ASTM C374-14
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Fusion Flow of Porcelain Enamel Frits (Flow-Button Methods)
Standard Test Methods for Fusion Flow of Porcelain Enamel Frits (Flow-Button Methods)
ABSTRACT
These test methods cover evaluation of the relative fusion flow characteristics of samples of a given porcelain enamel by comparison with an established standard for that frit. Two test methods are included, differing only in certain details of the samples and in the apparatus and procedure for preparation of test specimens. Both test methods give equally reproducible results and provide a satisfactory basis for comparison of fusion flow of the sample with that of the established standard. Test Method A employs granular particles of frit to which a bonding agent has been added. Button specimens are formed under high pressure in a hydraulic press. Test Method B employs crushed, sized particles of frit to which a bonding agent has been added. Button specimens are formed in a steel mold by hand. Both Test Methods use a hard steel mortar that is resistant to abrasion by the porcelain enamel frit, a hydraulic press, and a fusion flow rack. The test methods use sieves of different specifications. The steel mold assembly of both test methods consists of a die and plunger, however, Test Method B has an additional back-up disk.
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover evaluation of the relative fusion flow characteristics of samples of a given porcelain enamel frit by comparison with an established standard for that frit.
1.2 Two test methods are included, differing only in certain details of the samples and in the apparatus and procedure for preparation of test specimens. Both test methods give equally reproducible results and provide a satisfactory basis for comparison of fusion flow of the sample with that of the established standard.
1.2.1 Test Method A employs granular particles of frit to which a bonding agent has been added. Button specimens are formed under high pressure in a hydraulic press.
1.2.2 Test Method B employs crushed, sized particles of frit to which a bonding agent has been added. Button specimens are formed in a steel mold by hand.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: C374 − 14
StandardTest Methods for
Fusion Flow of Porcelain Enamel Frits (Flow-Button
1
Methods)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C374; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
This test provides a procedure to compare the fluidity of a glass frit or a porcelain enamel powder
to a standard reference material at a fixed temperature above the sample’s glass temperature.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Document
2
1.1 These test methods cover evaluation of the relative 2.1 ASTM Standards:
fusion flow characteristics of samples of a given porcelain E11 Specification for Woven Wire Test Sieve Cloth and Test
enamel frit by comparison with an established standard for that Sieves
frit.
TEST METHOD A
1.2 Two test methods are included, differing only in certain
details of the samples and in the apparatus and procedure for
3. Apparatus
preparation of test specimens. Both test methods give equally
3.1 Mortar, of hard steel, resistant to abrasion by the
reproducible results and provide a satisfactory basis for com-
porcelainenamelfrit,andconformingtothedimensionsshown
parisonoffusionflowofthesamplewiththatoftheestablished
in Fig. 1.
standard.
1.2.1 Test Method A employs granular particles of frit to
NOTE 1—Suitable mortars are available commercially under the desig-
which a bonding agent has been added. Button specimens are nation “tool steel crushing mortar.”
formed under high pressure in a hydraulic press.
3.2 Sieves—No. 12 (1.70-mm) and No. 200 (75-µm) sieves
1.2.2 Test Method B employs crushed, sized particles of frit
conforming to Specification E11.
to which a bonding agent has been added. Button specimens
NOTE 2—Tyler Standard Series sieves No. 12 (0.0060-in. (0.152-mm)
are formed in a steel mold by hand.
openings) and No. 200 (0.029-in. (0.07-mm) openings) correspond to
ASTM sieves Nos. 12 and 200 (U.S. Standard Sieves series numbers).
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
3.3 Hydraulic Press, capable of developing 3500-lbf
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
(15 600 N) force (Fig. 2).
and are not considered standard.
