ASTM F708-92(2022)
(Practice)Standard Practice for Design and Installation of Rigid Pipe Hangers
Standard Practice for Design and Installation of Rigid Pipe Hangers
ABSTRACT
This practice covers acceptable methods of fabricating and installing rigid pipe hangers used to support shipboard piping systems, it provides guidance for the design of hanger caps, straps and standoffs, selection of hanger and hanger liner materials, hanger bolting, and hanger spacing. The pipe hanger style includes: split cap hanger, 3strap hanger, welded hanger, U-bolt hanger, J band type hanger, Nelson hanger, clamp hanger assembled with mounting channel, poly-block twin clamp hanger, crimp-on weld stud-type hangers, banded weld stud-type hanger, and poly-block single-clamp hanger. Guidance in determining pipe hanger spacing are provided. Special consideration should be given to areas of concentrated loads, such as risers, valves, or groups of fittings, and to piping configurations that could create rotational forces. Hangers need not be lined unless the hanger and pipe are of dissimilar material. All hanger bolts within tanks or other inaccessible areas shall be secured with lock nuts, lock washers, or by some other means. Pipe hangers and standoffs located in areas subject to corrosion, such as in bilges, ballast tanks, and areas exposed to the weather, should be zinc-plated or blasted and coated with inorganic zinc or coated with the same material as that of the surrounding area. Standoffs fabricated from pipe should not be used within tanks. Consideration should be given to thermal growth of the piping when selecting or locating hangers so as not to overstress the piping or hangers.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice covers acceptable methods of fabricating and installing rigid pipe hangers used to support shipboard piping systems with temperatures of 650 °F (343 °C) or less.
1.2 This practice provides guidance for the design of hanger caps, straps and standoffs, selection of hanger and hanger liner materials, hanger bolting, and hanger spacing.
1.3 Other hanger designs may be used provided they result in an adequately supported vibration-free piping system and are compatible with the intended system service and temperature limitations.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: F708 − 92 (Reapproved 2022) An American National Standard
Standard Practice for
Design and Installation of Rigid Pipe Hangers
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationF708;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginal
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope 3. Terminology
1.1 This practice covers acceptable methods of fabricating 3.1 Definitions:
and installing rigid pipe hangers used to support shipboard 3.1.1 liner, n—the material used to isolate a pipe from its
piping systems with temperatures of 650 °F (343 °C) or less. hanger.
3.1.2 rider bar, n—a protective strip of material installed
1.2 This practice provides guidance for the design of hanger
between the pipe and the hanger where frequent linear move-
caps, straps and standoffs, selection of hanger and hanger liner
ment of the pipe is expected.
materials, hanger bolting, and hanger spacing.
3.1.3 rigid pipe hanger, n—a device that transfers the load
1.3 Other hanger designs may be used provided they result
imposed by the piping, insulation, and system medium to the
in an adequately supported vibration-free piping system and
supporting structure.
are compatible with the intended system service and tempera-
ture limitations.
3.1.4 standoff, n—therigidmemberthatconnectsthehanger
strap, saddle, or band to the supporting structure. A standoff is
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
usually made up of one or more pieces of flat bar, pipe, angle
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
bar, or flanged plate to suit a specific location.
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
and are not considered standard.
4. List of Pipe Hanger Styles
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4.1 This practice incorporates 26 pipe hanger assemblies as
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
shown on Figs. 1-12(c) as follows:
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter- Hanger Fig. No.
