ASTM D5134-98(2003)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Detailed Analysis of Petroleum Naphthas through n-Nonane by Capillary Gas Chromatography
Standard Test Method for Detailed Analysis of Petroleum Naphthas through <i>n</i>-Nonane by Capillary Gas Chromatography
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
A knowledge of the hydrocarbon components comprising a petroleum naphtha, reformate, or alkylate is useful in valuation of crude oils, in alkylation and reforming process control, in product quality assessment, and for regulatory purposes. Detailed hydrocarbon composition is also used as input in the mathematical modeling of refinery processes.
Separation of naphtha components by the procedure described in this test method can result in some peaks that represent coeluting compounds. This test method cannot attribute relative concentrations to the coelutants. In the absence of supporting information, use of the results of this test method for purposes which require such attribution is not recommended.
SCOPE
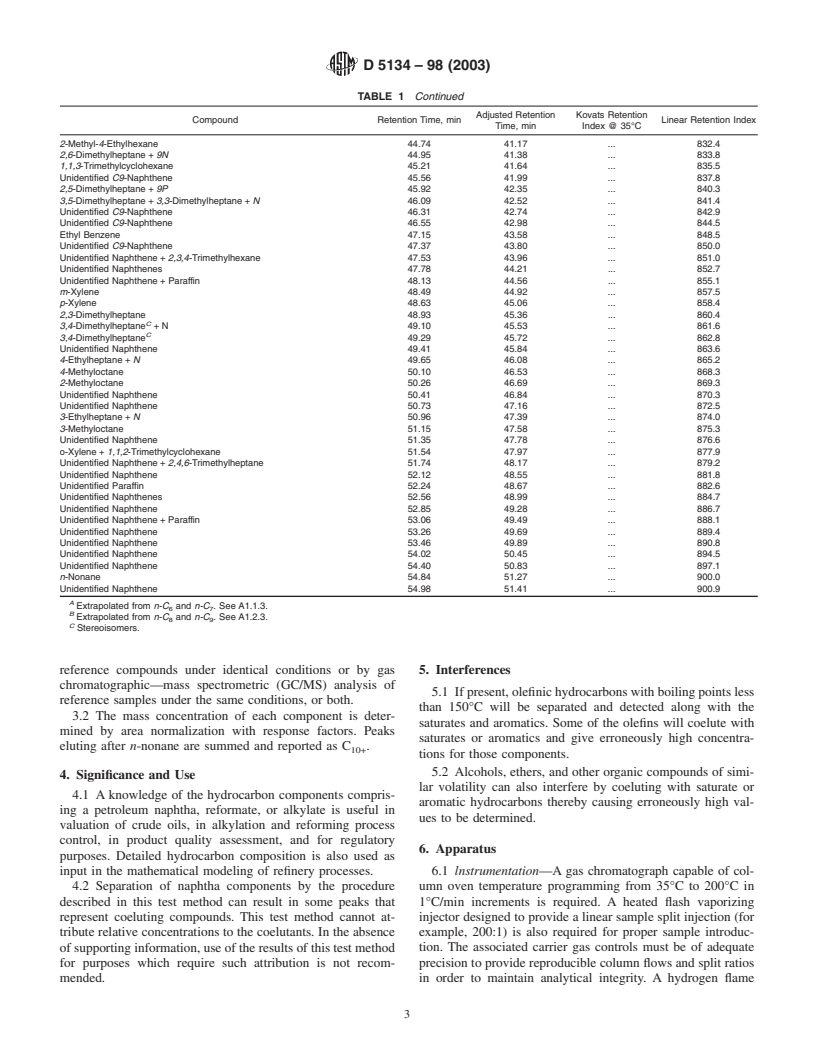
1.1 This test method covers the determination of hydrocarbon components of petroleum naphthas as enumerated in Table 1. Components eluting after n-nonane (bp 150.8°C) are determined as a single group.
1.2 This test method is applicable to olefin-free (
1.3 Components that are present at the 0.05 mass % level or greater can be determined.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific warning statements are given in Section 7.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
Designation:D5134–98 (Reapproved 2003)
Standard Test Method for
Detailed Analysis of Petroleum Naphthas through n-Nonane
1
by Capillary Gas Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5134; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
Despite the many advances in capillary gas chromatography instrumentation and the remarkable
resolution achievable, it has proven difficult to standardize a test method for the analysis of a mixture
as complex as petroleum naphtha. Because of the proliferation of numerous, similar columns and the
endless choices of phase thickness, column internal diameter, length, etc., as well as instrument
operating parameters, many laboratories use similar but not identical methods for the capillary GC
analysis of petroleum naphthas. Even minute differences in column polarity or column oven
temperature, for example, can change resolution or elution order of components and make their
identification an individual interpretive process rather than the desirable, objective application of
standard retention data. To avoid this, stringent column specifications and temperature and flow
conditions have been adopted in this test method to ensure consistent elution order and resolution and
reproducible retention times. Strict adherence to the specified conditions is essential to the successful
application of this test method.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
1.1 This test method covers the determination of hydrocar- 2.1 ASTM Standards:
boncomponentsofpetroleumnaphthasasenumeratedinTable D1319 Test Method for Hydrocarbon Types in Liquid
2
1. Components eluting after n-nonane (bp 150.8°C) are deter- Petroleum Products by Fluorescent Indicator Adsorption
mined as a single group. D3700 Practice for Obtaining LPG Samples Using a Float-
3
1.2 This test method is applicable to olefin-free (<2% ing Piston Cylinder
olefins by liquid volume) liquid hydrocarbon mixtures includ- D3710 Test Method for Boiling Range Distribution of
3
ing virgin naphthas, reformates, and alkylates. Olefin content GasolineandGasolineFractionsbyGasChromatography
can be determined by Test Method D1319. The hydrocarbon D4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
3
mixturemusthavea98%pointof250°Corlessasdetermined Petroleum Products
by Test Method D3710.
3. Summary of Test Method
1.3 Componentsthatarepresentatthe0.05mass%levelor
greater can be determined. 3.1 A representative sample of the naphtha is introduced
into a gas chromatograph equipped with a methyl silicone
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
bondedphasefusedsilicacapillarycolumn.Heliumcarriergas
standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the transports the vaporized sample through the column in which
the components are separated. Components are sensed by a
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- flame ionization detector as they elute from the column. The
detector signal is processed by an electronic data acquisition
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific warning system or integrating computer. Each eluting peak is identified
by comparing its retention index to a table of retention indices
statements are given in Section 7.
and by visual matching with a standard chromatogram. The
table of retention indices has been established by running
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.04 on Hydrocarbon Analysis.
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.01.
Current edition approved May 10, 2003. Published August 2003. Originally
3
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.02.
approved in 1990. Last previous edition approved in 1998 as D5134–98.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5134–98 (2003)
TABLE 1 Typical Retention Characteristics of Naphtha Components
NOTE—The abbreviations N and P refer to unidentified naphthenes and paraffins respectively.
Adjusted Retention Kovats Retention
Compound Retention Time, min Linear Retention Index
Time, min Index @ 35°C
Methane 3.57 0.00 100.0 .
Ethane 3.65 0.08 200.0 .
Propane 3.84 0.27 300.0 .
Isobutane 4.14 0.57 367.3 .
n-Butane 4.39 0.82 400.0 .
2,2-Dimethylpropane 4.53 0.96 415.5 .
Isopentane 5.33 1.76 475.0
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.