ASTM D2837-13e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Obtaining Hydrostatic Design Basis for Thermoplastic Pipe Materials or Pressure Design Basis for Thermoplastic Pipe Products
Standard Test Method for Obtaining Hydrostatic Design Basis for Thermoplastic Pipe Materials or Pressure Design Basis for Thermoplastic Pipe Products
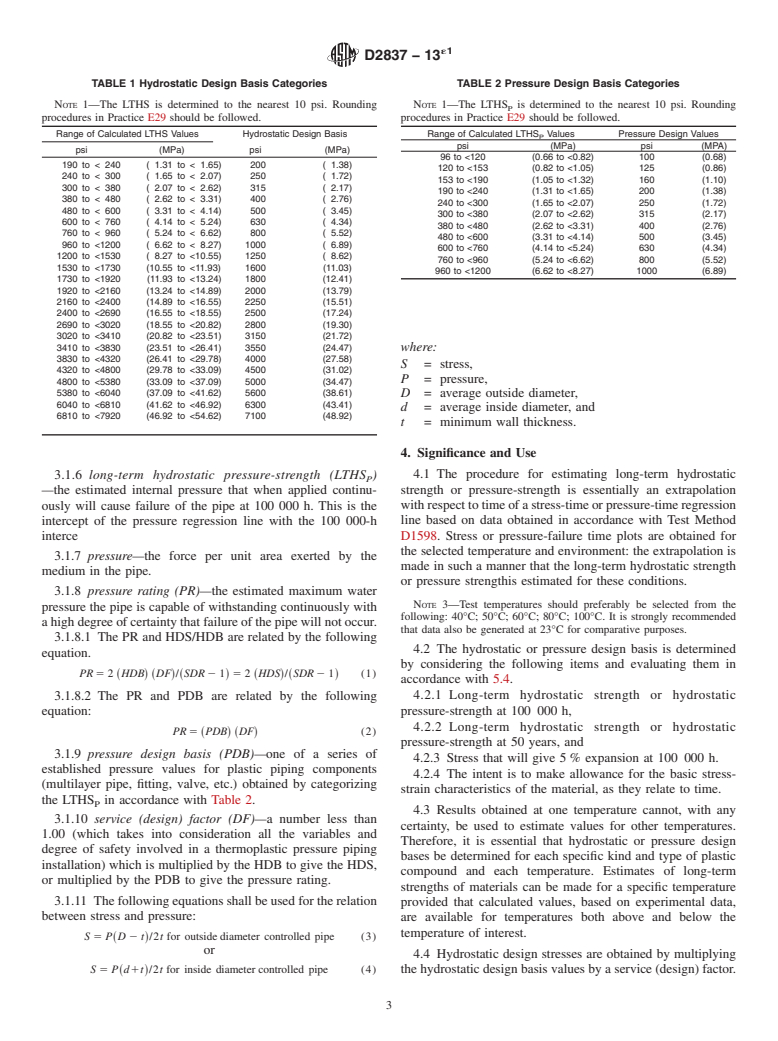
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 The procedure for estimating long-term hydrostatic strength or pressure-strength is essentially an extrapolation with respect to time of a stress-time or pressure-time regression line based on data obtained in accordance with Test Method D1598. Stress or pressure-failure time plots are obtained for the selected temperature and environment: the extrapolation is made in such a manner that the long-term hydrostatic strength or pressure strengthis estimated for these conditions. Note 3—Test temperatures should preferably be selected from the following: 40°C; 50°C; 60°C; 80°C; 100°C. It is strongly recommended that data also be generated at 23°C for comparative purposes.
4.2 The hydrostatic or pressure design basis is determined by considering the following items and evaluating them in accordance with 5.4.
4.2.1 Long-term hydrostatic strength or hydrostatic pressure-strength at 100 000 h,
4.2.2 Long-term hydrostatic strength or hydrostatic pressure-strength at 50 years, and
4.2.3 Stress that will give 5 % expansion at 100 000 h.
4.2.4 The intent is to make allowance for the basic stress-strain characteristics of the material, as they relate to time.
4.3 Results obtained at one temperature cannot, with any certainty, be used to estimate values for other temperatures. Therefore, it is essential that hydrostatic or pressure design bases be determined for each specific kind and type of plastic compound and each temperature. Estimates of long-term strengths of materials can be made for a specific temperature provided that calculated values, based on experimental data, are available for temperatures both above and below the temperature of interest.
4.4 Hydrostatic design stresses are obtained by multiplying the hydrostatic design basis values by a service (design) factor.
4.5 Pressure ratings for pipe may be calculated from the hydrostatic design stress (HDS) value for the specific material used to make the pipe, and its dimensions using the...