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Split cap hanger (single leg standoff) 1(a)
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
Split cap hanger (dual leg standoff) 1(b)
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard- Split cap hanger (chair type) 1(c)
Strap hanger 2(a)
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Strap hanger (assembled for clearance with rider bar) 2(b)
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
Strap hanger (assembled for clearance with TFE-fluorocarbon 2(c)
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical strip)
Welded hanger (flat bar U-type) 3(a)
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Welded hanger (round bar U-type) 3(b)
Welded hanger (square bar U-type) 3(b)
2. Referenced Documents
U-bolt hanger 4(a)
U-bolt hanger (assembled for clearance with rider bar) 4(b)
2.1 ASTM Standards:
U-bolt hanger (assembled for clearance with TFE-fluorocarbon 4(c)
strip)
A307 Specification for Carbon Steel Bolts, Studs, and
Welded hanger (single leg standoff welded direct to pipe) 5(a)
Threaded Rod 60 000 PSI Tensile Strength
Welded hanger (dual leg standoff welded direct to pipe) 5(b)
“J” band type hanger (insulated pipe) 6(a)
“J” band type hanger (bare pipe) 6(b)
Nelson hanger 7
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F25 on Ships and
Clamp hanger assembled with mounting channel 8
Marine Technology and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F25.11 on
Machinery and Piping Systems.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2022. Published October 2022. Originally
ɛ1
approved in 1981. Last previous edition approved in 2018 as F708 – 92 (2018) .
DOI: 10.1520/F0708-92R22. The sole source of supply of the apparatus known to the committee at this time
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or is TRW Nelson Div., Toledo Ave. and E. 28th St., Lorain, OH 44055. If you are
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM aware of alternative suppliers, please provide this information to ASTM Interna-
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on tional Headquarters. Your comments will receive careful consideration at a meeting
the ASTM website. of the responsible technical committee, which you may attend.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
F708 − 92 (2022)
4,5
7. Application and Limitations
Poly-block twin clamp hanger (assembled with welding plate) 9(a)
4,5
Poly-block twin clamp hanger (assembled with welding stud) 9(b)
7.1 Unless otherwise noted, application and limitations on
Poly-block twin clamp hanger (assembled with mounting 9(c)
4,5
channel) the use of various style hangers should be as noted with each
Crimp-on weld stud-type hangers 10
hanger detail.
Banded weld stud-type hanger 11
Poly-block single-clamp hanger (assembled with welding plate) 12(a)
Poly-block single-clamp hanger (assembled with welding stud) 12(b) 8. Hanger Spacing
Poly-block single-clamp hanger (assembled with mounting 12(c)
8.1 Table 8 provides general guidance in determining pipe
channel)
hanger spacing. Special consideration should be given to areas
5. Hanger Designs
of concentrated loads, such as risers, valves, or groups of
5.1 Figs. 1-5 and Fig. 6(a) hangers are designs generally fittings, and to piping configurations that could create rota-
manufactured by shipyards or their subcontractors. See also
tional forces.
Tables 1-6.
9. General Requirements
5.2 Fig. 6, Fig. 8, Fig. 10, and Fig. 11 hangers are commer-
cially available from various vendors. Fig. 8, Fig. 10, and Fig. 9.1 The following general requirements and conditions are
11 hangers are primarily designed for use in supporting
applicable to all styles of hangers:
electrical cables, but are suitable for hanging small size pipe 9.1.1 Hangers need not be lined unless the hanger and pipe
and tubing. are of dissimilar material, or when the system internal operat-
5.2.1 The Fig. 7 hanger is a specific design that has been ing temperature is 300 °F (149 °C) and over, or 50 °F (10 °C)
patented by Nelson Division of TRW. and under and the heat transmitted to the other side of the
4,5
5.2.2 The Fig. 9 and Fig. 12 hangers are primarily structure to which the hanger is attached may be objectionable.
designed for use when supporting multiple runs of pipe or For hanger liner materials, see 6.5.
tubing. 9.1.2 All hanger bolts within tanks or other inaccessible
areas shall be secured with lock nuts, lock washers, or by some
6. Materials and Manufacture
other means.
6.1 Hanger materials for straps, saddles, and U-bolts for 9.1.3 Pipe hangers and standoffs located in areas subject to
Figs. 1-5 hangers and standoffs should be fabricated from
corrosion, such as in bilges, ballast tanks, and areas exposed to
commercial quality carbon steel. The steel should be a weld- the weather, should be zinc-plated or blasted and coated with
able grade with a minimum tensile strength of 47 ksi (324
inorganic zinc or coated with the same material as that of the
MPa) and capable of being bent at room temperature through surrounding area.
90° to an inside radius equal to the material thickness without
9.1.4 Standoffs fabricated from pipe should not be used
cracking on the outside of the bend. within tanks.
