ASTM D1760-96
(Specification)Standard Specification for Pressure Treatment of Timber Products
Standard Specification for Pressure Treatment of Timber Products
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers treatment of timber products by pressure processes in closed vessels with preservative materials and solutions.
1.2 This specification is divided into two general sections. Sections 1 - 9 cover requirements relating to all species and commodities, while Tables 1 - 7 show requirements relating to specific species and commodities. The purchaser should note that these individual requirements vary widely and, consequently, great care must be used in applying them in specific instances.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be considered as standard.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: D 1760 – 96 An American National Standard
Standard Specification for
Pressure Treatment of Timber Products
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 1760; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D 1628 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Chromated
Copper Arsenate
1.1 This specification covers treatment of timber products
D 1858 Specification for Creosote-Petroleum Solution
by pressure processes in closed vessels with preservative
D 1860 Test Method for Moisture and Creosote-Type Pre-
materials and solutions.
servative in Wood
1.2 This specification is divided into two general sections.
D 2085 Test Method for Determining Chloride Used in
Sections 1-9 cover requirements relating to all species and
Calculating Pentachlorophenol in Solutions or Wood
commodities, while Tables 1-7 show requirements relating to
(Lime Ignition Method)
specific species and commodities. The purchaser should note
D 2604 Specification for High-Boiling Hydrocarbon Sol-
that these individual requirements vary widely and, conse-
vent for Preparing Oil-Borne Preservative Solutions
quently, great care must be used in applying them in specific
D 2605 Specification for Volatile Petroleum Solvent (LPG)
instances.
for Preparing Pentachlorophenol Solutions
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be consid-
D 3225 Specification for Low-Boiling Hydrocarbon Sol-
ered as standard.
vent for Oil-Borne Preservatives
2. Referenced Documents
D 5653 Specification for Copper bis (Dimethyldithiocar-
bamate)
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 5655 Test Method for Analysis of Copper Dimeth-
D 347 Tables for Volume and Specific Gravity Correction
yldithiocarbamate (CDDC) Treated Wood by Colorimetry
for Creosote and Coal Tar
D 390 Specification for Coal-Tar Creosote for the Preserva-
3. Terminology
tive Treatment of Piles, Poles, and Timbers for Marine,
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
Land, and Fresh Water Use
3.1.1 preservative materials and solutions—materials that
D 391 Specification for Creosote-Coal Tar Solution
when injected into wood protect it from the destructive action
D 1034 Specification for Fluor-Chrome-Arsenate-Phenol
of fungi, insects, and marine borers.
D 1035 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Fluor-
3.1.2 timber products—include round, sawn, and otherwise
Chrome-Arsenate-Phenol
fabricated materials of various species. Examples are utility
D 1272 Specification for Pentachlorophenol
poles, piles, posts, crossties, lumber, timbers, glued laminated
D 1325 Specification for Ammoniacal Copper Arsenate and
2 timbers, plywood, and so forth.
Ammoniacal Copper Zinc Arsenate
D 1326 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Ammoniacal
ALL TIMBER PRODUCTS
Copper Arsenate and Ammoniacal Copper Zinc Arsenate
D 1624 Specification for Acid Copper Chromate
4. General Requirements
D 1625 Specification for Chromated Copper Arsenate
4.1 The following requirements, except as modified, or
D 1627 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Acid Copper
supplemented by Tables 1-7, for the various species and types
Chromate
of material, apply to each of the treating processes and to all
species and types of material. If these requirements are to be
1 otherwise modified to meet special conditions, complete de-
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-7 on Wood
tailed instructions shall be given by the purchaser or specifier.
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D07.06 on Treatments for Wood
Products.