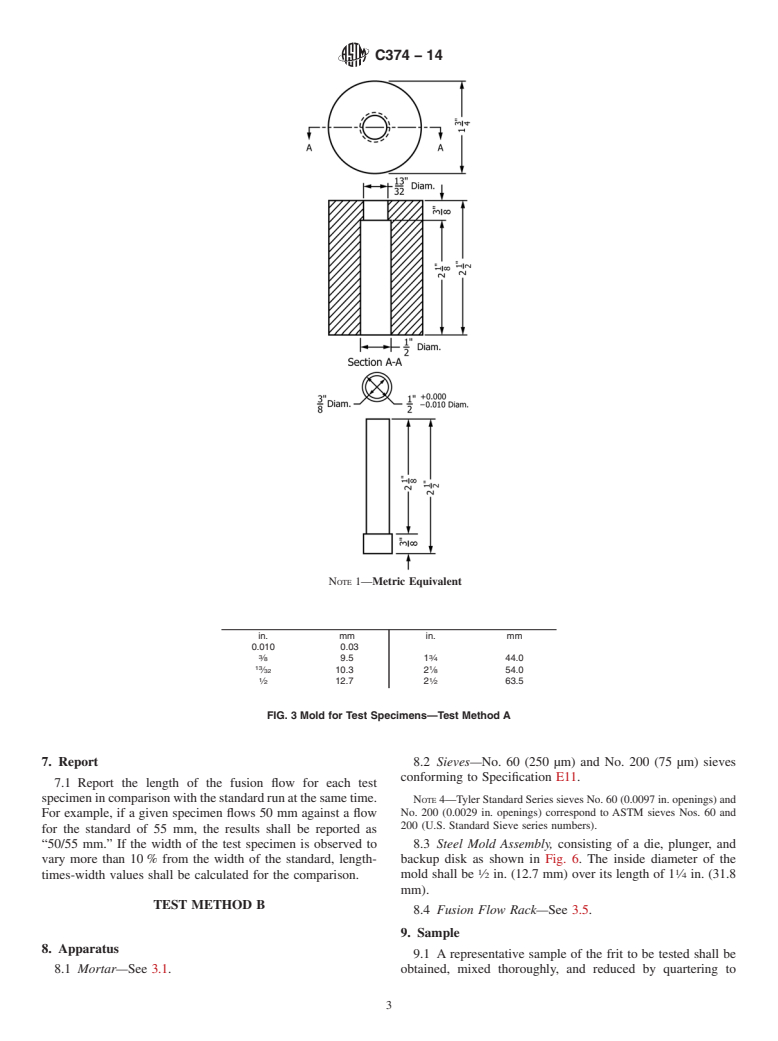
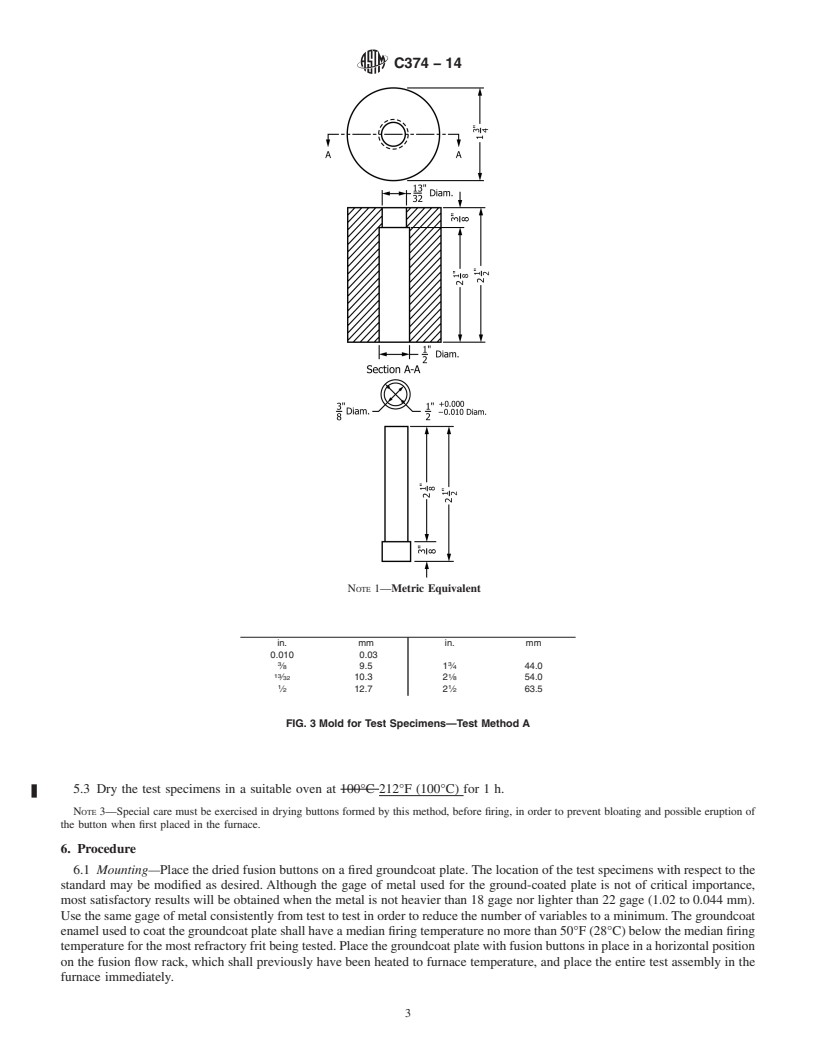
3.4 Steel Mold Assembly, consisting of a die and plunger,
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the 1
and having an inside diameter of ⁄2 in. (12.7 mm) over its
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
1
length of 2 ⁄8 in. (54 mm) as illustrated in Fig. 3.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.5 Fusion Flow Rack, preferably constructed of heat-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
resisting alloy and conforming to the detailed requirements
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
shown in Fig. 4.
