ASTM D4067-96
(Specification)Standard Specification for Reinforced and Filled Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) Injection Molding and Extrusion Materials
Standard Specification for Reinforced and Filled Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) Injection Molding and Extrusion Materials
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers reinforced and filled polyphenylene sulfide materials suitable for injection molding and extrusion.
1.2 This specification is not intended for the selection of materials, but only as a means to call out plastic materials to be used for the manufacture of parts. The selection of these materials is to be made by personnel with expertise in the plastics field where the environment, inherent properties of the materials, performance of the parts, part design, manufacturing process, and economics are considered.
1.3 The properties included in this specification are those required to identify the compositions covered. There may be other requirements necessary to identify particular characteristics important to specific applications. These will be agreed upon between the user and the supplier by using the suffixes as given in Section 5.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.5 This precautionary statement pertains only to the test method portion of this specification, section 13. This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: D 4067 – 96
Standard Specification for
Reinforced and Filled Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) Injection
Molding and Extrusion Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 4067; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope D 256 Test Methods for Impact Resistance of Plastics and
Electrical Insulating Materials
1.1 This specification covers reinforced and filled polyphe-
D 257 Test Methods for DC Resistance or Conductance of
nylene sulfide materials suitable for injection molding and
Insulating Materials
extrusion.
D 495 Test Method for High-Voltage, Low-Current, Dry
1.2 This specification is not intended for the selection of
Arc Resistance of Solid Electrical Insulation
materials, but only as a means to call out plastic materials to be
D 618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics and Electrical
used for the manufacture of parts. The selection of these
Insulating Materials for Testing
materials is to be made by personnel with expertise in the
D 638 Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics
plastics field where the environment, inherent properties of the
D 648 Test Method for Deflection Temperature of Plastics
materials, performance of the parts, part design, manufacturing
Under Flexural Load
process, and economics are considered.
D 790 Test Methods for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced
1.3 The properties included in this specification are those
and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materi-
required to identify the compositions covered. There may be
als
other requirements necessary to identify particular character-
D 792 Test Methods for Specific Gravity (Relative Density)
istics important to specific applications. These will be agreed
and Density of Plastics by Displacement
upon between the user and the supplier by using the suffixes as
D 883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
given in Section 5.
D 1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
Plastics
standard.
D 1897 Practice for Injection Molding Test Specimens of
1.5 This precautionary statement pertains only to the test
Thermoplastic Molding and Extrusion Materials
method portion of this specification, section 13. This standard
D 1898 Practice for Sampling of Plastics
does not purport to address all of the safety concerns associ-
D 3418 Test Method for Transition Temperatures of Poly-
ated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this
mers by Thermal Analysis
standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices
D 3892 Practice for Packaging/Packing of Plastics
and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior
D 4000 Classification System for Specifying Plastic Mate-
to use.
rials
2. Referenced Documents E 29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
Determine Conformance with Specification
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E 595 Test Method for Total Mass Loss and Collected
D 149 Test Method for Dielectric Breakdown Voltage and
Volatile Condensable Materials from Outgassing in a
Dielectric Strength of Solid Electrical Insulating Materials
Vacuum Environment
at Commercial Power Frequencies
E 662 Test Method for Specific Optical Density of Smoke
D 150 Test Methods for AC Loss Characteristics and Per-
Generated by Solid Materials
mittivity (Dielectric Constant) of Solid Electrical Insulat-
F 814 Test Method for Specific Optical Density of Smoke
ing Materials
Generated by Solid Materials for Aerospace Applications
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-20 on
Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.15 on Thermoplastic Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.01.
Materials (Section D20.15.17). Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.02.
Current edition approved March 10, 1996. Published July 1996. Originally Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02.
published as D 4067 – 82. Last previous edition D 4067 – 93. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 15.03.
