ASTM D2596-97
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Measurement of Extreme-Pressure Properties of Lubricating Grease (Four-Ball Method)
Standard Test Method for Measurement of Extreme-Pressure Properties of Lubricating Grease (Four-Ball Method)
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the load-carrying properties of lubricating greases. Two determinations are made:
1.1.1 Load-Wear Index (formerly called Mean-Hertz Load), and
1.1.2 Weld Point, by means of the Four-Ball Extreme-Pressure (EP) Tester.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific precautionary statements are given in 7.1 and 7.2.
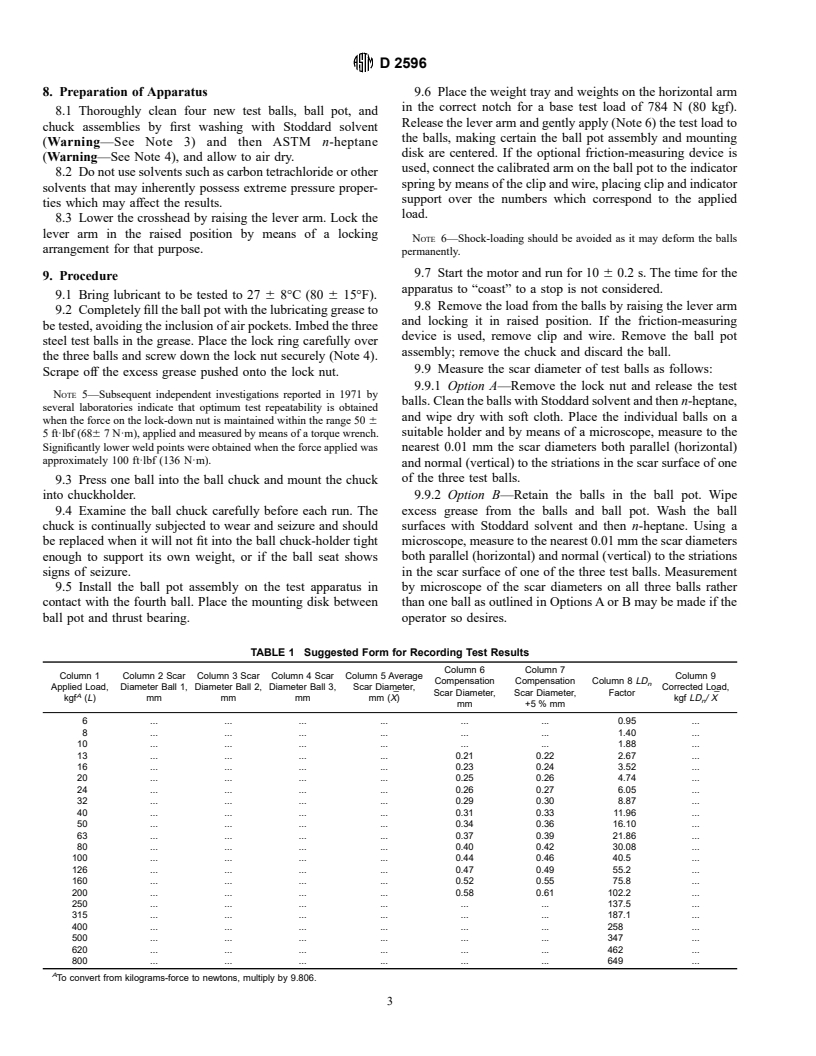
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or
withdrawn. Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: D 2596 – 97 An American National Standard
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS
100 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 19428
Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright ASTM
Standard Test Method for
Measurement of Extreme-Pressure Properties of Lubricating
1
Grease (Four-Ball Method)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 2596; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the load-
carrying properties of lubricating greases. Two determinations
are made:
1.1.1 Load-Wear Index (formerly called Mean-Hertz Load),
and
1.1.2 Weld Point, by means of the Four-Ball Extreme-
Pressure (EP) Tester.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific precau-
tionary statements are given in Note 3 and Note 4.
2. Referenced Documents
FIG. 1 Schematic Plot of Scar Diameter Versus Applied Load
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 235 Specification for Mineral Spirits (Petroleum Spirits)
3.1.3 corrected load, n—the load in kilograms-force (or
2
(Hydrocarbon Dry Cleaning Solvent)
Newtons) obtained by multiplying the applied load by the ratio
2.2 American National Standard:
of the Hertz scar diameter to the measured scar diameter at that
3
B3.12 Metal Balls
load.
3.1.3.1 Discussion—In this test method, the corrected load
3. Terminology
is calculated for each run.
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.4 hertz line, n—a line of plot on log-log paper where the
3.1.1 compensation line, n—a line of plot on log-log paper
coordinates are scar diameter in millimetres and applied load in
where the coordinates are scar diameter in millimetres and
kilograms-force (or Newtons) obtained under static conditions.
applied load in kilograms-force (or Newtons) obtained under
3.1.4.1 Discussion—Shown in Fig. 1 as a hertz line.
dynamic conditions.
3.1.5 hertz scar diameter, n—the average diameter, in
3.1.1.1 Discussion—Shown in Fig. 1 as line ABE.
millimetres, of an indentation caused by the deformation of the
3.1.2 compensation scar diameter—the average diameter, in
balls under static load (prior to test). It may be calculated from
millimetres, of the wear scar on the stationary balls caused by
the equation:
the rotating ball under an applied load in the presence of a
–2 1/3
D 5 8.73 3 10 ~P! (1)
lubricant, but without causing either seizure or welding. h
where:
D is the Hertz diameter of the contact area in millimetres and
h
1
This method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-2 on Petroleum
P is the static applied load in kilograms-force.
Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D02.G on
3.1.6 immediate seizure region, n—that region of the scar-
Lubricating Grease.
Current edition approved June 10, 1997. Published October 1997. Originally
load curve characterized by seizure or welding at the startup or
published as D 2596 – 67 T. Last previous edition D 2596 – 96.
by large wear scars.
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 06.04.
3
3.1.6.1 Discussion—Under conditions of this test method,
Available from American National Standards Institute, 11 W. 42nd St., 13th
Floor, New York, NY 10036. the immediate seizure region is shown by line CD. Also, initial
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D 2596
deflection of indicating pen on the optional friction-measuring 6. Apparatus
5
device is larger than with nonseizure loads.
6.1 Four-Ball Extreme-Pressure Lubricant Tester, illus-
3.1.7 incipient seizure or initial seizure region, n—that trated in Fig. 2.
region at which, with an applied load, there is a momentary
NOTE 1—It is important to distinguish between the Four-Ball EP Tester
breakdown of the lubricating film.
and the Four-Ball Wear Tester. The Four-Ball Wear Tester can be used
3.1.7.1 Discussion—This breakdown is noted by a sudden under a variety of test conditions at loads up to 490 N (50 kgf). The
Four-Ball EP Tester is designed for testing under more severe conditions
increase in the measured scar diameter, shown in Fig. 1 as line
and lacks the sensitivity necessary for the Four-Ball Wear Test.
BC, and a momentary deflection of the indicating pen of the
5
o
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.