ASTM D7818-12(2016)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Enumeration of Proteolytic Bacteria in Fresh (Uncured) Hides and Skins
Standard Test Method for Enumeration of Proteolytic Bacteria in Fresh (Uncured) Hides and Skins
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This test method enumerates proteolytic bacteria. Proteolytic bacteria have been known to cause damage to hides and skins.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the enumeration of bacteria that can hydrolyze protein/collagen in fresh (uncured) hides and skins. This test method is applicable to uncured hides and skins.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D7818 − 12 (Reapproved 2016)
Standard Test Method for
Enumeration of Proteolytic Bacteria in Fresh (Uncured)
1
Hides and Skins
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7818; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 4. Significance and Use
4.1 This test method enumerates proteolytic bacteria. Pro-
1.1 Thistestmethodcoverstheenumerationofbacteriathat
can hydrolyze protein/collagen in fresh (uncured) hides and teolytic bacteria have been known to cause damage to hides
and skins.
skins. This test method is applicable to uncured hides and
skins.
5. Apparatus
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this 5.1 Incubator, 35 6 1°C.
standard.
5.2 Colony counter—(not mandatory, but highly recom-
mended).
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
5.3 Sterile pipets.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
5.4 Bent glass rods, sterile.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
5.5 Stomacher, for mixing initial dilution. (If stomacher is
unavailable, hand-mix.)
2. Referenced Documents
5.6 Balance.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5.7 Sterile petri dishes.
D6715Practice for Sampling and Preparation of Fresh or
5.8 Autoclave (sterilizer). (Check the effectiveness of ster-
Salt-Preserved (Cured) Hides and Skins for Chemical and
ilizationweekly.Forexample,placesporesuspensionsorstrips
Physical Tests
of Bacillus stearothermophilus(commerciallyavailable)inside
E691Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
glassware for a full autoclave cycle. Follow manufacturer’s
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
directions for sterilization of specific media.)
E177Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
ASTM Test Methods
5.9 Stomacher bags, or sterile, sealable quart plastic bag
(e.g. food storage type, sterile bag).
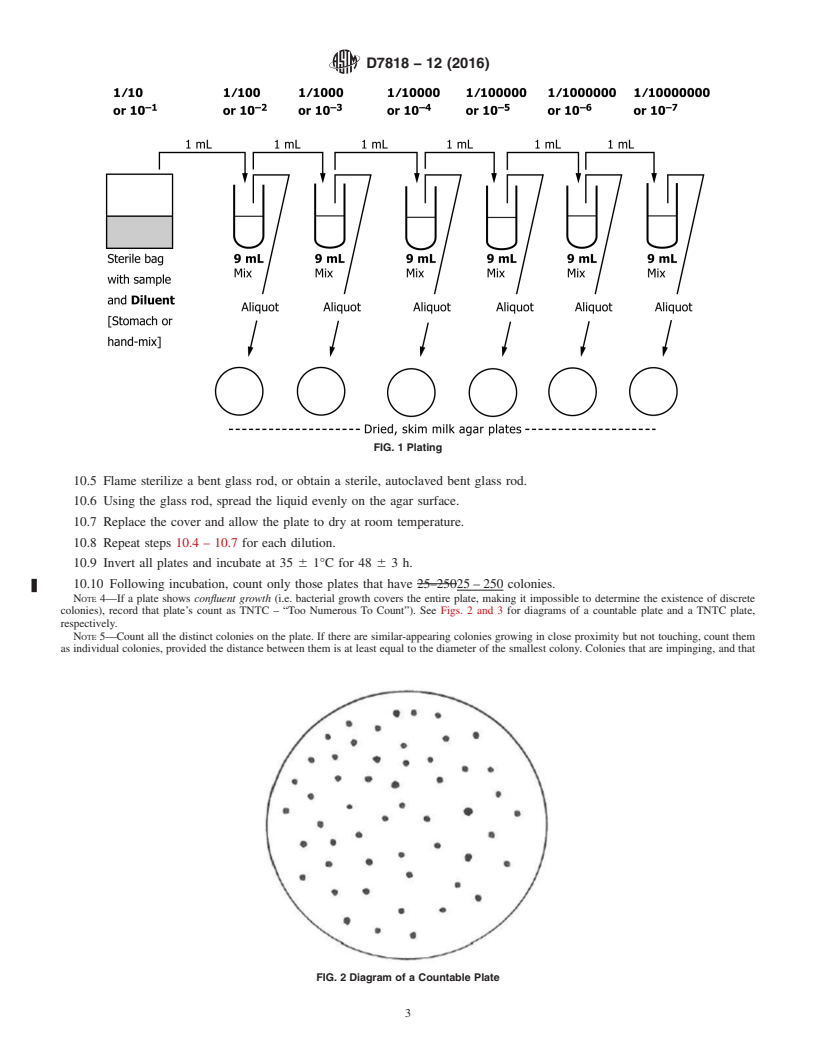
3. Summary of Test Method
5.10 Cutting tool, sterile (e.g. scalpel blade and forcep, as
3.1 Samples of uncured hides and skins are serially diluted
needed for cutting fresh hides and skins).
and plated on agar containing casein from skim milk. The
5.11 Vortex mixer, for mixing dilution tubes (optional).
plates are incubated under aerobic conditions at 35°C for 48 h.
5.12 pH meter.
After incubation, to determine bacteria that can hydrolyze
protein(proteolytic),theplatesarefloodedwithdiluteacidand
5.13 Waterbath, 45 6 1°C.
the colonies showing a halo are counted.