2 7
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 10.01. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.07.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D 4067
Phase—Liquid
Cell thickness—0.025 mm
Sample—Pyrolyzate
Prism—NaCl
FIG. 1 Infrared Spectrum of Polyphenylene Sulfide Pyrolyzate
TABLE 1 Detail Requirements
A
Property Condition Units A B C D E F G H I
B
Dielectric constant max E-48/50 + D24/23
1 KHz E-48/50 + D24/23 4.0 4.0 4.2 4.5 4.8 5.3 6.8 5.8 9.0
1 MHz E-48/50 + D24/23 4.0 4.0 4.1 4.4 4.5 4.8 6.3 6.3 9.0
B
Dissipation factor max E-48/50 + D24/23
1 KHz E-48/50 + D24/23 0.002 0.002 0.004 0.008 0.02 0.08 0.10 0.10 0.10
1 MHz E-48/50 + D24/23 0.007 0.007 0.007 0.010 0.02 0.01 0.03 0.03 0.10
C 16 14 16 14 15 15 15 15 14
Volume resistivity , min C-24/23/50 ohm-cm 1 3 10 1 3 10 1 3 10 1 3 10 1 3 10 1 3 10 1 3 10 1 3 10 1 3 10
D
Dielectric strength , min E-48/50 + 96/23/50 KY/mm 14.6 (375) 14.6 (375) 13.6 (350) 11.7 (300) 11.7 (300) 11.7 (300) 11.7 (300) 11.7 (300) 11.7 (300)
(Y/mil)
E
Arc resistance , min second 30 10 30 0 150 150 150 180 150
Comparative tracking Y 130 130 130 130 200 200 150 230 200
A
index,
F
min
A
In accordance with Methods D 618.
B
ASTM Test Method D 150.
C
ASTM Test Method D 257.
D
ASTM Test Method D 149.
E
ASTM Test Method D 495.
F
UL Method 746A.
MIL-M-24519 Molding Plastics, Electrical, Thermoplastic
2.2 Military Standards:
2.3 Underwriters Laboratories:
MIL-STD-105 Sampling Procedures and Tables for Inspec-
UL Standard 94 Tests for Flammability of Plastic Materials
tion by Attributes
for Parts in Devices and Appliances
MIL-P-46174 (MR) Plastic Molding Material, Polyphe-
UL Standard 746A Polymeric Materials—Short-Term Prop-
nylene Sulfide, Glass Fiber Reinforced
erty Evaluation
Available from Underwriters Laboratories, Inc. Publications Stock, 333 Pfing-
Available from Standardization Documents, Order Desk, Bldg. 4 Section D,
700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5094, Attn: NPODS. sten Road, Northbrook, IL 60062.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
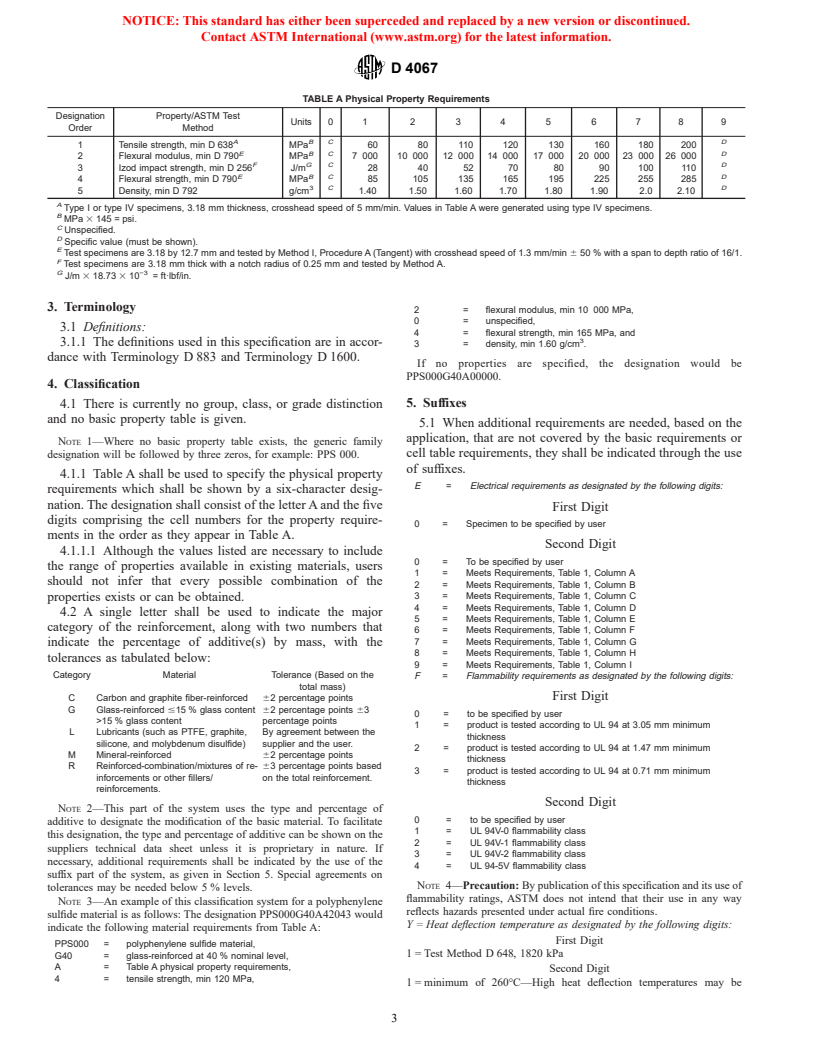
D 4067
TABLE A Physical Property Requirements
Designation Property/ASTM Test
Units 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Order Method
A BC D
1 Tensile strength, min D 638 MPa 60 80 110 120 130 160 180 200
E BC D
2 Flexural modulus, min D 790 MPa 7 000 10 000 12 000 14 000 17 000 20 000 23 000 26 000
F GC D
3 Izod impact strength, min D 256 J/m 28 40 52 70 80 90 100 110
E BC D
4 Flexural strength, min D 790 MPa 85 105 135 165 195 225 255 285
3 C D
5 Density, min D 792 g/cm 1.40 1.50 1.60 1.70 1.80 1.90 2.0 2.10
A
Type I or type IV specimens, 3.18 mm thickness, crosshead speed of 5 mm/min. Values in Table A were generated using type IV specimens.
B
MPa 3 145 = psi.
C
Unspecified.
D
Specific value (must be shown).
E