9.1.5 Wherethermalgrowthofpipingexceeds0.100in.(2.5
6.2 Hangers in Fig. 1, Fig. 6, Fig. 7, Fig. 10, and Fig. 11 are
mm) or long runs of pipe are affected by ship flexing, such as
generally manufactured from carbon steel. Fig. 8 is furnished
long runs on the weather deck, or long runs in longitudinal
in carbon steel and stainless steel. Fig. 9 and Fig. 12 hanger
passageways, a metal rider bar attached to the pipe or a
clamp halves are injected molded plastic furnished with carbon
TFE-fluorocarbon wear strip should be used in conjunction
steel or stainless steel hardware.
with a clearance type hanger, or other means should be
6.3 Bands and buckles for Fig. 6 and Fig. 11 hangers should
provided to prevent chaffing of the pipe.
be carbon steel electroplated zinc or stainless steel.
9.1.6 Consideration should be given to thermal growth of
the piping when selecting or locating hangers so as not to
6.4 Hanger bolts and nuts should be regular series hex type
electroplated zinc with unified national coarse threads Class 2 overstress the piping or hangers.
9.1.7 Nonmetallic pipe should be hung in accordance with
fit in accordance with Specification A307, Grade B.
the manufacturer’s recommendations.
6.5 Table 7 is a listing of hanger liner materials generally
used to isolate the pipe from the hanger (see 9.1.1).
10. Workmanship, Finish, and Appearance
10.1 Finished hanger components shall have a workman-
The sole source of supply of the apparatus known to the committee at this time
like appearance and be free of cracks or other injurious defects.
is Stauff Corp., 41 Newman St., Hackensack, NJ 07601. If you are aware of
alternative suppliers, please provide this information to ASTM International
Surface scale, rust, welding slag, or any foreign material (such
Headquarters.Your comments will receive careful consideration at a meeting of the
as oil) shall be removed before painting or coating.
responsible technical committee, which you may attend.
The sole source of supply of the poly-block hangers known to the committee at
this time is Behringer Corp., 108 Jabez St., Newark, NJ 07105. If you are aware of 11. Keywords
alternative suppliers, please provide this information to ASTM International
11.1 design; fabrication; installation; piping systems; rigid
Headquarters.Your comments will receive careful consideration at a meeting of the
responsible technical committee, which you may attend. pipe hangers
F708 − 92 (2022)
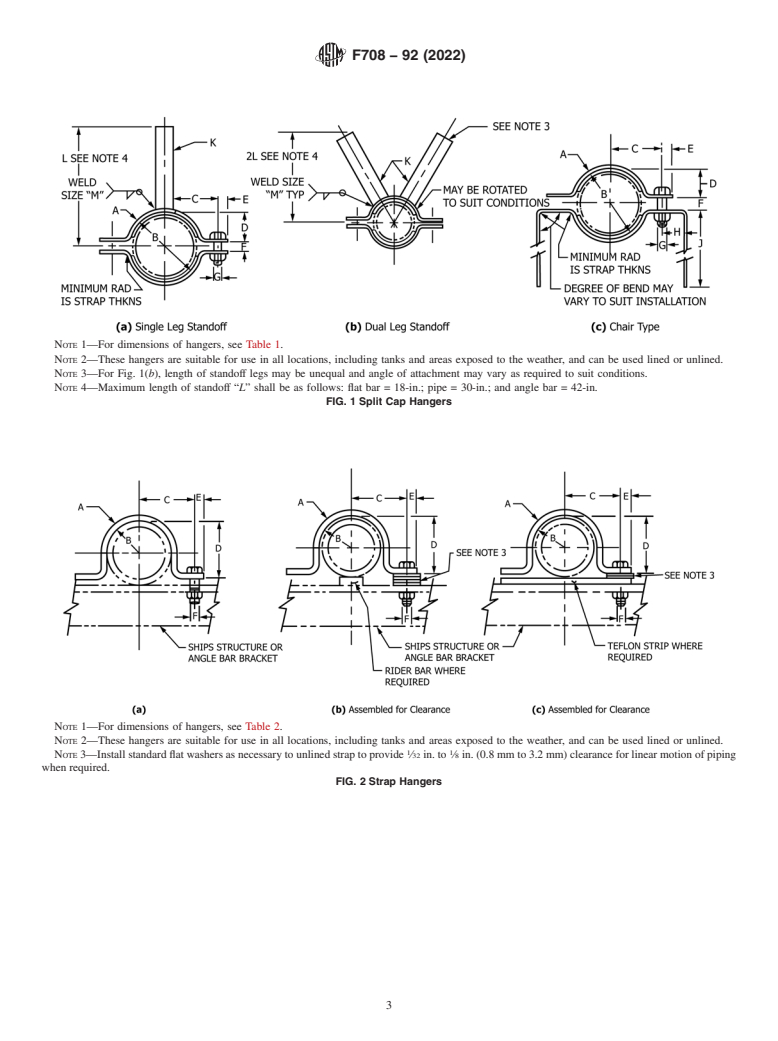
NOTE 1—For dimensions of hangers, see Table 1.
