ASTM D4251-89(2003)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Active Matter in Anionic Surfactants by Potentiometric Titration
Standard Test Method for Active Matter in Anionic Surfactants by Potentiometric Titration
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Anionic surfactants are the most widely used of the synthetic detergents. ASTM methods in current use for their determination involve two-phase aqueous/chloroform titrations with the organic dyes methylene blue (Test Method D 1681) or disulphine blue/dimidium bromide (Test Method D 3049) as indicators. One advantage of the potentiometric method is that it eliminates the use of chloroform whose use is restricted for environmental and toxicological reasons.
This test method is intended for use as described in 1.1.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method describes a potentiometric titration procedure for determining the anionic active matter in detergents. It is intended for the analysis of anionic surfactants such as detergent range alkylbenzenesulfonates, α-olefin sulfonates, alcohol sulfates, and alcohol ethosulfates. It has not been tested for surfactant formulations.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Material Safety Data Sheets are available for reagents and materials. Review them for hazards prior to usage.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation:D4251–89(Reapproved 2003)
Standard Test Method for
Active Matter in Anionic Surfactants by Potentiometric
Titration
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4251; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
TABLE 1 Active Matter Content of Various Anionic Surfactants
1. Scope
by the Potentiometric Titration and Two-Phase Titration Methods
1.1 This test method describes a potentiometric titration
Active Matter Content, % weight
procedure for determining the anionic active matter in deter-
Potentiometric Titration Two-
Anionic Surfactant
gents.Itisintendedfortheanalysisofanionicsurfactantssuch
Orion Orion “Old” HNU Phase
− − −
NO (#1) NO (#2) NO Titration
3 3 3
as detergent range alkylbenzenesulfonates, a-olefin sulfonates,
A
Sulframin AOS (alpha- 41.03 41.49 40.91 39.21
alcoholsulfates,andalcoholethosulfates.Ithasnotbeentested
olefin sulfonate) 42.50 40.74 41.05 39.26
for surfactant formulations. 42.64 41.34 41.05
B
Sulframin 1298 (alkylaryl 94.15 96.26 94.91 95.12
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
sulfonate) 95.31 95.67 95.50 95.12
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
94.73 96.26 94.91
B
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- NEODOLT 25-3S (alcohol 58.12 57.94 57.75 58.19
ethoxysulfate sodium 58.81 57.74 57.95 58.24
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
salt) 58.12 57.94 57.95
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Material Safety
A
Methylene blue method.
Data Sheets are available for reagents and materials. Review
B
Mixed indicator method.
them for hazards prior to usage.
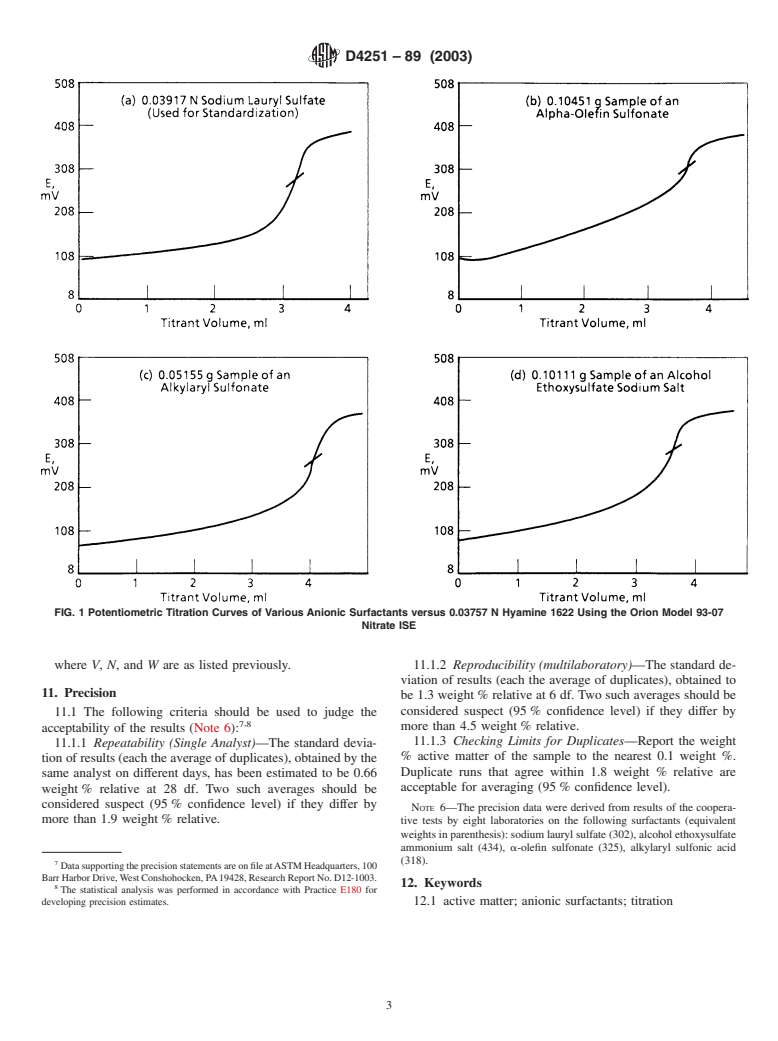
4. Summary of Test Method
2. Referenced Documents
4.1 A detergent sample containing active matter is titrated
2.1 ASTM Standards:
potentiometrically in an aqueous medium with a standard
D459 Terminology Relating to Soaps and Other Detergents
solution of Hyamine 1622 using a nitrate ion-selective elec-
trode. The titration reaction involves the formation of a
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
complex between the cationic quaternary ammonium titrant
D1681 TestMethodforSyntheticAnionicActiveIngredient
(Hyamine 1622) and the anionic surfactant which precipitates.
