ASTM F856-97(2014)
(Practice)Standard Practice for Mechanical Symbols, Shipboard—Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC)
Standard Practice for Mechanical Symbols, Shipboard—Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
2.1 When symbolic representation is required for an item not covered in this standard, the character of the symbol shall be adequately identified and shall be subject to one interpretation only. If necessary, a note shall be attached to the symbol for further clarity.
2.2 Symbolic representation does not require exact or scale layouts of the actual system. Therefore, the symbols may be used in all views of the system layout.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice covers symbols used on heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) detailed engineering drawings.
1.2 These symbols may be useful on contract and preliminary design drawings.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: F856 − 97 (Reapproved 2014) An American National Standard
Standard Practice for
Mechanical Symbols, Shipboard—Heating, Ventilation, and
Air Conditioning (HVAC)
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationF856;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginal
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope
CW = clockwise
EH = turret heater, electric
1.1 This practice covers symbols used on heating,
EP = duct preheater, electric
ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) detailed engineering
ER = duct reheater, electric
drawings.
EU = electric unit heater
1.2 These symbols may be useful on contract and prelimi-
F = filter
nary design drawings.
FA = flame arrester
FCA = fan coil assembly
2. Significance and Use
FCU = fan coil unit
G = grille
2.1 When symbolic representation is required for an item
GC = gravity cooling coil
not covered in this standard, the character of the symbol shall
H = humidistat, humidifier
be adequately identified and shall be subject to one interpreta-
L = louver
tion only. If necessary, a note shall be attached to the symbol
M = motor
for further clarity.
MFD = manual fire damper
2.2 Symbolic representation does not require exact or scale
NE = natural exhaust
layouts of the actual system. Therefore, the symbols may be
NS = natural supply
R = return air
used in all views of the system layout.
RO = remote operated
3. Abbreviations
SFD = solenoid fire damper
SP = preheater, steam
3.1 The abbreviations (for use only in this practice) are
SR = reheater, steam
defined as follows:
SU = steam unit heater
T = thermostat
AF = axial fan
TE = tempered air, electric
AFD = automatic fire damper with manual override
TS = tempered air, steam
BD = balance damper
U = undercut
CC = cooling coil
UC = unit cooler
CCW = counter clockwise
V = volume, volumetric
CE = convection heater, electric
VC = volume control
CF = centrifugal fan
CS = convection heater, steam
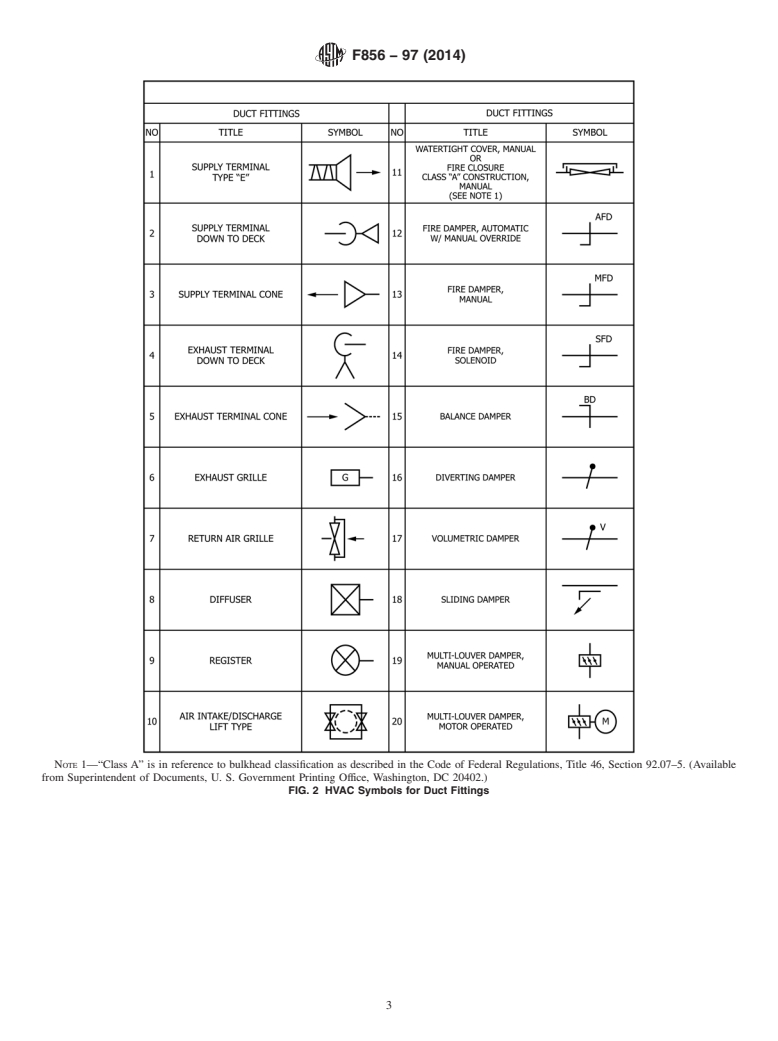
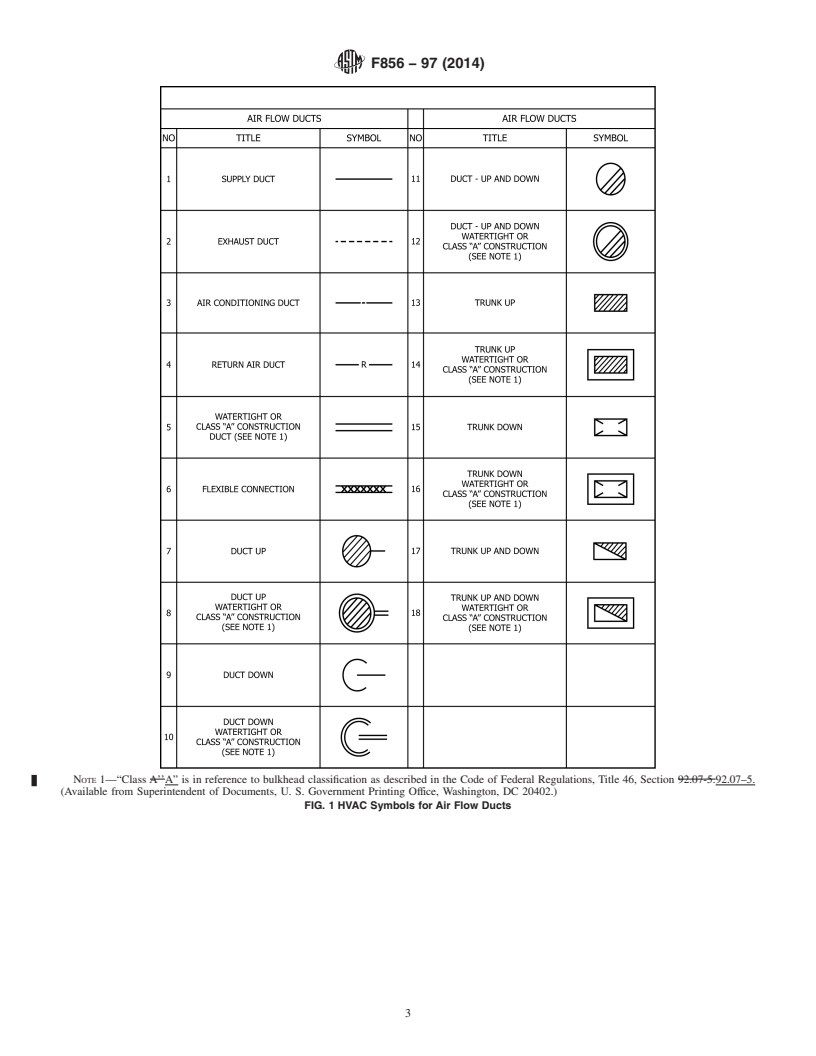
4. Illustrations
4.1 Illustrations for HVAC symbols are given in Figs. 1-4.
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F25 on Ships and
Marine Technology and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F25.11 on