NOTE 2—These hangers are suitable for use in all locations, including tanks and areas exposed to the weather, and can be used lined or unlined.
NOTE 3—For Fig. 1(b), length of standoff legs may be unequal and angle of attachment may vary as required to suit conditions.
NOTE 4—Maximum length of standoff “L” shall be as follows: flat bar = 18-in.; pipe = 30-in.; and angle bar = 42-in.
FIG. 1 Split Cap Hangers
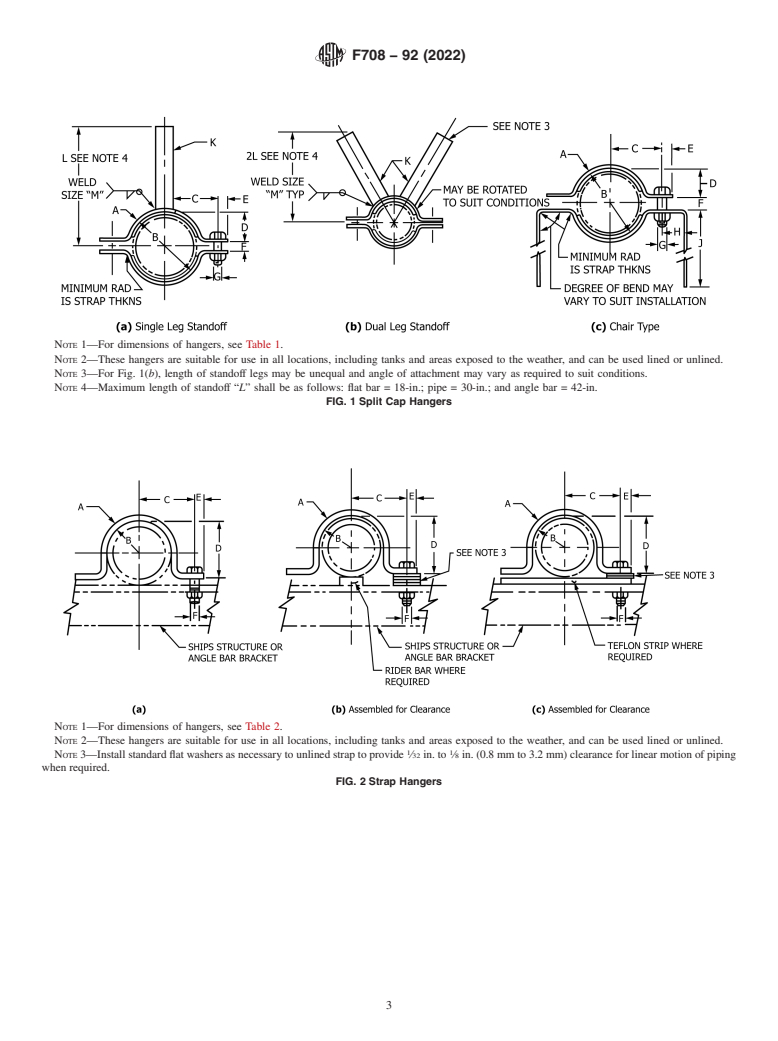
NOTE 1—For dimensions of hangers, see Table 2.
NOTE 2—These hangers are suitable for use in all locations, including tanks and areas exposed to the weather, and can be used lined or unlined.