4.1.1 Maximum time duration (total elapsed time of a
Current edition approved June 10, 1996. Published August 1996. Originally
treating phase), maximum temperature, and maximum pressure
published as D 1760 – 60. Last previous edition D 1760 – 95a.
limits shall not be exceeded. A phase shall begin when a
Some requirements in this specification are similar to those in the Commodities
Standards of the American Wood-Preservers’ Association for treatment of timber change in conditions within the cylinder is initiated and shall
products by pressure processes in closed vessels with preservative materials and
end when either new conditions are imposed, or the cylinder is
solutions. Acknowledgment is made to the American Wood-Preservers’ Association
emptied of preservative.
for its development of subject matter used in this specification.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.10.
Copyright © ASTM, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D 1760
TABLE 1 Treatment of Lumber, Timbers, Bridge Ties, and Mine Ties by Pressure Processes
A B
Hemfir, Pacific Coast Douglas Fir, Western Hemlock and
Southern Pine and Ponderosa Pine
C
Western Larch
Conditioning air seasoning, kiln drying, Boulton drying, heating in air seasoning, kiln drying, Boulton drying, steaming (water-
preservative or a combination borne treatments only), heating in preservative or a
combination
D
Steaming:
Temperature, max, °F (°C) 245 (120) 240 (117)
Duration, max, h 17 6
Vacuum, min, in. (mm) at sea 22 (558.8) 22 (558.8)
level
Heating in preservative:
Temperature, max, °F (°C) 220 (104) 210 (99)
Duration, max, h optional 6 if seasoned, optional if green
Incising not required required
Treatment:
Pressure, psig (kPa)
min 75 (517) 50 (345)
max 200 (1379) 150 (1034)
Expansion bath: temperature,
max, °F (°C) 220 (104) 220 (104)
Final steaming:
Temperature, max, °F (°C) 240 (117) (not permitted for service in coastal waters) 240 (117) (not permitted for service in coastal waters)
Duration, max, h 2 2
Above Above
Ground Contact Coastal Waters Ground Contact Coastal Waters
Ground Ground
Results of treatment:
3 3
Retention, min, lb/ft (kg/m ):
(sampling zone for assay 0 to
0.60 in. (0 to 15.2 mm) from
surface):
Creosote and creosote
solutions—by assay:
Creosote 6 (96) 8 (128) 20 (320) full cell 8 (128) 10 (160) 20 (320) full cell
Creosote-coal tar solution 6 (96) 8 (128) 20 (320) full cell 8 (128) 10 (160) 20 (320) full cell
Creosote-petroleum solution 6 (96) 8 (128) not recommended 8 (128) 10 (160) not recommended
Oil-borne preservatives—by assay
Pentachlorophenol using Specifi- 0.30 (4.81) 0.40 (6.4) not recommended 0.40 (6.4) 0.50 (8.0) not recommended
cations D 2604, D 2605, or
D 3225 solvents
Water-borne preservatives—by as-
say:
ACC 0.25 (4.0) 0.50 (8.0) not recommended 0.25 (4.0) 0.50 (8.0) not recommended
E
ACA and ACZA 0.25 (4.0) 0.40 (6.4) 2.50 (40.0) 0.25 (4.0) 0.40 (6.4) 2.50 (40.0)
CCA, Types A and C 0.25 (4.0) 0.40 (6.4) 2.50 (40.0) 0.25 (4.0) 0.40 (6.4) not recommended
0.45 (7.2) not recommended not recommended 0.45 (7.2) not recommended not recommended
H
CDDC (as copper metal) 0.10 (1.6) 0.20 (3.2) not recommended
FCAP 0.25 (4.0) not recommended not recommended 0.25 (4.0) not recommended not recommended
Penetration 2.5 in. (64 mm) unless 85 % of sapwood 0.40 in. (10.2 mm) and 90 % of sapwood less than 5 in. (127 mm) in
thickness, 0.50 in. (12.7 mm) and 90 % of sapwood thicker than 5
in. and for coastal waters service
F
Determination of penetration A borer core shall be taken from the incised faces of 20 pieces in
each charge. If 80 % of the borings meet the penetration
requirements the charge shall be accepted. Borings not meeting the
penetration requirements shall show evidence of preservative
penetration.
