ASTM D4583-95(2015)
(Practice)Standard Practice for Carbon Black—Calculation of Process Indexes From an Analysis of Process Control Data
Standard Practice for Carbon Black—Calculation of Process Indexes From an Analysis of Process Control Data
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This practice will provide the following: (1) a statistical summary of individual production run data plotted on a control chart; (2) a statistical summary of data from multiple production runs; (3) a procedure to relate the average and variation of these data groups to specification limits, and (4) indexes for comparing different manufacturing units for projecting future capabilities or as historical reference.
SCOPE
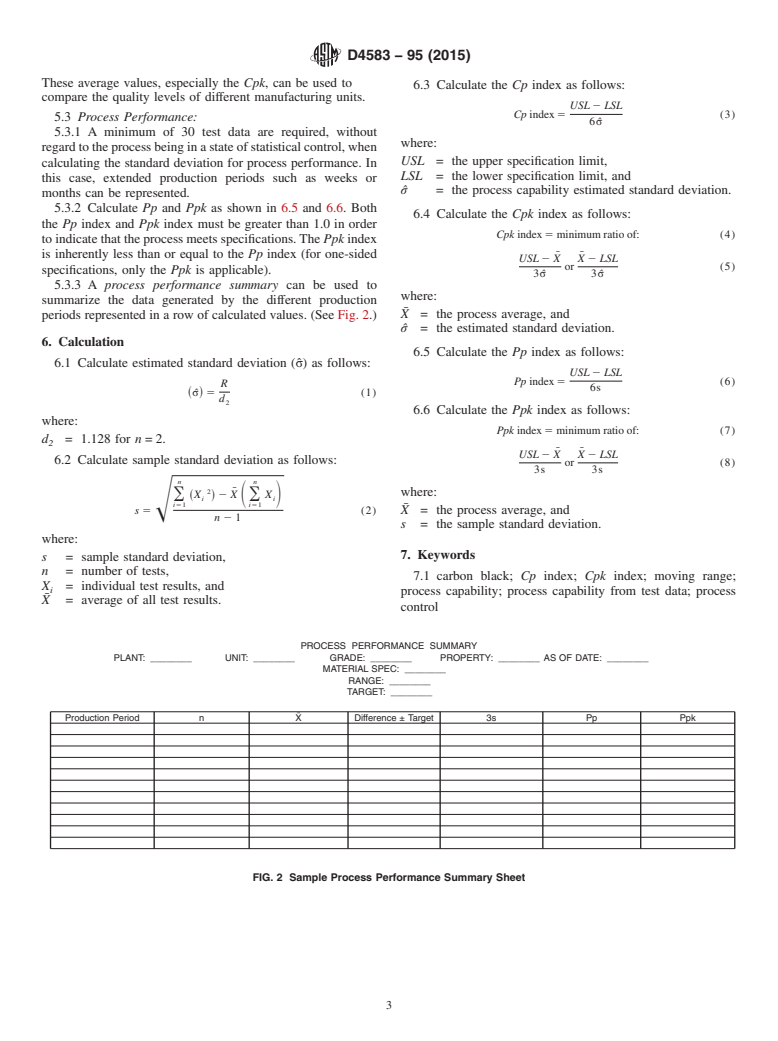
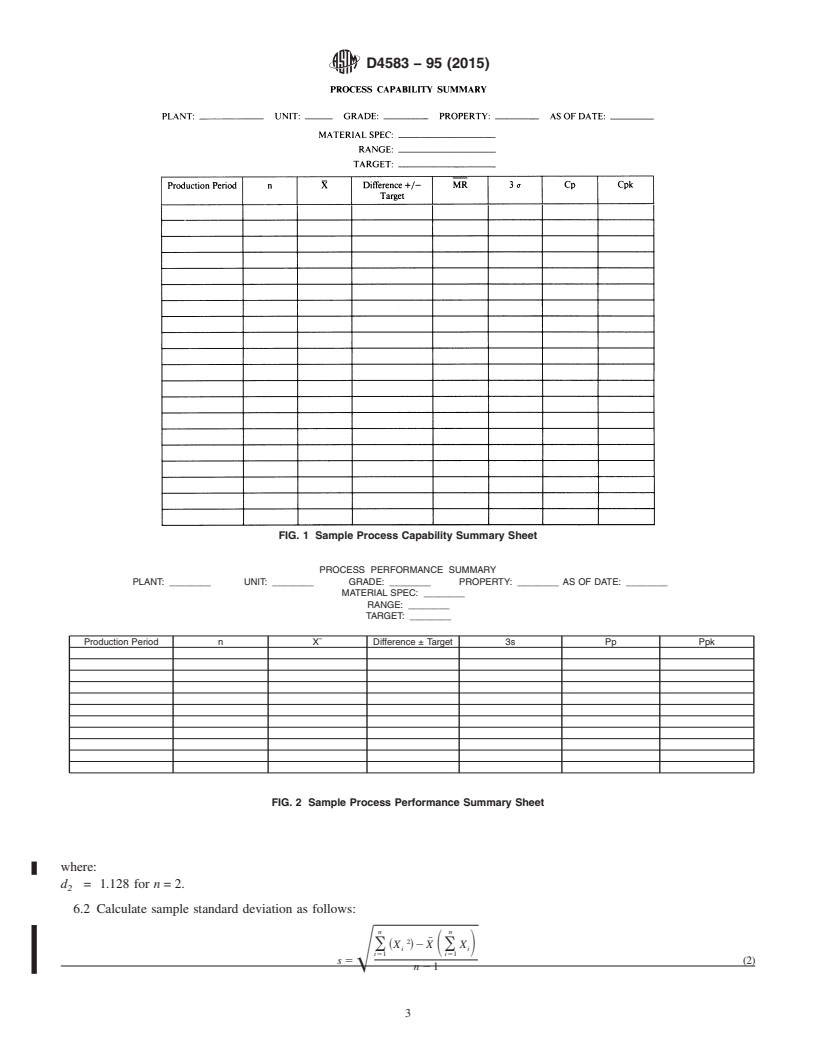
1.1 This practice covers (1) a statistical procedure for analyzing the test data generated in the statistical process control of a carbon black manufacturing process; (2) a format for reporting process capability determined from the analysis of control chart data of an individual production run, and (3) a format for reporting process performance determined from the analysis of control chart data of an individual production run.
1.2 This practice specifically applies to the analysis of pelleted carbon black samples taken during the manufacturing process prior to storage. This practice does not apply to shipment samples taken from hopper cars or other containers or packages.
1.3 This practice is specifically designed to be used for those test methods given in Classification D1765 which specify target values. However, these techniques are applicable to other test methods on carbon black.
1.4 This practice describes the calculation for two methods of determining capability factors from an analysis of process control data.
1.4.1 Process capability (Cp) is a measurement of variation calculated from the process control chart data with the use of an estimated standard deviation (^σ) from the mean value of the moving range (R) chart. The calculation of the process capability (Cp and Cpk) indexes can be used as historical information or to predict future performance of the process, but are only valid when the process is in a state of statistical control.
1.4.2 Process performance (Pp) is a measurement of variation calculated from the process control chart data using sample standard deviation(s). The calculation of the process performance (Pp and Ppk) indexes are used for a historical reference of a process' performance and does not require a state of statistical control.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D4583 − 95 (Reapproved 2015)
Standard Practice for
Carbon Black—Calculation of Process Indexes From an
Analysis of Process Control Data
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4583; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.1 This practice covers (1) a statistical procedure for
D1765 Classification System for Carbon Blacks Used in
analyzing the test data generated in the statistical process
Rubber Products
control of a carbon black manufacturing process; (2) a format
for reporting process capability determined from the analysis
3. Terminology
of control chart data of an individual production run, and (3)a
,4
format for reporting process performance determined from the
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
¯
analysis of control chart data of an individual production run.