1 1
NOTE 3—Install standard flat washers as necessary to unlined strap to provide ⁄32 in. to ⁄8 in. (0.8 mm to 3.2 mm) clearance for linear motion of piping
when required.
FIG. 2 Strap Hangers
F708 − 92 (2022)
NOTE 1—For dimensions of hangers, see Table 3.
NOTE 2—These hangers are suitable for use in all locations, including tanks and areas exposed to the weather, and are intended to be used unlined only.
NOTE 3—Weld as indicated for size 3-in. NPS and above. For 2 ⁄2-in. NPS and below, weld hanger on outside only.
FIG. 3 Welded Hangers
NOTE 1—For dimensions of hangers, see Table 4.
NOTE 2—These hangers are suitable for use in all locations, including tanks and areas exposed to the weather, and are intended to be used unlined.
FIG. 4 U-Bolt Hangers
F708 − 92 (2022)
NOTE 1—For dimensions of hangers, see Table 5.
NOTE 2—These hangers are limited to use on normally dry ferrous piping systems, such as sounding tubes. Air escapes and plumbing drains with a
wall thickness of 0.200 in. (5.1 mm) or more.
NOTE 3—These hangers should not be used where takedown is required or in the steering gear room, inner bottoms, fore peak, aft peak or deep tanks,
or other high vibration or inaccessible areas.
NOTE 4—For Fig. 5(b), length of standoff legs may be unequal and angle of attachment may vary as required to suit conditions.
FIG. 5 Welded Hangers
NOTE 1—For dimensions of hangers, see Table 6.
NOTE 2—These hangers are suitable for use in all locations, except tanks and areas exposed to the weather, and can be used lined or unlined.
FIG. 6 J-Band Type Hangers
F708 − 92 (2022)
NOTE 1—This hanger is suitable for use in all locations except tanks.
NOTE 2—This hanger is limited to use on pipe 4-in. NPS and below with a system operating temperature of 200 °F (93.3 °C) or less.
FIG. 7 Nelson Hanger
NOTE 1—These hangers are suitable for use in all locations, including tanks and areas exposed to the weather. When used in areas subject to high
corrosion, such as salt water ballast tanks or weather decks, stainless steel hanger components shall be used.
NOTE 2—These hangers are suitable for supporting single or multiple runs of piping 2 in. (50.8 mm) or smaller.
FIG. 8 Clamp Hanger Assembled with Mounting Channel
F708 − 92 (2022)
NOTE 1—These hangers are suitable for use in all locations, including tanks and areas exposed to the weather. When used in areas subject to high
corrosion, such as salt water ballast tanks or weather decks, stainless steel hanger components shall be used.
1 1
NOTE 2—These hangers are limited to use on pipe 1 ⁄4-in. NPS and below and tubing 1 ⁄2-in. outside diameter and below with a system operating
temperature of 300 °F (149 °C) or less.
NOTE 3—These hangers may be used for multiple pipe installations installed vertically, horizontally, or stacked using a welding plate, welding stud,
or attached to a mounting channel.
4,5
FIG. 9 Stauff Twin Clamp Hanger
NOTE 1—These hangers are suitable for use in all locations, except tanks, and should be coated with neoprene or other similar material when used to
support nonferrous tubing.
NOTE 2—These hangers are limited to use on tubing with an outside diameter of 1 ⁄8 in. (28.6 mm) or smaller with a system operating temperature
of 180 °F (82.2 °C) or less.
NOTE 3—Size and quantity of tubes may be varied provided they are arranged so as to be securely clamped.
FIG. 10 Crimp-On Weld Stud Hangers
F708 − 92 (2022)
NOTE 1—These ha
...
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: F708 − 92 (Reapproved 2022) An American National Standard
Standard Practice for
Design and Installation of Rigid Pipe Hangers
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F708; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A superscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope 3. Terminology
1.1 This practice covers acceptable methods of fabricating 3.1 Definitions:
and installing rigid pipe hangers used to support shipboard 3.1.1 liner, n—the material used to isolate a pipe from its
piping systems with temperatures of 650 °F (343 °C) or less. hanger.