Machinery and Piping Systems. 5. Keywords
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2014. Published September 2014. Originally
5.1 air conditioning; design symbols; engineering symbols;
approved in 1983. Last previous edition approved in 2008 as F856 – 97 (2008).
DOI: 10.1520/F0856-97R14. heating; HVAC; marine; ship; symbols; ventilation
Copyright © A
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: F856 − 97 (Reapproved 2008) F856 − 97 (Reapproved 2014)An American National Standard
Standard Practice for
Mechanical Symbols, Shipboard—Heating, Ventilation, and
Air Conditioning (HVAC)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F856; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A superscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope
1.1 This practice covers symbols used on heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) detailed engineering drawings.
1.2 These symbols may be useful on contract and preliminary design drawings.
2. Significance and Use
2.1 When symbolic representation is required for an item not covered in this standard, the character of the symbol shall be
adequately identified and shall be subject to one interpretation only. If necessary, a note shall be attached to the symbol for further
clarity.
2.2 Symbolic representation does not require exact or scale layouts of the actual system. Therefore, the symbols may be used
in all views of the system layout.
3. Abbreviations
3.1 The abbreviations (for use only in this practice) are defined as follows:
AF = axial fan,
AFD = automatic fire damper with manual override,
BD = balance damper,
CC = cooling coil,
CCW = counter clockwise,
CE = convection heater, electric,
CF = centrifugal fan,
CS = convection heater, steam,
CW = clockwise,
EH = turret heater electric,
EP = duct preheater, electric,
ER = duct reheater, electric,
EU = electric unit heater,
F = filter,
FA = flame arrester,
FCA = fan coil assembly,
FCU = fan coil unit,
G = grille,
GC = gravity cooling coil,
H = humidistat, humidifier,
L = louver,
M = motor,
MFD = manual fire damper,
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F25 on Ships and Marine Technology and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F25.11 on Machinery
and Piping Systems.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2008Aug. 1, 2014. Published December 2008September 2014. Originally approved in 1983. Last previous edition approved in 20042008
as F856 – 97 (2008).(2004). DOI: 10.1520/F0856-97R08.10.1520/F0856-97R14.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
F856 − 97 (2014)
NE = natural exhaust,
NS = natural supply,
R = return air,
RO = remote operated,
SFD = solenoid fire damper,
SP = preheater, steam,
SR = reheater, steam,
SU = steam unit heater,
T = thermostat,
TE = tempered air, electric,
TS = tempered air, steam,
U = undercut,
UC = unit cooler,
V = volume, volumetric, and
VC = volume control.
AF = axial fan
AFD = automatic fire damper with manual override
BD = balance damper
CC = cooling coil
CCW = counter clockwise
CE = convection heater, electric
CF = centrifugal fan
CS = convection heater, steam
CW = clockwise
EH = turret heater, electric
EP = duct preheater, el
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.