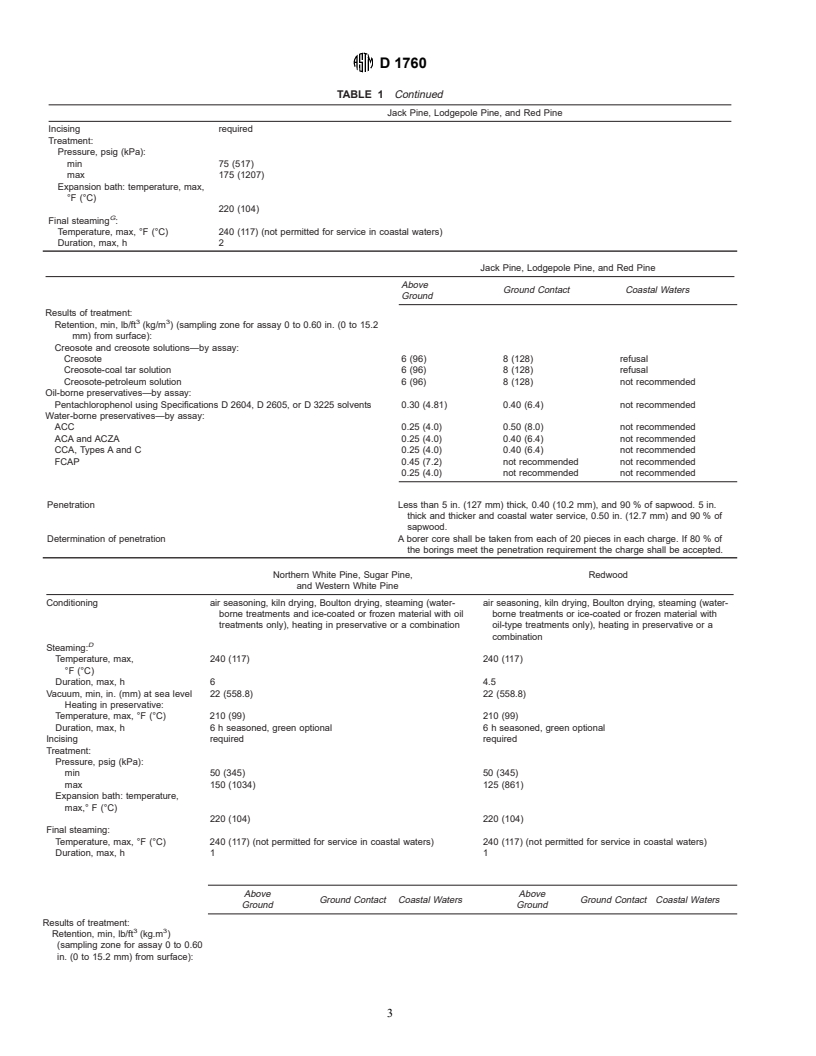
Jack Pine, Lodgepole Pine, and Red Pine
Conditioning air seasoning, kiln drying, Boulton drying, steaming (water-borne treatments or ice-coated or frozen materials with oil
treatments only), heating in the preservative or a combination
G
Steaming:
Temperature, max, °F (°C) 240 (117)
Duration, max, h 6
Vacuum, min, in. (mm) at sea level 22 (558.8)
Heating in preservative:
Temperature, max, °F (°C) 210 (99)
Duration, max, h 6 h seasoned, green optional
D 1760
TABLE 1 Continued
Jack Pine, Lodgepole Pine, and Red Pine
Incising required
Treatment:
Pressure, psig (kPa):
min 75 (517)
max 175 (1207)
Expansion bath: temperature, max,
°F (°C)
220 (104)
G
Final steaming :
Temperature, max, °F (°C) 240 (117) (not permitted for service in coastal waters)
Duration, max, h 2
Jack Pine, Lodgepole Pine, and Red Pine
Above
Ground Contact Coastal Waters
Ground
Results of treatment:
3 3
Retention, min, lb/ft (kg/m ) (sampling zone for assay 0 to 0.60 in. (0 to 15.2
mm) from surface):
Creosote and creosote solutions—by assay:
Creosote 6 (96) 8 (128) refusal
Creosote-coal tar solution 6 (96) 8 (128) refusal
Creosote-petroleum solution 6 (96) 8 (128) not recommended
Oil-borne preservatives—by assay:
Pentachlorophenol using Specifications D 2604, D 2605, or D 3225 solvents 0.30 (4.81) 0.40 (6.4) not recommended
Water-borne preservatives—by assay:
ACC 0.25 (4.0) 0.50 (8.0) not recommended
ACA and ACZA 0.25 (4.0) 0.40 (6.4) not recommended
CCA, Types A and C 0.25 (4.0) 0.40 (6.4) not recommended
FCAP 0.45 (7.2) not recommended not recommended
0.25 (4.0) not recommended not recommended
Penetration Less than 5 in. (127 mm) thick, 0.40 (10.2 mm), and 90 % of sapwood. 5 in.
thick and thicker and coastal water service, 0.50 in. (12.7 mm) and 90 % of
sapwood.
Determination of penetration A borer core shall be taken from each of 20 pieces in each charge. If 80 % of
the borings meet the penetration requirement the charge shall be accepted.
Northern White Pine, Sugar Pine, Redwood
and Western White Pine
Conditioning air seasoning, kiln drying, Boulton drying, steaming (water- air seasoning, kiln drying, Boulton drying, steaming (water-
borne treatments and ice-coated or frozen material with oil borne treatments or ice-coated or frozen material with