Test specimens are 3.18 by 12.7 mm and tested by Method I, Procedure A (Tangent) with crosshead speed of 1.3 mm/min 6 50 % with a span to depth ratio of 16/1.
F
Test specimens are 3.18 mm thick with a notch radius of 0.25 mm and tested by Method A.
G −3
J/m 3 18.73 3 10 = ft·lbf/in.
3. Terminology
2 = flexural modulus, min 10 000 MPa,
0 = unspecified,
3.1 Definitions:
4 = flexural strength, min 165 MPa, and
3.1.1 The definitions used in this specification are in accor-
3 = density, min 1.60 g/cm .
dance with Terminology D 883 and Terminology D 1600.
If no properties are specified, the designation would be
PPS000G40A00000.
4. Classification
4.1 There is currently no group, class, or grade distinction 5. Suffixes
and no basic property table is given.
5.1 When additional requirements are needed, based on the
application, that are not covered by the basic requirements or
NOTE 1—Where no basic property table exists, the generic family
designation will be followed by three zeros, for example: PPS 000. cell table requirements, they shall be indicated through the use
of suffixes.
4.1.1 Table A shall be used to specify the physical property
E = Electrical requirements as designated by the following digits:
requirements which shall be shown by a six-character desig-
nation. The designation shall consist of the letter A and the five
First Digit
digits comprising the cell numbers for the property require-
0 = Specimen to be specified by user
ments in the order as they appear in Table A.
Second Digit
4.1.1.1 Although the values listed are necessary to include
0 = To be specified by user
the range of properties available in existing materials, users
1 = Meets Requirements, Table 1, Column A
should not infer that every possible combination of the
2 = Meets Requirements, Table 1, Column B
3 = Meets Requirements, Table 1, Column C
properties exists or can be obtained.
4 = Meets Requirements, Table 1, Column D
4.2 A single letter shall be used to indicate the major
5 = Meets Requirements, Table 1, Column E
category of the reinforcement, along with two numbers that
6 = Meets Requirements, Table 1, Column F
7 = Meets Requirements, Table 1, Column G
indicate the percentage of additive(s) by mass, with the
8 = Meets Requirements, Table 1, Column H
tolerances as tabulated below:
9 = Meets Requirements, Table 1, Column I
Category Material Tolerance (Based on the
F = Flammability requirements as designated by the following digits:
total mass)
C Carbon and graphite fiber-reinforced 62 percentage points First Digit
G Glass-reinforced #15 % glass content 62 percentage points 63
0 = to be specified by user
>15 % glass content percentage points
1 = product is tested according to UL 94 at 3.05 mm minimum
L Lubricants (such as PTFE, graphite, By agreement between the
thickness
silicone, and molybdenum disulfide) supplier and the user.
