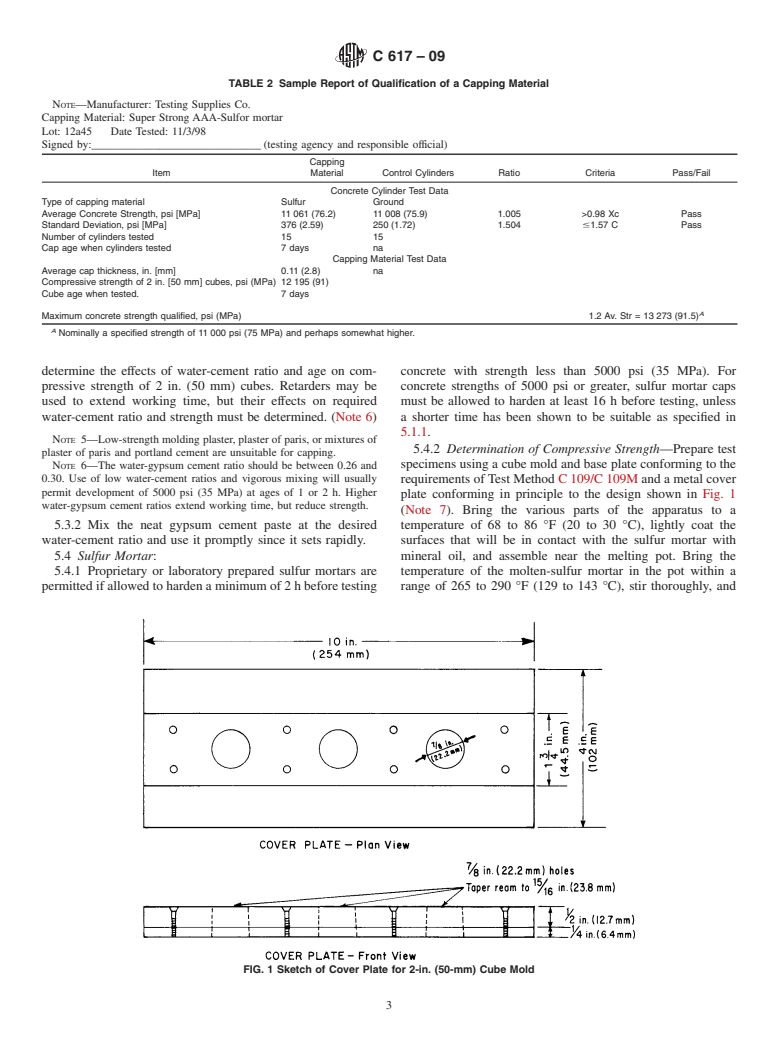
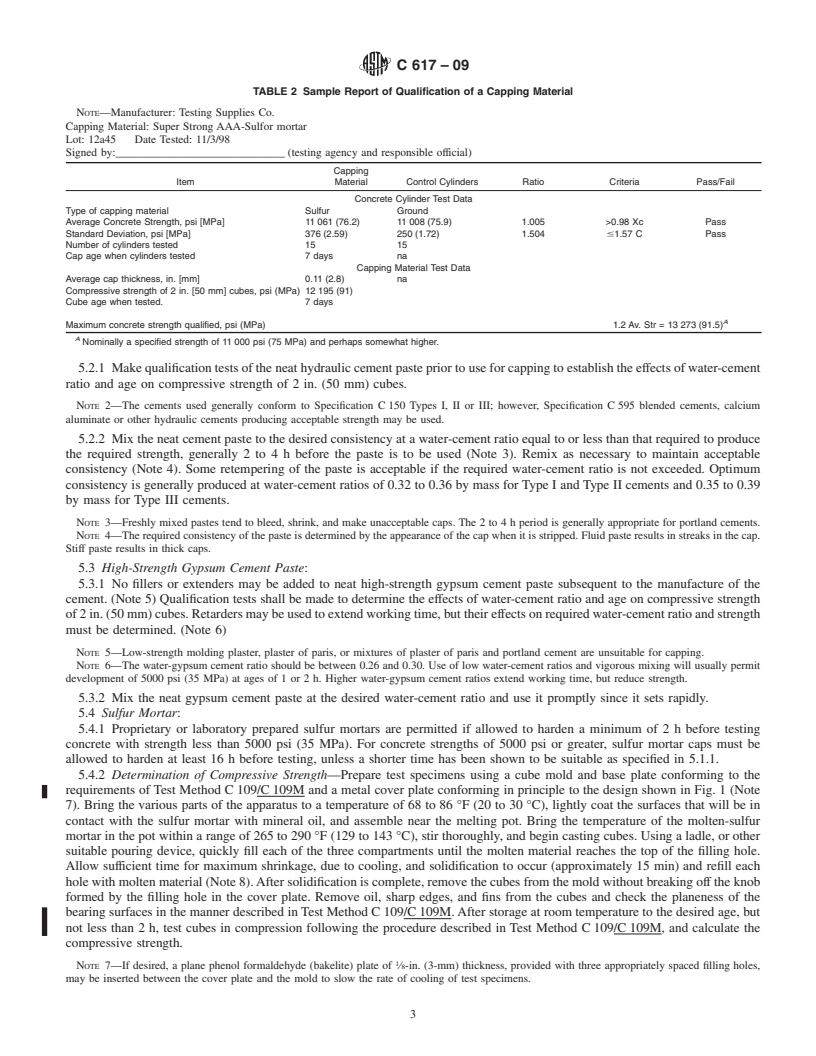
ASTM C617-09
(Practice)Standard Practice for Capping Cylindrical Concrete Specimens
Standard Practice for Capping Cylindrical Concrete Specimens
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This practice describes procedures for providing plane surfaces on the ends of freshly molded concrete cylinders, hardened cylinders, or drilled concrete cores when the end surfaces do not conform with the planeness and perpendicularity requirements of applicable standards. Practice C 1231/C 1231M describes alternative procedures using unbonded caps or pad caps.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice covers apparatus, materials, and procedures for capping freshly molded concrete cylinders with neat cement and hardened cylinders and drilled concrete cores with high-strength gypsum plaster or sulfur mortar.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific precaution statements see 4.3.1 and 6.2.4.1.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: C 617 – 09
Standard Practice for
1
Capping Cylindrical Concrete Specimens
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C 617; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope* B46.1 Standard for Surface Texture (Surface, Roughness,
Waviness and Lay)
1.1 This practice covers apparatus, materials, and proce-
dures for capping freshly molded concrete cylinders with neat
3. Significance and Use
cement and hardened cylinders and drilled concrete cores with
3.1 This practice describes procedures for providing plane
high-strength gypsum plaster or sulfur mortar.