3.1.2 rider bar, n—a protective strip of material installed
1.2 This practice provides guidance for the design of hanger
between the pipe and the hanger where frequent linear move-
caps, straps and standoffs, selection of hanger and hanger liner
ment of the pipe is expected.
materials, hanger bolting, and hanger spacing.
3.1.3 rigid pipe hanger, n—a device that transfers the load
1.3 Other hanger designs may be used provided they result
imposed by the piping, insulation, and system medium to the
in an adequately supported vibration-free piping system and
supporting structure.
are compatible with the intended system service and tempera-
ture limitations.
3.1.4 standoff, n—the rigid member that connects the hanger
strap, saddle, or band to the supporting structure. A standoff is
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
usually made up of one or more pieces of flat bar, pipe, angle
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
bar, or flanged plate to suit a specific location.
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
and are not considered standard.
4. List of Pipe Hanger Styles
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4.1 This practice incorporates 26 pipe hanger assemblies as
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
shown on Figs. 1-12(c) as follows:
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter- Hanger Fig. No.
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Split cap hanger (single leg standoff) 1(a)
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
Split cap hanger (dual leg standoff) 1(b)
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
Split cap hanger (chair type) 1(c)
Strap hanger 2(a)
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Strap hanger (assembled for clearance with rider bar) 2(b)
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
Strap hanger (assembled for clearance with TFE-fluorocarbon 2(c)
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical strip)
Welded hanger (flat bar U-type) 3(a)
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Welded hanger (round bar U-type) 3(b)
Welded hanger (square bar U-type) 3(b)
2. Referenced Documents U-bolt hanger 4(a)
U-bolt hanger (assembled for clearance with rider bar) 4(b)
2.1 ASTM Standards:
U-bolt hanger (assembled for clearance with TFE-fluorocarbon 4(c)
strip)
A307 Specification for Carbon Steel Bolts, Studs, and
Welded hanger (single leg standoff welded direct to pipe) 5(a)
Threaded Rod 60 000 PSI Tensile Strength
Welded hanger (dual leg standoff welded direct to pipe) 5(b)
“J” band type hanger (insulated pipe) 6(a)
“J” band type hanger (bare pipe) 6(b)
Nelson hanger 7
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F25 on Ships and
Clamp hanger assembled with mounting channel 8
Marine Technology and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F25.11 on
Machinery and Piping Systems.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2022. Published October 2022. Originally
ɛ1
approved in 1981. Last previous edition approved in 2018 as F708 – 92 (2018) .
DOI: 10.1520/F0708-92R22. The sole source of supply of the apparatus known to the committee at this time
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or is TRW Nelson Div., Toledo Ave. and E. 28th St., Lorain, OH 44055. If you are
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM aware of alternative suppliers, please provide this information to ASTM Interna-
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on tional Headquarters. Your comments will receive careful consideration at a meeting
the ASTM website. of the responsible technical committee, which you may attend.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
F708 − 92 (2022)
4,5
7. Application and Limitations
Poly-block twin clamp hanger (assembled with welding plate) 9(a)
4,5
Poly-block twin clamp hanger (assembled with welding stud) 9(b)
7.1 Unless otherwise noted, application and limitations on
Poly-block twin clamp hanger (assembled with mounting 9(c)
4,5
channel)
the use of various style hangers should be as noted with each
Crimp-on weld stud-type hangers 10
hanger detail.
Banded weld stud-type hanger 11
Poly-block single-clamp hanger (assembled with welding plate) 12(a)
Poly-block single-clamp hanger (assembled with welding stud) 12(b) 8. Hanger Spacing
Poly-block single-clamp hanger (assembled with mounting 12(c)
8.1 Table 8 provides general guidance in determining pipe
channel)
hanger spacing. Special consideration should be given to areas
5. Hanger Designs
of concentrated loads, such as risers, valves, or groups of
5.1 Figs. 1-5 and Fig. 6(a) hangers are designs generally
fittings, and to piping configurations that could create rota-
manufactured by shipyards or their subcontractors. See also tional forces.
Tables 1-6.
