ASTM D1603-11
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Carbon Black Content in Olefin Plastics
Standard Test Method for Carbon Black Content in Olefin Plastics
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The information provided by this test method is useful for manufacturing quality control, technical service, and research purposes; and is required by various material specifications and for the calculation of optical absorptivity.
Test Method D4218 is available for determining the carbon black content of polyethylene compounds if so desired.
SCOPE
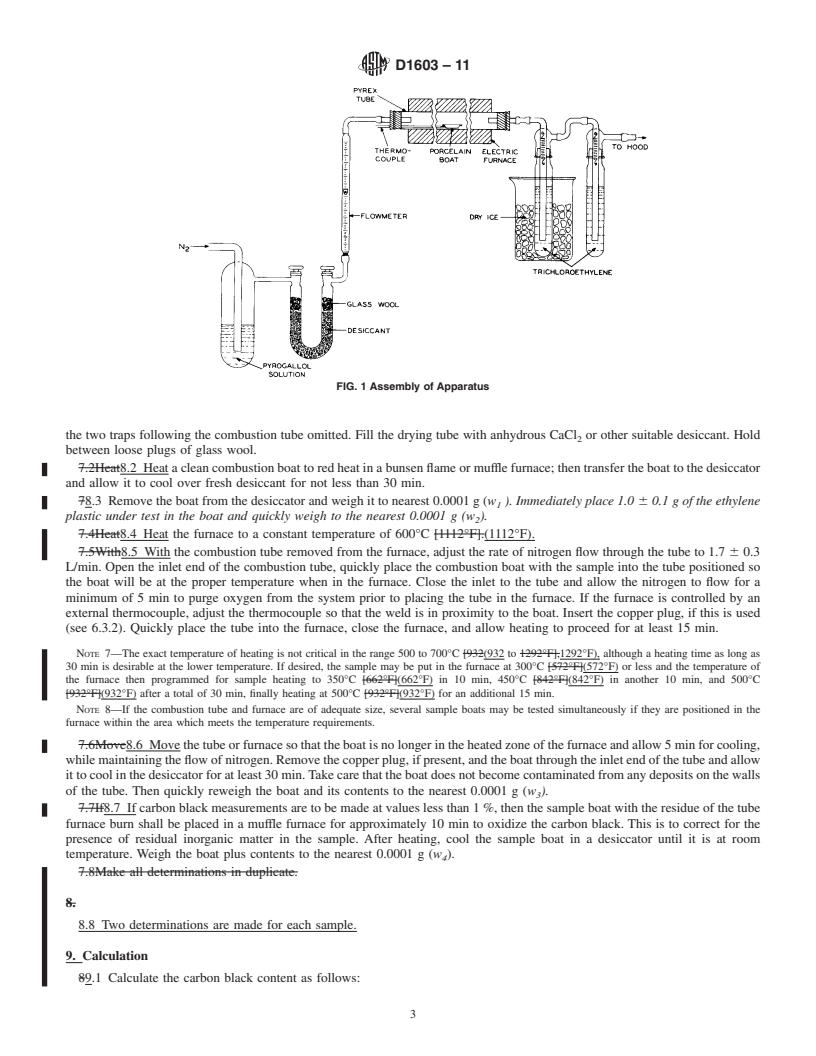
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the carbon black content in polyethylene, polypropylene, and polybutylene plastics. Its use with acrylic or other polar monomer modifications which might affect the accuracy is not recommended. Determinations of carbon black content are made gravimetrically after pyrolysis of the sample under nitrogen. This test method is not applicable to compositions that contain nonvolatile pigments or fillers other than carbon black.
1.1.1 This test method is not applicable to materials containing brominated flame retardant additives at the end.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values in parentheses are given for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Note 1—This standard and ISO 6964-1986(E) address the same subject matter, but differ in technical content.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Please contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: D1603 – 11
Standard Test Method for
1
Carbon Black Content in Olefin Plastics
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1603; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope* ISO 6964-1986(E) Polyolefin Pipes and Fittings—
Determination of Carbon Black by Calcination and
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the carbon
3
Pyrolysis—Test Method and Basic Specification
black content in polyethylene, polypropylene, and polybuty-
lene plastics. Its use with acrylic or other polar monomer
3. Terminology
modifications which might affect the accuracy is not recom-
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of technical terms pertain-
mended. Determinations of carbon black content are made
ing to plastics used in this specification, see Terminology
gravimetrically after pyrolysis of the sample under nitrogen.
D883.
This test method is not applicable to compositions that contain
nonvolatile pigments or fillers other than carbon black.
4. Significance and Use
1.1.1 This test method is not applicable to materials con-
4.1 The information provided by this test method is useful
taining brominated flame retardant additives at the end.
for manufacturing quality control, technical service, and re-
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
search purposes; and is required by various material specifica-
standard. The values in parentheses are given for information
tions and for the calculation of optical absorptivity.
only.
