ASTM F30-96(2017)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Iron-Nickel Sealing Alloys
Standard Specification for Iron-Nickel Sealing Alloys
ABSTRACT
This specification covers the characteristics and requirements for iron-nickel alloys intended primarily for sealing to glass in electronic applications. The alloys shall conform to chemical composition, surface finish, temper, grain size, and thermal expansion requirements as stated herein.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers iron-nickel alloys that are intended primarily for sealing to glass in electronic applications.
Note 1: Some of these alloys may be used for sealing to ceramics, but this specification in its present form is not intended to cover material for metal-to-ceramic seals.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. The hazard statement pertains only to the test method sections, Sections 10 and 12.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation:F30 −96 (Reapproved 2017)
Standard Specification for
Iron-Nickel Sealing Alloys
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationF30;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginal
adoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope F14Practice for Making andTesting Reference Glass-Metal
Bead-Seal
1.1 This specification covers iron-nickel alloys that are
F140Practice for Making Reference Glass-Metal Butt Seals
intended primarily for sealing to glass in electronic applica-
and Testing for Expansion Characteristics by Polarimetric
tions.
Methods
NOTE1—Someofthesealloysmaybeusedforsealingtoceramics,but
F144Practice for Making Reference Glass-Metal Sandwich
this specification in its present form is not intended to cover material for
Seal and Testing for Expansion Characteristics by Polari-
metal-to-ceramic seals.
metric Methods
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
3. Ordering Information
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
3.1 Ordersformaterialunderthisspecificationshallinclude
and are not considered standard.
the following information:
1.3 This standard does not purport to address the safety
3.1.1 Size,
concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
3.1.2 Temper (Section 6),
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and
3.1.3 Surface finish (Section 8),
health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
3.1.4 Marking and packaging (Section 16), and
limitations prior to use. The hazard statement pertains only to
3.1.5 Certification if required.
the test method sections, Sections 10 and 12.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
4. Chemical Composition
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
4.1 The material shall conform to the requirements as to
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
chemical composition prescribed in Table 1.
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
5. Surface Lubricants
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
5.1 All lubricants used in processing shall be thoroughly
removed. Protective coatings present on the material as
2. Referenced Documents
shipped shall be readily removable by any of the common
2.1 ASTM Standards:
organic degreasing solvents.
E18Test Methods for Rockwell Hardness of Metallic Ma-
terials
6. Temper
E29Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
6.1 The desired temper of the material shall be specified on
Determine Conformance with Specifications
the purchase order. Unless otherwise specified, wire, rod, bar,
E112Test Methods for Determining Average Grain Size
and tubing shall be given a final bright anneal by the manu-
E228Test Method for Linear Thermal Expansion of Solid
facturer. Strip and sheet shall be annealed properly to develop
Materials With a Push-Rod Dilatometer
deep drawing properties. For deep drawing the hardness shall
notexceedRockwellB82formaterial0.100in.(2.54mm)and
1 less in thickness, and B85 for material over 0.100 in. thick
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committtee F01 on
Electronics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F01.03 on Metallic when determined in accordance with Test Methods E18.
Materials, Wire Bonding, and Flip Chip.
CurrenteditionapprovedJune1,2017PublishedJune2017.Originallyapproved
7. Grain Size
in 1977. Last previous edition approved in 2012 as F30–96 (2012). DOI:
10.1520/F0030-96R17.
7.1 Strip and sheet for deep drawing applications shall have
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
anaveragegrainsizenotlargerthanASTMNo.5(Note2)and
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
no more than 10% of the grains shall be larger than No. 5
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. when measured in accordance with Test Methods E112. For
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
F30−96 (2017)
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements
10. Test for Thermal Expansion
Composition, %
10.1 Determinethethermalexpansioncharacteristicswitha
42 Alloy 46 Alloy 48 Alloy 52 Alloy
precision dilatometer after heating the specimen as follows:
UNS UNS UNS 51 Alloy UNS
10.1.1 Heat the specimen in a hydrogen atmosphere for 1 h
K94100 K94600 K94800 N14052
A
at 900°C and then cool it from 900 to 200°C at a rate not
Nickel, nominal 41 46 48 51.5 50.5
Manganese, max 0.80 0.80 0.80 0.60 0.60
exceeding 5°C/min.
Silicon, max 0.30 0.30 0.30 0.30 0.30
10.1.2 The thermal expansion properties are determined in
Carbon, max 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05
accordance with Test Method E228.
Chromium, max 0.25 0.25 0.25 0.25 0.25
BBBBB
Cobalt, max
10.2 The thermal expansion match between the alloy and a
Phosphorus, max 0.025 0.025 0.025 0.0250 0.025
Sulfur, max 0.025 0.025 0.025 0.0250 0.025 glass may be evaluated by testing the assembly in accordance
Aluminum, max 0.10 0.10 0.10 0.100 0.10
with Practices F14, F140,or F144.