3.1.1 average moving range ~R!—the arithmetic mean of n
¯
moving ranges, R5 R/n.
(
1.2 This practice specifically applies to the analysis of
pelleted carbon black samples taken during the manufacturing 3.1.2 Cpk index—an index that indicates how well the
common cause process variability is actually contained within
process prior to storage. This practice does not apply to
shipmentsamplestakenfromhoppercarsorothercontainersor the specifications. (See 6.4.)
packages.
3.1.3 moving range (R)—the absolute difference between
consecutive, individual test values.
1.3 This practice is specifically designed to be used for
3.1.4 Ppk index—indicates how well the common and
those test methods given in Classification D1765 which specify
special cause process variability is actually contained within
targetvalues.However,thesetechniquesareapplicabletoother
the specifications. (See 6.6.)
test methods on carbon black.
3.1.5 processcapabilityindex(Cp)—an index that compares
1.4 This practice describes the calculation for two methods
the magnitude of common cause process variability to the
of determining capability factors from an analysis of process
range of upper and lower specification limits (USL and LSL)
control data.
without regard to where the process is centered; Cp in-
1.4.1 Process capability (Cp) is a measurement of variation
dex=(USL − LSL)/(6σˆ). (See 6.3.)
calculated from the process control chart data with the use of
3.1.6 process performance index(Pp)—an index that com-
an estimated standard deviation (σˆ) from the mean value of the
pares the magnitude of common and special cause process
moving range (R) chart. The calculation of the process capa-
variability to the range of the upper and lower specification
bility (Cp and Cpk) indexes can be used as historical informa-
limits (USL and LSL) without regard to where the process is
tion or to predict future performance of the process, but are
centered; Pp index = (USL − LSL)/(6s). (See 6.5.)
only valid when the process is in a state of statistical control.
1.4.2 Process performance (Pp) is a measurement of varia-
4. Significance and Use
tion calculated from the process control chart data using
4.1 This practice will provide the following: (1) a statistical
sample standard deviation(s). The calculation of the process
summary of individual production run data plotted on a control
performance (Pp and Ppk) indexes are used for a historical
reference of a process’ performance and does not require a
state of statistical control.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D24 on Carbon the ASTM website.
Blackand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D24.61 on Carbon Black Manual on Presentation of Data and Control ChartAnalysis, STP15D,ASTM
Sampling and Statistical Analysis. International, 1976.
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2015. Published February 2015. Originally Ford Motor Company Manual on “Process Capability and Continuing Process
approved in 1986. Last previous edition approved in 2009 as D4583 – 95 (2009). Control,” Publication No. 80-01-251. Available in packs of five from Ford Motor
DOI: 10.1520/D4583-95R15. Company, Statistical Methods Publications, P.O. Box 1000, Plymouth, MI 48170.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D4583 − 95 (2015)
chart; (2) a statistical summary of data from multiple produc- recommended for estimating a process capability standard
tion runs; (3) a procedure to relate the average and variation of deviation. In that case, the number (n) of moving ranges
these data groups to specification limits, and (4) indexes for averaged will be 29.
comparing different manufacturing units for projecting future
5.2.2 CalculateCp andCpk as shown in 6.3 and 6.4.TheCp
capabilities or as historical reference.
index and the Cpk index must be greater than 1.00 in order to
indicate the capability of the process to meet the established
5. Procedure
specifications.TheCpk index is inherently less than or equal to
the Cp index (for one-sided specifications, only the Cpk index
5.1 Sampling:
is applicable).