1
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B08 on
Metallic and Inorganic Coatings and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
2
B08.12 on Materials for Porcelain Enamel and Ceramic-Metal Systems. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved May 1, 2014. Published June 2014. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
ε1
approved in 1955. Last previous edition approved in 2009 as C374 – 70 (2009) . Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
DOI: 10.1520/C0374-14. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C374 − 14
sampleasdirectedin5.2.Fordryelectrostaticpowdersamples,
use four to five drops of acetone instead of the aqueous gum
arabic solution.
5.2 Place the sample in the steel mold. Place the mold
assembly containing the sample in a hydraulic press and bring
the press up to 3000 to 3500 lbf (13.3 to 15.6 kN) total load,
and immediately release (Fig. 2). Force the formed button out
of the mold with the plunger, taking care not to damage the
button in any way that might change the dimensions.
5.3 Dry the test specimens in a suitable oven at 212°F
(100°C) for 1 h.
NOTE 3—Special care must be exercised in drying buttons formed by
this method, before firing, in order to prevent bloating and possible
eruption of the button when first placed in the furnace.
NOTE 1—1 in. = 25.4 mm.
6. Procedure
FIG. 1 Mortar
6.1 Mounting—Place the dried fusion buttons on a fired
groundcoat plate. The location of the test specimens with
respect to the standard may be modified as desired
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: C374 − 70 (Reapproved 2009) C374 − 14
Standard Test Methods for
Fusion Flow of Porcelain Enamel Frits (Flow-Button
1
Methods)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C374; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
This test provides a procedure to compare the fluidity of a glass frit or a porcelain enamel powder
to a standard reference material at a fixed temperature above the sample’s glass temperature.
1. Scope
1.1 These test methods cover evaluation of the relative fusion flow characteristics of samples of a given porcelain enamel frit
by comparison with an established standard for that frit.
1.2 Two test methods are included, differing only in certain details of the samples and in the apparatus and procedure for
preparation of test specimens. Both test methods give equally reproducible results and provide a satisfactory basis for comparison
of fusion flow of the sample with that of the established standard.
1.2.1 Test Method A employs granular particles of frit to which a bonding agent has been added. Button specimens are formed
under high pressure in a hydraulic press.
1.2.2 Test Method B employs crushed, sized particles of frit to which a bonding agent has been added. Button specimens are
formed in a steel mold by hand.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Document
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E11 Specification for Woven Wire Test Sieve Cloth and Test Sieves
TEST METHOD A
3. Apparatus
3.1 Mortar, of hard steel, resistant to abrasion by the porcelain enamel frit, and conforming to the dimensions shown in Fig.
1.
NOTE 1—Suitable mortars are available commercially under the designation “tool steel crushing mortar.”
3.2 Sieves—No. 12 (1.70-mm) and No. 200 (75-μm) sieves conforming to Specification E11.
NOTE 2—Tyler Standard Series sieves No. 12 (0.0060-in. (0.152-mm) openings) and No. 200 (0.029-in. (0.07-mm) openings) correspond to ASTM
sieves Nos. 12 and 200 (U.S. Standard Sieves series numbers).
3.3 Hydraulic Press, capable of developing 3500-lbf (15 600 N) force (Fig. 2).
1
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B08 on Metallic and Inorganic Coatings and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B08.12
on Materials for Porcelain Enamel and Ceramic-Metal Systems.
Current edition approved April 15, 2009May 1, 2014. Published June 2009June 2014. Originally approved in 1955. Last previous edition approved in 20042009 as
ε1
C374 – 70 (2004)(2009) . DOI: 10.1520/C0374-70R09.10.1520/C0374-14.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C374 − 14
NOTE 1—1 in. = 25.4 mm.
FIG. 1 Mortar
FIG. 2 Hydraulic Press
1
3.4 Steel Mold Assembly, consisting of a die and plunger, and having an inside diameter of ⁄2 in. (12.7 mm) over its length of
1
2 ⁄8 in. (54 mm) as illustrated in Fig. 3.
3.5 Fusion Flow Rack, preferably constructed of heat-resisting alloy and conforming to the detailed requirements shown in Fig.
4.
4. Sample
4.1 A representative sample of the frit to be tested shall be obtained, mixed thoroughly, and reduced by quartering to about 25
g. This sample shall be crushed in a hard steel mortar to pass a No. 12 (1.70-mm) (1.70 mm) sieve and be retained on a No. 200
(75-μm) (75 μm) sieve.
4.2 For wet-ground enamels the sample shall be evaporated to dryness in an evaporation dish. After cooling, the dried enamel
shall be loosened and again pulverized using a pestle and mortar or similar apparatus.
4.3 Dry ground samples of frit
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.