treatments only), heating in preservative or a combination oil-type treatments only), heating in preservative or a
combination
D
Steaming:
Temperature, max, 240 (117) 240 (117)
°F (°C)
Duration, max, h 6 4.5
Vacuum, min, in. (mm) at sea level 22 (558.8) 22 (558.8)
Heating in preservative:
Temperature, max, °F (°C) 210 (99) 210 (99)
Duration, max, h 6 h seasoned, green optional 6 h seasoned, green optional
Incising required required
Treatment:
Pressure, psig (kPa):
min 50 (345) 50 (345)
max 150 (1034) 125 (861)
Expansion bath: temperature,
max,° F (°C)
220 (104) 220 (104)
Final steaming:
Temperature, max, °F (°C) 240 (117) (not permitted for service in coastal waters) 240 (117) (not permitted for service in coastal waters)
Duration, max, h 1 1
Above Above
Ground Contact Coastal Waters Ground Contact Coastal Waters
Ground Ground
Results of treatment:
3 3
Retention, min, lb/ft (kg.m )
(sampling zone for assay 0 to 0.60
in. (0 to 15.2 mm) from surface):
D 1760
TABLE 1 Continued
Above Above
Ground Contact Coastal Waters Ground Contact Coastal Waters
Ground Ground
Creosote and creosote solutions—by
assay:
Creosote 6 (96) 8 (128) refusal 8 (128) 10 (160) 20 (320) full cell
Creosote-coal tar solution 6 (96) 8 (128) refusal 8 (128) 10 (160) 20 (320) full cell
Creosote-petroleum solution 6 (96) 8 (128) not recommended 8 (128) 10 (160) not recommended
Northern White Pine, Sugar Pine, and Western White Pine Redwod
Above Above
Ground Contact Coastal Waters Ground Contact Coastal Waters
Ground Ground
Oil-borne preservatives—by assay:
Pentachlorophenol using Specifi- 0.30 (4.81) 0.40 (6.4) not recommended 0.60 (9.6) 0.50 (8.0) not recommended
cations D 2604, D 2605, or
D 3225 solvents
Water-borne preservatives—by as-
say:
ACC 0.25 (4.0) 0.50 (8.0) not recommended 0.25 (4.0) 0.50 (8.0) not recommended
ACA and ACZA 0.25 (4.0) 0.40 (6.4) not recommended 0.25 (4.0) 0.40 (6.4) not recommended
CCA, Types A and C 0.25 (4.0) 0.40 (6.4) not recommended 0.25 (4.0) 0.40 (6.4) not recommended
FCAP 0.45 (7.2) not recommended not recommended 0.45 (7.2) not recommended not recommended
0.25 (4.0) not recommended not recommended 0.25 (4.0) not recommended not recommended
Penetration Less than 5 in. (127 mm) thick, 0.40 (6.4 mm) and Less than 5 in. (127 mm) thick, 0.40 (6.4 mm), and 90 % sapwood.