5.1.1 In order to provide uniformity and the ability to make
valid comparisons of process
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D4583 − 95 (Reapproved 2009) D4583 − 95 (Reapproved 2015)
Standard Practice for
Carbon Black—Calculation of Process Indexes From an
Analysis of Process Control Data
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4583; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This practice covers (1) a statistical procedure for analyzing the test data generated in the statistical process control of a
carbon black manufacturing process; (2) a format for reporting process capability determined from the analysis of control chart
data of an individual production run, and (3) a format for reporting process performance determined from the analysis of control
chart data of an individual production run.
1.2 This practice specifically applies to the analysis of pelleted carbon black samples taken during the manufacturing process
prior to storage. This practice does not apply to shipment samples taken from hopper cars or other containers or packages.
1.3 This practice is specifically designed to be used for those test methods given in Classification D1765 which specify target
values. However, these techniques are applicable to other test methods on carbon black.
1.4 This practice describes the calculation for two methods of determining capability factors from an analysis of process control
data.
1.4.1 Process capability (Cp) is a measurement of variation calculated from the process control chart data with the use of an
estimated standard deviation (σˆ) from the mean value of the moving range (R) chart. The calculation of the process capability (Cp
and Cpk) indexes can be used as historical information or to predict future performance of the process, but are only valid when
the process is in a state of statistical control.
1.4.2 Process performance (Pp) is a measurement of variation calculated from the process control chart data using sample
standard deviation(s). The calculation of the process performance (Pp and Ppk) indexes are used for a historical reference of a
process’ performance and does not require a state of statistical control.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1765 Classification System for Carbon Blacks Used in Rubber Products
3. Terminology
, 4
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
¯ ¯ ¯ ¯
3.1.1 average moving range ~R!~R!—the arithmetic mean of n moving ranges, R5 R/n.R5 R/n.
( (
3.1.2 Cpk index—an index that indicates how well the common cause process variability is actually contained within the
specifications. (See 6.4.)
3.1.3 moving range (R)—the absolute difference between consecutive, individual test values.
3.1.4 Ppk index—indicates how well the common and special cause process variability is actually contained within the
specifications. (See 6.6.)
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D24 on Carbon Blackand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D24.61 on Carbon Black Sampling
and Statistical Analysis.
Current edition approved May 1, 2009Jan. 1, 2015. Published May 2009February 2015. Originally approved in 1986. Last previous edition approved in 20042009 as
D4583 – 95 (2004).(2009). DOI: 10.1520/D4583-95R09.10.1520/D4583-95R15.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Manual on Presentation of Data and Control Chart Analysis, STP 15D, ASTM International, 1976.
Ford Motor Company Manual on “Process Capability and Continuing Process Control,” Publication No. 80-01-251. Available in packs of five from Ford Motor
Company, Statistical Methods Publications, P.O. Box 1000, Plymouth, MI 48170.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D4583 − 95 (2015)
3.1.5 process capability index (Cp)—an index that compares the magnitude of common cause process variability to the range
of upper and lower specification limits (USL and LSL) without regard to where the process is centered; Cp index = (USL − LSL)/
(6σˆ). (See 6.3.)
3.1.6 process performance index(Pp)—an index that compares the magnitude of common and special cause process variability
to the range of the upper and lower specification limits (USL and LSL) without regard to where the process is centered; Pp
index = (USL − LSL)/(6s). (See 6.5.)
4. Significance and Use
4.1 This practice will provide the following: (1) a statistical summary of individual production run data plotted on a control
chart; (2) a statistical summary of data from multiple production runs; (3) a procedure to relate the average and variation of these
data groups to specification limits, and (4) indexes for comparing different manufacturing units for projecting future capabilities
or as historical reference.
5. Procedure
5.1 Sampling:
5.1.1 In order to provide uniformity and the ability to make valid comparisons of process capability and process performance
indexes, all samples used for these calculations shall be collected in the same way. Samples that are to be tested for properties on
which capability or performance indexes will be calculated shall be collected as follows:
5.1.1.1 All samples shall be taken from the process at the finished pellet discharge and tested individually. Compositing of
samples is not
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.