surfaces on the ends of freshly molded concrete cylinders,
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
hardened cylinders, or drilled concrete cores when the end
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
surfaces do not conform with the planeness and perpendicu-
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
larity requirements of applicable standards. Practice C 1231/
and are not considered standard.
C 1231M describes alternative procedures using unbonded
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
caps or pad caps.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4. Capping Equipment
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
4.1 Capping Plates—Neat cement caps and high-strength
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific
gypsum-plaster caps shall be formed against a glass plate at
precaution statements see 4.3.1 and 6.2.4.1.
1
least ⁄4 in. (6 mm) thick, a machined metal plate at least 0.45
2. Referenced Documents in. (11 mm) thick, or a polished plate of granite or diabase at
2 least 3 in. (76 mm) thick. Sulfur mortar caps shall be formed
2.1 ASTM Standards:
against similar metal or stone plates except that the recessed
C 109/C 109M Test Method for Compressive Strength of
1
area which receives molten sulfur shall not be deeper than ⁄2
Hydraulic Cement Mortars (Using 2-in. or [50-mm] Cube
in. (12 mm). In all cases, plates shall be at least 1 in. (25 mm)
Specimens)
greater in diameter than the test specimen and the working
C 150 Specification for Portland Cement
surfaces shall not depart from a plane by more than 0.002 in.