Iron remainder remainder remainder remainder remainder
A
The nickel contents listed are nominal.The nickel contents of the alloys shall be
11. Dimensions and Permissible Variations
adjusted by the manufacturer so that the alloys meet the requirements for thermal
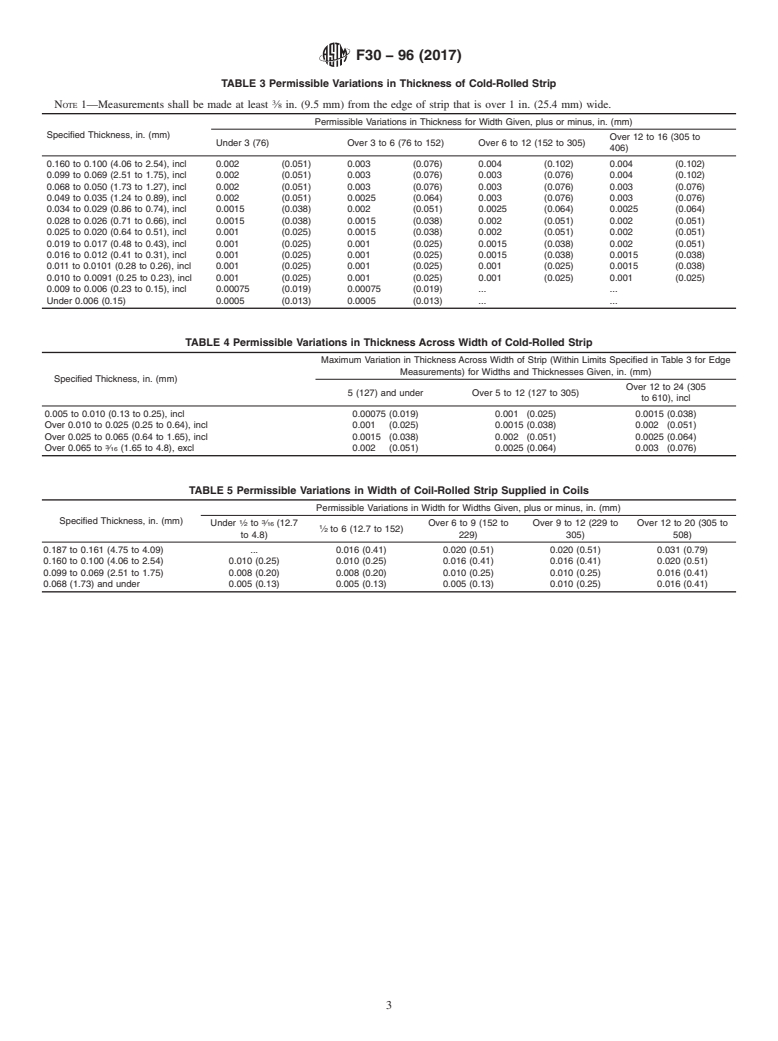
11.1 Cold-Rolled Strip—Cold-rolled strip shall conform to
expansion.The52Alloyisspecificallyintendedtomatchlead(Pb)sealingglasses.
B
Cobalt is present as an incidental element and shall be reported separately.
the permissible variations in dimensions prescribed in Table 3,
Table 4, and Table 5.
11.2 Round Wire and Rod—Wire and rod shall conform to
materials less than 0.005 in. (0.13 mm) in thickness the grain
the permissible variations in dimension prescribed in Table 6.
size shall be such that there are no less than 4 grains across the
thickness.
11.3 Cold-Drawn Tubing—Cold-drawn tubing, available ei-
ther as seamless or welded, shall conform to the permissible
NOTE 2—This corresponds to a grain size of 0.065 mm or 16 grains/in.
variations prescribed in Table 7.
of image of 100×.
12. Rounding Results
8. Surface Finish
12.1 Observed or calculated values obtained from analysis,
8.1 The standard surface finishes available shall be those
measurements, or tests shall be rounded in accordance with
resulting from the following operations:
PracticeE29,tothenearestunitinthelastrightplaceoffigures
8.1.1 Hot-rolling,
used in expressing the specified limit.
8.1.2 Forging,
8.1.3 Centerless grinding (rod),
13. General Requirements
8.1.4 Belt polishing,
8.1.5 Cold rolling, and drawing, and 13.1 Thematerialshallbecommerciallysmooth,uniformin
8.1.6 Wire drawing. cross section, in composition, and in temper; it shall be free
from scale, corrosion, porosity, cracks, seams, scratches,
9. Thermal Expansion Characteristics
slivers, and other defects as best commercial practice will
9.1 The average linear coefficients of thermal expansion permit.
shall be within the limits specified in Table 2.
14. Packaging and Package Marking
A
TABLE 2 Thermal Expansion Requirements 14.1 Packaging shall be subject to agreement between the
Average Linear purchaser and the seller.
Coefficient of
Temperature
14.2 The material as furnished under this spe
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.