90 % of sapwood. 5 in. and thicker and for service in 5 in. and thicker and coastal waters service, 0.50 (8.0 mm) and
coastal waters, 0.50 in. (8.0 mm) and 90 % of 90 % of sapwood
sapwood
F
Determination of penetration A borer core shall be taken from each of 20 pieces in each charge.
If 80 % of the borings meet the penetration requirement, the
charge shall be accepted. Borings not meeting the penetration
requirements shall show evidence of preservative penetration.
Black Gum and Red Gum Oak
Conditioning air seasoning, kiln drying, Boulton drying, steaming, air seasoning, kiln drying, Boulton drying, heating
heating in preservative or a combination in preservative or a combination
D
Steaming:
Temperature, max, °F (°C) 240 (117) not permitted
Duration, max, h 6
Vacuum, min, in. (mm) at sea level 22 (558.8)
Heating in preservative:
Temperature, max, °F (°C) 220 (104) 220 (104)
Duration, max, h optional optional
Incising
Treatment:
Pressure, psig (kPa):
min 125 (861) 125 (861)
max 200 (1379) 250 (1724)
Expansion bath: temperature,
max, °F (°C) 220 (104) 220 (104)
Final steaming:
Temperature, max, °F (°C) 240 (117) (not permitted for service in coastal waters) 240 (117) (not permitted for service in coastal
waters)
Duration, max, h 1 1
Above Above
Ground Contact Coastal Waters Ground Contact Coastal Waters
Ground Ground
Results of treatment:
3 3 E
Retention, min, lb/ft (kg/m ) (by gage):
Creosote and creosote solutions:
Creosote 6 (96) 8 (128) refusal 6 (96) 7 (112) refusal min 10
(160)
Creosote-coal tar solution 6 (96) 8 (128) 12 (192) minimum 6 (96) 7 (112) refusal min 10
(160)
Creosote-petroleum solution 6 (96) 8 (128) not recommended 6 (96) 7 (112) not recommended
Oil-borne preservatives:
Pentachlorophenol using Specifi- 0.30 (4.81) 0.40 (6.4) not recommended 0.30 (4.81) 0.40 (6.4) not recommended
cations D 2604, D 2605, or
D 3225 solvents
Water-borne preservatives:
D 1760
TABLE 1 Continued
ACC 0.25 (4.0) 0.50 (8.0) not recommended 0.25 (4.0) 0.50 (8.0) not recommended
ACA and ACZA 0.25 (4.0) 0.40 (6.4) not recommended 0.25 (4.0) 0.40 (6.4) not recommended
CCA, Types A and C 0.25 (4.0) 0.40 (6.4) not recommended 0.25 (4.0) 0.40 (6.4) not recommended
FCAP 0.45 (7.2) not recommended not recommended 0.45 (7.2) not recommended not recommended
0.25 (4.0) not recommended not recommended 0.25 (4.0) not recommended not recommended
Penetration 1.5 in. (38 mm) unless 85 % of sapwood White oaks, 90 % of sapwood. Red oaks, 65 % of annual rings to
center of cross section. Charges of recalcitr
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.