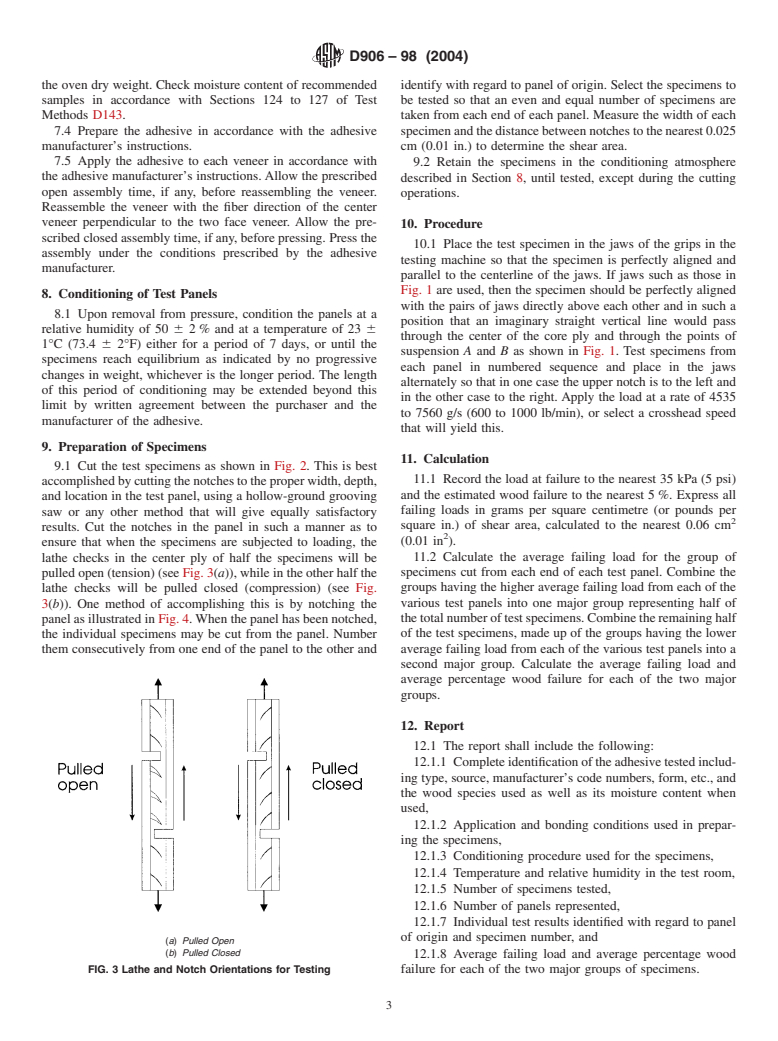
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D906–98(Reapproved2004)
Standard Test Method for
Strength Properties of Adhesives in Plywood Type
1
Construction in Shear by Tension Loading
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D906; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
INTRODUCTION
The accuracy of the results of strength tests of adhesive bonds will depend on the conditions under
which the bonding process is carried out. Unless otherwise agreed upon between the manufacturer and
the purchaser, the bonding conditions shall be prescribed by the manufacturer of the adhesive. In order
to ensure that complete information is available to the individual conducting the tests, the
manufacturer of the adhesive shall furnish numerical values and other specific information for each of
the following variables:
(1) The moisture content of the wood at the time of bonding.
(2) Complete mixing directions for the adhesive.
(3) Conditions for application of the adhesive including the rate of spread or thickness of film,
number of coats to be applied, whether more than one coat is required.
(4) Assembly conditions before application of pressure, including the room temperature, length of
time, and whether open or closed assembly is to be used.
(5) Curing conditions, including the amount of pressure to be applied, the length of time under
pressure and the temperature of the assembly when under pressure. It should be stated whether this
temperature is that of the bond line, or of the atmosphere at which the assembly is to be maintained.
(6) Conditioning procedure before testing, unless a standard procedure is specified, including the
length of time, temperature, and relative humidity.
Arange may be prescribed for any variable by the manufacturer of the adhesive if it can be assumed
by the test operator that any arbitrarily chosen value within such a range or any combination of such
values for several variables will be acceptable to both the manufacturer and the purchaser of the
adhesive.
1. Scope specified conditions of preparation, conditioning, and testing.
This test method is intended to be applied only to adhesives
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the com-
used in bonding wood to wood.
parative shear strengths of adhesives in plywood-type con-
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
struction, when tested on a standard specimen and under
standard. The values given in parentheses are provided for
information purposes only.
1
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D14 on
Adhesives and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D14.30 on Wood
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
Adhesives.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
Current edition approved April 1, 2004. Published April 2004. Originally
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
approved in 1947. Last previous edition approved in 1998 as D906 – 98. DOI:
10.1520/D0906-98R04. bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D906–98 (2004)
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D143 Test Methods for Small Clear Specimens of Timber
D907 Terminology of Adhesives
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—Many terms in this test method are defined
in Terminology D907.
3.1.1 plywood, n—a panel generally flat built up of layers of
veneer called plies, united under pressure by an adhesive to
create a panel with the bond between the plies as strong as, or
stronger than, the wood, and that has the following character-
istics: (1) is constructed of an odd number of layers with grain
of adjacent layers perpendicular, (2) with a layer consisting of
either a single ply or two or more plies laminated with parallel
grain direction, and (3) with outer layers and all odd numbered
layers generally having the grain direction oriented parallel to FIG. 1 Grips and Jaws
the long dimension of the panel.
3.1.1.1 Discussion—Generally, the grain of one or more
plies is approximately at right angles to the other plies, and
almost always an odd number of plies are used.
3.1.2 shear, n—in an adhesively bonded joint, stress, strain
or failure resulting from applied forces that tend to cause
adjacent planes of a body to slide parallel in opposite direc-
tions.
Metric Equivalents
4
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.