ASTM D6507-19
(Practice)Standard Practice for Fiber Reinforcement Orientation Codes for Composite Materials
Standard Practice for Fiber Reinforcement Orientation Codes for Composite Materials
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
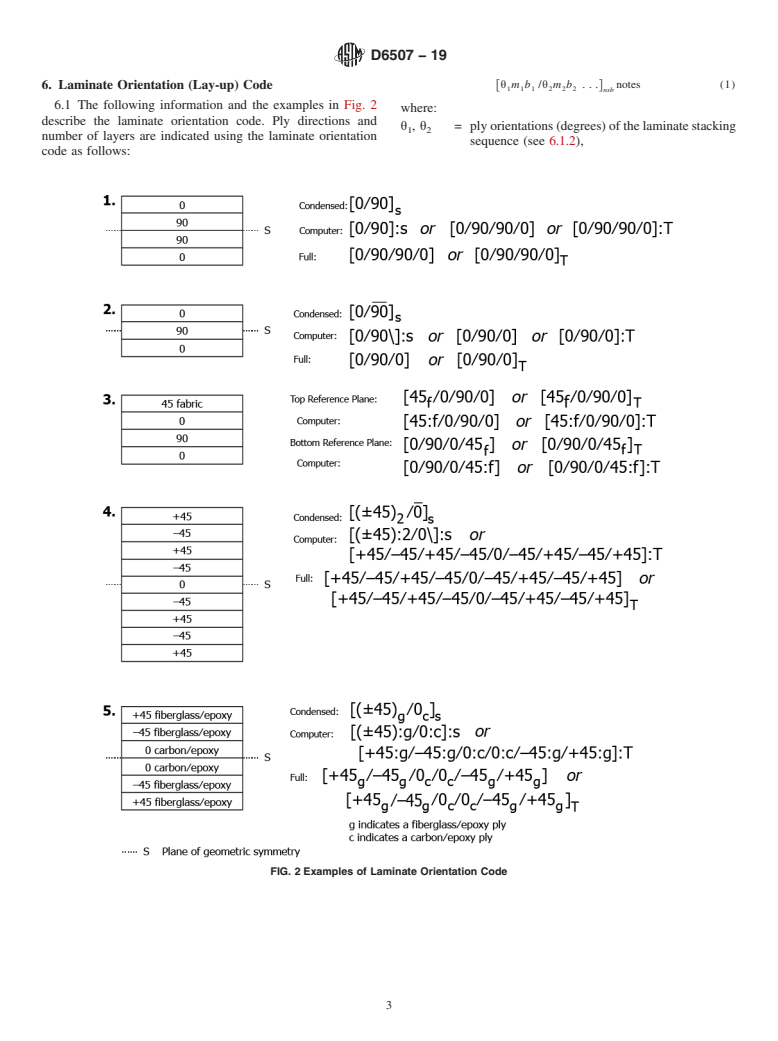
4.1 The purpose of a laminate orientation code is to provide a simple, easily understood method of describing the lay-up of a laminate. The laminate orientation code is based largely on a combination of industry practice and the codes used in the NASA/DOD Advanced Composites Design Guide,5 CMH-17-2G, and ISO 1268-1.
4.2 The braiding orientation code provides similar information for a two-dimensional braid, based largely on Standard Test Methods for Textile Composites.6
SCOPE
1.1 This practice establishes orientation codes for continuous-fiber-reinforced composite materials. Orientation codes are explicitly provided for two-dimensional laminates and braids. The laminate code may also be used for filament-wound materials. A method is included for presenting subscript information in computerized formats that do not permit subscript notation.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.3 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D6507 − 19
Standard Practice for
Fiber Reinforcement Orientation Codes for Composite
1
Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6507; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
4
1. Scope Stacking Designation Systems
1.1 This practice establishes orientation codes for
3. Terminology
continuous-fiber-reinforced composite materials. Orientation
codes are explicitly provided for two-dimensional laminates 3.1 Definitions—Definitions in accordance with Terminol-
ogy D3878 shall be used where applicable.
and braids. The laminate code may also be used for filament-
wound materials.Amethod is included for presenting subscript
4. Significance and Use
information in computerized formats that do not permit sub-
script notation.
4.1 The purpose of a laminate orientation code is to provide
a simple, easily understood method of describing the lay-up of
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the a laminate. The laminate orientation code is based largely on a
combination of industry practice and the codes used in the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
5
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter- NASA/DOD Advanced Composites Design Guide, CMH-17-
2G, and ISO 1268-1.
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.3 This international standard was developed in accor-
4.2 The braiding orientation code provides similar informa-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
tion for a two-dimensional braid, based largely on Standard
6
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Test Methods for Textile Composites.