5.14 Autoclave thermometer.
6. Reagents and Materials
1
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeD31onLeather
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D31.02 on Wet Blue.
6.1 5 % acetic acid.
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2016. Published October 2016. Originally
approved in 2012. Last previous edition approved in 2012 as D7818–12. DOI: 6.2 Butterfield’s Phosphate Stock Solution: Dissolve 34 g
10.1520/D7818-12R16.
KH PO (Potassium Phosphate monobasic) in 500 mL DI
2 4
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
water.Adjust the pH to 7.2 6 0.1 with 1N – 6N NaOH. Bring
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
volume to 1 L with DI water. Sterilize for 15 min at 121°C.
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. NOTE 1—Typical autoclave setting is 120–124°C. (See 5.8.)
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7818 − 12 (2016)
6.3 Butterfield’s Phosphate Diluent (BPD):Take1.25mLof 9.3 Prepare a 10 % powdered skim milk mixture by adding
Butterfield’s Phosphate Stock solution (6.2) and bring to 1 L 10gpowderedskimmilkto100mLDIwater,thenstirringthe
with DI water. Dispense into 1-L bottles and 9-mL dilution mixture to dissolve it. Autoclave the mixture for 15 min at
tubes. Sterilize for 15 min at 121°C. (See Note 1.) 121°C. (See Note 1.)
6.4 Standard plate count agar containing 100 mL of 10 %
9.4 Cooltheagar(9.2)to45 61°C,thenadd100mLofthe
powdered skim milk solution per litre of agar. sterile10%powderedskimmilkmixture(9.3)perlitreofagar.
NOTE 2—Do not allow agar to solidify prior to pouring (9.5).
6.5 Alcohol (for flame sterilizing), e.g. 70 % Isopropyl
9.5 Pour the sterile agar into petri dishes. Replace the cover
alcohol.
and swirl to evenly distribute the agar. Allow to solidify at
6.6 Bent glass rod (“hockey-stick”)
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D7818 − 12 D7818 − 12 (Reapproved 2016)
Standard Test Method for
Enumeration of Proteolytic Bacteria in Fresh (Uncured)
1
Hides and Skins
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7818; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the enumeration of bacteria that can hydrolyze protein/collagen in fresh (uncured) hides and skins.
This test method is applicable to uncured hides and skins.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D6715 Practice for Sampling and Preparation of Fresh or Salt-Preserved (Cured) Hides and Skins for Chemical and Physical
Tests
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in ASTM Test Methods
3. Summary of Test Method
3.1 Samples of uncured hides and skins are serially diluted and plated on agar containing casein from skim milk. The plates are
incubated under aerobic conditions at 35°C for 48 h. After incubation, to determine bacteria that can hydrolyze protein
(proteolytic), the plates are flooded with dilute acid and the colonies showing a halo are counted.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 This test method enumerates proteolytic bacteria. Proteolytic bacteria have been known to cause damage to hides and skins.
5. Apparatus
5.1 Incubator, 35 6 1°C.
5.2 Colony counter—(not mandatory, but highly recommended).
5.3 Sterile pipets.
5.4 Bent glass rods, sterile.
5.5 Stomacher, for mixing initial dilution. (If stomacher is unavailable, hand-mix.)
5.6 Balance.
5.7 Sterile petri dishes.
5.8 Autoclave (sterilizer). (Check the effectiveness of sterilization weekly. For example, place spore suspensions or strips of
Bacillus stearothermophilus (commercially available) inside glassware for a full autoclave cycle. Follow manufacturer’s directions
for sterilization of specific media.)
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D31 on Leather and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D31.02 on Wet Blue.
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2012Sept. 1, 2016. Published October 2012October 2016. Originally approved in 2012. Last previous edition approved in 2012 as
D7818 – 12. DOI: 10.1520/D7818-1210.1520/D7818-12R16.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7818 − 12 (2016)
5.9 Stomacher bags, or sterile, sealable quart plastic bag (e.g. food storage type, sterile bag).
5.10 Cutting tool, sterile (e.g. scalpel blade and forcep, as needed for cutting fresh hides and skins).
5.11 Vortex mixer, for mixing dilution tubes (optional).
5.12 pH meter.
5.13 Waterbath, 45 6 1°C.
5.14 Autoclave thermometer.
6. Reagents and Materials
6.1 5 % acetic acid.
6.2 Butterfield’s Phosphate Stock Solution: Dissolve 34 g KH PO (Potassium Phosphate monobasic) in 500 mL DI water.
2 4
Adjust the pH to 7.2 6 0.1 with 1N – 6N NaOH. Bring volume to 1 L with DI water. Sterilize for 15 min at 121°C.
NOTE 1—Typical autoclave setting is 120–124°C.120 – 124°C. (See 5.8.)
6.3 Butterfield’s Phosphate Diluent (BPD): Take 1.25 mL of Butterfield’s Phosphate Stock solution (6.2) and bring to 1 L with
DI water. Dispense into 1 L 1-L bottles and 9 mL 9-mL dilution tubes. Sterilize for 15 min at 121°C. (See Note 1.)
6.4 Standard plate count agar containing 100 mL of 10 % powdered skim milk solution per litre of agar.
6.5 Alcohol (for flame sterilizing), e.g. 70 % Isopropyl alcohol.
6.6 Bent glass rod (“hockey-stick”).
6.7 Powdered skim milk.
6.8 Distilled or deionized water.
6.9 Bacillus stearot
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.