2 = product is tested according to UL 94 at 1.47 mm minimum
M Mineral-reinforced 62 percentage points
thickness
R Reinforced-combination/mixtures of re- 63 percentage points based
3 = product is tested according to UL 94 at 0.71 mm minimum
inforcements or other fillers/ on the total reinforcement.
thickness
reinforcements.
Second Digit
NOTE 2—This part of the system uses the type and percentage of
0 = to be specified by user
additive to designate the modification of the basic material. To facilitate
1 = UL 94V-0 flammability class
this designation, the type and percentage of additive can be shown on the
2 = UL 94V-1 flammability class
suppliers technical data sheet unless it is proprietary in nature. If
3 = UL 94V-2 flammability class
necessary, additional requirements shall be indicated by the use of the
4 = UL 94-5V flammability class
suffix part of the system, as given in Section 5. Special agreements on
NOTE 4—Precaution: By publication of this specification and its use of
tolerances may be needed below 5 % levels.
flammability ratings, ASTM does not intend that their use in any way
NOTE 3—An example of this classification system for a polyphenylene
reflects hazards presented under actual fire conditions.
sulfide material is as follows: The designation PPS000G40A42043 would
Y = Heat deflection temperature as designated by the following digits:
indicate the following material requirements from Table A:
First Digit
PPS000 = polyphenylene sulfide material,
1 = Test Method D 648, 1820 kPa
G40 = glass-reinforced at 40 % nominal level,
A = Table A physical property requirements,
Second Digit
4 = tensile strength, min 120 MPa,
1 = minimum of 260°C—High heat deflection temperatures may be
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D 4067
obtained by heat treating the test specimens at 260°C for 4 h.
11. Specimen Preparation
5.1.1 Additional suffixes will be added to this specification
11.1 Unless otherwise specified, test specimens shall be
as required. See Table 3 of Classification D 4000.
prepared by injection molding in accordance with Practice
D 1897. Unless otherwise recommended, minimum mold tem-
NOTE 5—If the requirements for the polyphenylene sulfide material in
perature shall be 121°C and stock temperature shall be 316 6
Note 3 also included electrical requirements, the following example
indicates the call-out: PPS000G40A42043E12 6°C.
PPS000G40A42043E12 = Same as Note 3
E = electrical requirements
12. Conditioning
0 = Specimen to be specified by user
2 = property requirements of Table 1,
12.1 Conditioning—Condition test specimens at 23 6 2°C
Column B
and 50 6 5 % relative humidity for not less than 40 h prior to
testing in accordance with Procedure A of Practice D 618,
6. Basic Requirements
where conditioning is specified.
6.1 Basic requirements from Table A, as they apply, are
12.2 Test Conditions—Conduct tests in the standard labora-
always in effect unless superseded by specific suffix require-
tory atmosphere of 23 6 2°C and 50 6 5 % relative humidity
ments, which always take precedence.
unless otherwise specified.
7. General Requirements
13. Test Methods
7.1 The plastics composition shall be uniform and shall
13.1 Reinforcement and Additive Concentrations—Method
conform to the requirements specified herein. The color and
to be agreed upon between the supplier and the user.
form of the material shall be as agreed upon between the
supplier and the user.
14. Rejection and Rehearing
8. Detail Requirements
14.1 Material that fails to conform to the requirements as
8.1 Test specimens for the various materials shall conform
agreed upon between the user and the supplier may be rejected.
to the requirements prescribed in Table A and suffix require-
If any failure occurs, the materials may be retested to establish
ments as they apply.
conformity in accordance with the agreement between the user
8.2 For the purpose of determining conformance with this
and supplier. Rejection should be reported to the supplier
specification, all specified limits in this specification are
promptly and in writing. In case of dissatisfaction with the
absolute limits, as defined in Practice E 29.
results of the test, the supplier may make claim for a rehearing.
8.2.1 With the absolute method, an observed value or a
calculated value is not rounded
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.