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
5. Reference Systems
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
5.1 A set of reference coordinate axes and associated
reference plane and direction are selected before writing the
2. Referenced Documents
orientation code.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5.1.1 The reference plane is selected as the bottom or top
D3518/D3518M Test Method for In-Plane Shear Response
layer for the laminate orientation code. The orientation code is
of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials byTensileTest of
thendeterminedbyprogressingthroughthelaminatethickness.
a 645° Laminate
For a laminate symmetric about its midplane, the orientation
D3878 Terminology for Composite Materials
code using the top layer as the reference plane is identical to
2.2 Other Documents:
the orientation code using the bottom layer as the reference
CMH-17-2G, Polymer Matrix Composites, Volume 2 Ma-
plane.
3
terials Properties, Section 1.6.1
5.1.2 The reference direction, from which ply orientation is
ISO 1268-1 Fibre-reinforced Plastics—Methods of Produc-
measured,issomewhatarbitrarilyselectedforconvenienceand
ing Test Plates—Part 1: General Conditions, Annex
relevance to the application. Often, a dominant fiber direction,
such as that aligned with the laminate principal axis, is defined
1
to be 0°. An example in which relevance to testing determines
This practice is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D30 on Composite
Materials and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D30.01 on Editorial and
the reference direction is the Test Method D3518/D3518M
Resource Standards.
Current edition approved Oct. 15, 2019. Published November 2019. Originally
approved in 2000. Last previous edition approved in 2016 as D6507 – 16. DOI:
4
10.1520/D6507-19. Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
5
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM NASA/DOD Advanced Composites Design Guide, Vol. 4, Section 4.0.5, Air
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Force Wright Aeronautical Laboratories, Day, OH, prepared by Rockwell Interna-
the ASTM website. tional Corp., 1983 (distribution limited).
3 6
Available from SAE International (SAE), 400 Commonwealth Dr., Warrendale, Masters, J. E., and Portanova, M. A., Standard Test Methods for Textile
PA 15096, http://www.sae.org. Composites, NASA CR-4751, NASA Langley Research Center, 1996.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, W
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D6507 − 16 D6507 − 19
Standard Practice for
Fiber Reinforcement Orientation Codes for Composite
1
Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6507; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This practice establishes orientation codes for continuous-fiber-reinforced composite materials. Orientation codes are
explicitly provided for two-dimensional laminates and braids. The laminate code may also be used for filament-wound materials.
A method is included for presenting subscript information in computerized formats that do not permit subscript notation.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.3 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D3518/D3518M Test Method for In-Plane Shear Response of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials by Tensile Test of a 645°
Laminate
D3878 Terminology for Composite Materials
2.2 Other Documents:
3
CMH-17-2G, Polymer Matrix Composites, Volume 2 Materials Properties, Section 1.6.1
ISO 1268-1 Fibre-reinforced Plastics—Methods of Producing Test Plates—Part 1: General Conditions, Annex Stacking
4
Designation Systems
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—Definitions in accordance with Terminology D3878 shall be used where applicable.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 The purpose of a laminate orientation code is to provide a simple, easily understood method of describing the lay-up of a
laminate. The laminate orientation code is based largely on a combination of industry practice and the codes used in the
5
NASA/DOD Advanced Composites Design Guide, CMH-17-2G, and ISO 1268-1.
4.2 The braiding orientation code provides similar information for a two-dimensional braid, based largely on Standard Test
6
Methods for Textile Composites.
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D30 on Composite Materials and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D30.01 on Editorial and
Resource Standards.
Current edition approved July 1, 2016Oct. 15, 2019. Published July 2016November 2019. Originally approved in 2000. Last previous edition approved in 20112016 as
D6507 – 11.D6507 – 16. DOI: 10.1520/D6507-16.10.1520/D6507-19.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from SAE International (SAE), 400 Commonwealth Dr., Warrendale, PA 15096, http://www.sae.org.
4
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St., 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
5
NASA/DOD Advanced Composites Design Guide, Vol. 4, Section 4.0.5, Air Force Wright Aeronautical Laboratories, Day, OH, prepared by Rockwell International Corp.,
1983 (distribution limited).
6
Masters, J. E., and Portanova, M. A., Standard Test Methods for Textile Composites, Standard Test Methods for Textile Composites, NASA CR-4751, NASA Langley
Research Center, 19961996.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6507 − 19
5. Reference SystemSystems
5.1 A reference set of reference coordinate axes and associated reference plane and direction are selected before writing the
orientation code. The reference plane is selected as the bottom or top layer for the laminate orientation code. For laminates
symmetric about their midplane, the orientation code using the top layer as the reference plane is identical to the orientation code
using the bottom layer as the reference plane; selection of the reference plane effectively determines the positive z- or three-axis
of the lamin
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.