in Detergents by Cationic Titration Procedure
Thenitrateelectrodeprobablyrespondstotheconcentrationof
D3049 Test Method for Synthetic Anionic Ingredient by
unreacted anionic surfactant.
Cationic Titration
E180 Practice for Determining the Precision of ASTM
5. Significance and Use
Methods for Analysis and Testing of Industrial and Spe-
5.1 Anionic surfactants are the most widely used of the
cialty Chemicals
synthetic detergents. ASTM methods in current use for their
3. Terminology
determinationinvolvetwo-phaseaqueous/chloroformtitrations
with the organic dyes methylene blue (Test Method D1681)or
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
disulphine blue/dimidium bromide (Test Method D3049)as
3.1.1 active matter—the organic surface-active material
indicators. One advantage of the potentiometric method is that
present in the detergent and defined in Terminology D459 as
it eliminates the use of chloroform whose use is restricted for
active ingredient of a synthetic detergent.
environmental and toxicological reasons.
5.2 This test method is intended for use as described in 1.1.
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D12 on Soaps
and Other Detergents and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D12.12 on
6. Apparatus
Analysis of Soaps and Synthetic Detergents.
6.1 Potentiometric Titration Assembly, consisting of an
Current edition approved May 26, 1989. Published July 1989. Originally
published as D4251–83. Last previous edition D4251–88. DOI: 10.1520/D4251-
automatic titrator (Metrohm E536 or equivalent) fitted with a
89R03.
nitrateion-selectiveelectrode(OrionModel93-07NitrateISE,
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 15.04.
3 or equivalent) and a Ag/AgCl reference electrode (Metrohm
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 11.01.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 15.05. EA440 or equivalent) together with a buret assembly having a
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D4251–89 (2003)
5-mL buret (Metrohm E575) and 150-mL beaker. A TFE-
B = normality of sodium lauryl sulfate, and
fluorocarbon star-head stirring bar can be used to provide
C = Hyamine solution consumed during titration, mL.
mixing and eliminate foaming during titration. Use of the
9. Procedure
Orion electrode with a Metrohm E536 requires an adapter
(Metrohm EA-1046/2).
9.1 Add to a 150-mL beaker a known weight of detergent
sample together with enough water to make 50 mLof solution
NOTE 1—The conditioning of the electrode is essential for obtaining a
(Note 4). The solution should cover the sensing tips of the
good break in the titration curve. Conditioning new electrodes in 0.01 M
electrodes. Titrate initially by adding Hyamine solution at
NaNO aqueous solution for 60 min (or more) prior to use is recom-
mended. Condition previously used electrodes by using again for the approximately 0.5 mL/min while stirring constantly. As the
titration of aqueous sodium lauryl sulfate with Hyamine.
inflection point is approached, reduce the addition rate, and
NOTE 2—Other electrodes (for example a calomel electrode) are
continue titrating well past the inflection in the titration curve.
suitable as the reference electrode provided they give a stable reference
(Automatic titrators can be preset to automatically slow down
potential during the titration. Reference electrodes having a ceramic or an
the addition rate as the inflection point is approached.)
asbestos junction tend to clog with use. Therefore, a ground-glass sleeve
electrode (such as the Metrohm EA 440) is suggested.
NOTE 4—To determine the amount of sample needed for an
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.