C 472 Test Methods for Physical Testing of Gypsum, Gyp-
(0.05 mm) in 6 in. (152 mm). The surface roughness of newly
sum Plasters and Gypsum Concrete
finished metal plates shall not exceed that set forth in Table 4
C 595 Specification for Blended Hydraulic Cements
ofAmerican National Standard B46.1, or 125 µin. (3.2 µm) for
C 1231/C 1231M Practice for Use of Unbonded Caps in
any type of surface and direction of lay. The surface, when
Determination of Compressive Strength of Hardened Con-
new, shall be free of gouges, grooves, or indentations beyond
crete Cylinders
3 those caused by the finishing operation. Metal plates that have
2.2 ANSI Standard:
been in use shall be free of gouges, grooves, and indentations
greater than 0.010 in. (0.25 mm) deep or greater than 0.05
2 2
in. (32 mm ) in surface area.
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C09 on Concrete
NOTE 1—A Rockwell hardness of 48 HRC is suggested for capping
andConcreteAggregatesandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeC09.61on
plates of devices used to form sulfur mortar caps.
Testing for Strength.
Current edition approved May 1, 2009. Published May 2009. Originally
4.2 Alignment Devices—Suitable alignment devices, such
approved in 1968. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as C 617 – 98 (2003).
2
as guide bars or bull’s-eye levels, shall be used in conjunction
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
with capping plates to ensure that no single cap will depart
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
from perpendicularity to the axis of a cylindrical specimen by
the ASTM website.
1
3 more than 0.5° (approximately equivalent to ⁄8 in. in 12 in.
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org. (3.2 mm in 305 mm)). The same requirement is applicable to
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
-----------------
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:C 617–98 (Reapproved 2003) Designation: C 617 – 09
Standard Practice for
1
Capping Cylindrical Concrete Specimens
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C 617; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This practice covers apparatus, materials, and procedures for capping freshly molded concrete cylinders with neat cement
and hardened cylinders and drilled concrete cores with high-strength gypsum plaster or sulfur mortar.
1.2The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The SI equivalents of inch-pound units may be
approximate.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. For specific precaution statements see 4.3 and 6.2.3.1. For specific precaution statements see 4.3.1 and
6.2.4.1.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C 109/C 109M Test Method for Compressive Strength of Hydraulic Cement Mortars (Using 2-in. or [50-mm] Cube Specimens)
C 150 Specification for Portland Cement
C472
C 472 Test Methods for Physical Testing of Gypsum, Gypsum Plasters and Gypsum Concrete
C595M
C 595 Specification for Blended Hydraulic Cements
C1231 1231/C 1231M Practice for Use of Unbonded Caps in Determination of Compressive Strength of Hardened Concrete
Cylinders
3
2.2 ANSI Standard:
B46.1 Standard for Surface Texture (Surface, Roughness, Waviness and Lay)
3. Significance and Use
3.1 This practice describes procedures for providing plane surfaces on the ends of freshly molded concrete cylinders, hardened
cylinders, or drilled concrete cores when the end surfaces do not conform with the planeness and perpendicularity requirements
of applicable standards. Practice C 1231/C 1231M describes alternative procedures using unbonded caps or pad caps.
4. Capping Equipment
1
4.1 Capping Plates— Neat cement caps and high-strength gypsum-plaster caps shall be formed against a glass plate at least ⁄4
in. (6 mm) thick, a machined metal plate at least 0.45 in. (11 mm) thick, or a polished plate of granite or diabase at least 3 in.
(76mm)thick.Sulfurmortarcapsshallbeformedagainstsimilarmetalorstoneplatesexceptthattherecessedareawhichreceives
1
molten sulfur shall not be deeper than ⁄2 in. (12 mm). In all cases, plates shall be at least 1 in. (25 mm) greater in diameter than
the test specimen and the working surfaces shall not depart from a plane by more than 0.002 in. (0.05 mm) in 6 in. (152 mm). The
surface roughness of newly finished metal plates shall not exceed that set forth in Table 4 of American National Standard B46.1,
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee C09 on Concrete and ConcreteAggregates and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C09.61 onTesting
for Strength.
Current edition approvedAugust 10, 1998.May 1, 2009. Published December 1998.May 2009. Originally approved in 1968. Last previous edition approved in 19982003
as C 617 – 98 (2003).
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 345 E. 47th Street, New York, NY 10017.
3
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St., 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C 617–09
or 125 µin. (3.2 µm) for any type of surface and direction of lay. The surface, when new, shall be free of gouges, grooves, or
indentations beyond those caused by the fin
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.