SCOPE
1.1 This test method describes two essentially equivalent procedures: one for obtaining a long-term hydrostatic strength category based on stress, referred to herein as the hydrostatic design basis (HDB); and the other for obtaining a long-term hydrostatic strength category based on pressure, referred to herein as the pressure design basis (PDB). The HDB is based on the material's long-term hydrostatic strength (LTHS),and the PDB is based on the product's long-term hydrostatic pressure-strength (LTHSP). The HDB is a material property and is obtained by evaluating stress rupture data derived from testing pipe made from the subject material. The PDB is a product specific property that reflects not only the properties of the material(s) from which the product is made, but also the influence on product strength by product design, geometry, and dimensions and by the specific method of manufacture. The PDB is obtained by evaluating pressure rupture data. The LTHS is determined by analyzing stress versus time-to-rupture (that is, stress-rupture) test data that cover a testing period of not less than 10 000 h and that are derived from sustained pressure testing of pipe made from the subject material. The data are analyzed by linear regression to yield a best-fit log-stress versus log time-to-fail straight-line equation. Using this equation, the material's mean strength at the 100 000-h intercept (LTHS) is determined by extrapolation. The resultant value of the LTHS determines the HDB strength category to which the material is assigned. The LTHS P is similarly determined except that the determination is based on pressure versus time data that are derived from a particular product. The categorized value of the LTHSP is the PDB. An HDB/PDB is one of a series of preferred long-term strength values. This test method is applicable to all known types of thermoplastic pipe materials and thermoplastic piping products. It is also applicab...
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
´1
Designation: D2837 − 13
Standard Test Method for
Obtaining Hydrostatic Design Basis for Thermoplastic Pipe
Materials or Pressure Design Basis for Thermoplastic Pipe
1
Products
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2837; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
ε NOTE—Table 8 was editorially corrected in April 2014.
1. Scope* cable for any practical temperature and medium that yields
stress-rupture data that exhibit an essentially straight-line
1.1 This test method describes two essentially equivalent
relationshipwhenplottedonlogstress(pound-forcepersquare
procedures: one for obtaining a long-term hydrostatic strength
inch) or log pressure (pound-force per square in. gage) versus
category based on stress, referred to herein as the hydrostatic
logtime-to-fail(hours)coordinates,andforwhichthisstraight-
design basis (HDB); and the other for obtaining a long-term
line relationship is expected to continue uninterrupted through
hydrostatic strength category based on pressure, referred to
at least 100000 h.
herein as the pressure design basis (PDB). The HDB is based
on the material’s long-term hydrostatic strength (LTHS),and
1.2 Unless the experimentally obtained data approximate a
the PDB is based on the product’s long-term hydrostatic
straight line, when calculated using log-log coordinates, it is
pressure-strength (LTHS ). The HDB is a material property
P not possible to assign an HDB/PDB to the material. Data that
and is obtained by evaluating stress rupture data derived from
exhibit high scatter or a “knee” (a downward shift, resulting in
testing pipe made from the subject material. The PDB is a
a subsequently steeper stress-rupture slope than indicated by
productspecificpropertythatreflectsnotonlythepropertiesof
the earlier data) but which meet the requirements of this test
the material(s) from which the product is made, but also the
method tend to give a lower forecast of LTHS/LTHS.Inthe
P
influenceonproductstrengthbyproductdesign,geometry,and
case of data that exhibit excessive scatter or a pronounced
dimensions and by the specific method of manufacture. The
“knee,” the lower confidence limit requirements of this test
PDB is obtained by evaluating pressure rupture data. The
methodarenotmetandthedataareclassifiedasunsuitablefor
LTHS is determined by analyzing stress versus time-to-rupture
analysis.
(that is, stress-rupture) test data that cover a testing period of
1.3 Afundamental premise of this test method is that when
not less than 10000 h and that are derived from sustained
the experimental data define a straight-line relationship in
pressure testing of pipe made from the subject material. The
accordance with this test method’s requirements, this straight
data are analyzed by linear regression to yield a best-fit
line may be assumed to continue beyond the experimental
log-stress versus log time-to-fail straight-line equation. Using
period, through at least 100000 h (the time intercept at which
this equation, the material’s mean strength at the 100000-h
the material’s LTHS/LTHS is determined). In the case of
P
intercept (LTHS) is determined by extrapolation. The resultant
polyethylene piping materials, this test method includes a
value of the LTHS determines the HDB strength category to
supplemental requirement for the “validating” of this assump-
which the material is assigned. The LTHS is similarly
P
tion. No such validation requirements are included for other
determined except that the determination is based on pressure
materials (see Note 1). Therefore, in all these other cases, it is
versustimedatathatarederivedfromaparticularproduct.The
uptotheuserofthistestmethodtodeterminebasedonoutside
categorized value of the LTHS is the PDB. An HDB/PDB is
P
information whether this test method is satisfactory for the
oneofaseriesofpreferredlong-termstrengthvalues.Thistest
forecasting of a material’s LTHS/LTHS for each particular
P
method is applicable to all known types of thermoplastic pipe
combination of internal/external environments and tempera-
materials and thermoplastic piping products. It is also appli-
ture.
1 NOTE 1—Extensive long-term data that have been obtained on com-
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F17 on Plastic
mercial pressure pipe grades of polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polybutylene
Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.40 on Test
(PB), and cross linked polyethylene (PEX) materials have shown that this
Methods.
assumption is appropriate for the establishing of HDB’s for these
Current edition approved Nov. 15, 2013.
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.