4.2 Test Method D4218 is available for determining the
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
carbon black content of polyethylene compounds if so desired.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
5. Apparatus
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
5.1 Electric Furnace, at least 20 cm (7.9 in.) long suitable
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
for use with the tubing described in 5.2.
4
NOTE 1—This standard and ISO 6964-1986(E) address the same sub-
5.2 High Temperature Glass Combustion Tube, of appro-
ject matter, but differ in technical content.
priate diameter and approximately twice as long as the furnace
described in 5.1.
2. Referenced Documents
5.3 Stoppers—Two rubber or neoprene stoppers, to fit the
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
tube described in 5.2, unless the tube is fitted with ground
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
joints and mating connectors.
D4218 Test Method for Determination of Carbon Black
5.4 Glass Tubing, approximately 10 mm (0.39 in.) in
Content in Polyethylene Compounds By the Muffle-
diameter, of sufficient amount, and matching rubber or plastic
Furnace Technique
tubing for connections.
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
5.5 Combustion Boat, approximately 8 by 1.9 by 1.3 cm
ASTM Test Methods
(3.15 by 0.75 by 0.51 in.). Glazed porcelain, quartz high-silica
2.2 ISO Standard:
glass, or platinum is suitable.
NOTE 2—A loose-fitting cover for the combustion boat is optional. If
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D20 on Plastics
used, it shall be considered a part of the boat and handled and weighed
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.70 on Analytical Methods
with it.
(Section D20.70.01).
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2011. Published September 2011. Originally
approved in 1958. Last previous edition approved in 2006 as D1603 - 06. DOI:
3
10.1520/D1603-11. ISO/IEC Selected Standards for Testing Plastics, Second Edition, published by
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or ASTM. Also available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM 43rd St., 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036.
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Borosilicate, high-silica, or equivalent glass tubing has been found satisfactory
the ASTM website. for this purpose.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Please contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D1603 – 11
FIG. 1 Assembly of Apparatus
5.6 Iron-Constantan Thermoc
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D1603–06 Designation: D1603 – 11
Standard Test Method for
1
Carbon Black Content in Olefin Plastics
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1603; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1This1.1 This test method covers the determination of the carbon black content in polyethylene, polypropylene, and
polybutylene plastics. Its use with acrylic or other polar monomer modifications which might affect the accuracy is not
recommended. Determinations of carbon black content are made gravimetrically after pyrolysis of the sample under nitrogen.This
test method is not applicable to compositions that contain nonvolatile pigments or fillers other than carbon black.
1.1.1 This test method is not applicable to materials containing brominated flame retardant additives at the end.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values in bracketsparentheses are given for information
only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
NOTE1—This test method is similar to ISO 6964-1986(E) in title only. The technical content is significantly different. 1—This standard and ISO
6964-1986(E) address the same subject matter, but differ in technical content.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
D4218 Test Method for Determination of Carbon Black Content in Polyethylene Compounds By the Muffle-FurnaceTechnique
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in ASTM Test Methods
2.2 ISO Standard:
ISO 6964-1986(E) Polyolefin Pipes and Fittings—Determination of Carbon Black by Calcination and Pyrolysis—Test Method
3
and Basic Specification
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of technical terms pertaining to plastics used in this specification, see Terminology D883.
4. Significance and Use
4.1The information provided by this test method is useful for control purposes and is required by various material specifications
and for the calculation of optical absorptivity. Significance and Use
4.1 The information provided by this test method is useful for manufacturing quality control, technical service, and research
purposes; and is required by various material specifications and for the calculation of optical absorptivity.
4.2 Test Method D4218 is available for determining the carbon black content of polyethylene compounds if so desired.
5. Apparatus
5.1 Electric Furnace, at least 20 cm [7.9 in.](7.9 in.) long suitable for use with the tubing described in 5.2.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D20 on Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.70 onAnalytical Methods (Section
D20.70.01).
Current edition approved March 15, 2006. Published March 2006. Originally approved in 1958. Last previous edition approved in 2001 as D1603-01. DOI:
10.1520/D1603-06.
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2011. Published September 2011. Originally approved in 1958. Last previous edition approved in 2006 as D1603 - 06. DOI:
10.1520/D1603-11.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
ISO/IEC Selected Standards for Testing Plastics, Second Edition, published by ASTM. Also available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd
St., 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D1603 – 11
4
5.2 High Temperature Glass Combustion Tube, of appropriate diameter and approximately twice as long as the furnace
described in 5.1.
5.3 Stoppers—Two rubber or neoprene stoppers, to fit the tube described in 5.2, unless the tube is fitted with ground joints and
mating connectors.
5.4
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.