9. General Requirements
5.2 Fig. 6, Fig. 8, Fig. 10, and Fig. 11 hangers are commer-
cially available from various vendors. Fig. 8, Fig. 10, and Fig.
9.1 The following general requirements and conditions are
11 hangers are primarily designed for use in supporting applicable to all styles of hangers:
electrical cables, but are suitable for hanging small size pipe 9.1.1 Hangers need not be lined unless the hanger and pipe
and tubing. are of dissimilar material, or when the system internal operat-
5.2.1 The Fig. 7 hanger is a specific design that has been ing temperature is 300 °F (149 °C) and over, or 50 °F (10 °C)
patented by Nelson Division of TRW. and under and the heat transmitted to the other side of the
4,5
5.2.2 The Fig. 9 and Fig. 12 hangers are primarily structure to which the hanger is attached may be objectionable.
designed for use when supporting multiple runs of pipe or For hanger liner materials, see 6.5.
tubing. 9.1.2 All hanger bolts within tanks or other inaccessible
areas shall be secured with lock nuts, lock washers, or by some
6. Materials and Manufacture
other means.
6.1 Hanger materials for straps, saddles, and U-bolts for 9.1.3 Pipe hangers and standoffs located in areas subject to
Figs. 1-5 hangers and standoffs should be fabricated from corrosion, such as in bilges, ballast tanks, and areas exposed to
commercial quality carbon steel. The steel should be a weld-
the weather, should be zinc-plated or blasted and coated with
able grade with a minimum tensile strength of 47 ksi (324 inorganic zinc or coated with the same material as that of the
MPa) and capable of being bent at room temperature through
surrounding area.
90° to an inside radius equal to the material thickness without 9.1.4 Standoffs fabricated from pipe should not be used
cracking on the outside of the bend.
within tanks.
9.1.5 Where thermal growth of piping exceeds 0.100 in. (2.5
6.2 Hangers in Fig. 1, Fig. 6, Fig. 7, Fig. 10, and Fig. 11 are
mm) or long runs of pipe are affected by ship flexing, such as
generally manufactured from carbon steel. Fig. 8 is furnished
long runs on the weather deck, or long runs in longitudinal
in carbon steel and stainless steel. Fig. 9 and Fig. 12 hanger
passageways, a metal rider bar attached to the pipe or a
clamp halves are injected molded plastic furnished with carbon
TFE-fluorocarbon wear strip should be used in conjunction
steel or stainless steel hardware.
with a clearance type hanger, or other means should be
6.3 Bands and buckles for Fig. 6 and Fig. 11 hangers should
provided to prevent chaffing of the pipe.
be carbon steel electroplated zinc or stainless steel.
9.1.6 Consideration should be given to thermal growth of
6.4 Hanger bolts and nuts should be regular series hex type the piping when selecting or locating hangers so as not to
overstress the piping or hangers.
electroplated zinc with unified national coarse threads Class 2
fit in accordance with Specification A307, Grade B. 9.1.7 Nonmetallic pipe should be hung in accordance with
the manufacturer’s recommendations.
6.5 Table 7 is a listing of hanger liner materials generally
used to isolate the pipe from the hanger (see 9.1.1).
10. Workmanship, Finish, and Appearance
10.1 Finished hanger components shall have a workman-
The sole source of supply of the apparatus known to the committee at this time
like appearance and be free of cracks or other injurious defects.
is Stauff Corp., 41 Newman St., Hackensack, NJ 07601. If you are aware of
alternative suppliers, please provide this information to ASTM International
Surface scale, rust, welding slag, or any foreign material (such
Headquarters. Your comments will receive careful consideration at a meeting of the
as oil) shall be removed before painting or coating.
responsible technical committee, which you may attend.
The sole source of supply of the poly-block hangers known to the committee at
this time is Behringer Corp., 108 Jabez St., Newark, NJ 07105. If you are aware of 11. Keywords
alternative suppliers, please provide this information to ASTM International
11.1 design; fabrication; installation; piping systems; rigid
Headquarters. Your comments will receive careful consideration at a meeting of the
responsible technical committee, which you may attend. pipe hangers
F708 − 92 (2022)
NOTE 1—For dimensions of hangers, see Table 1.
NOTE 2—These hangers are suitable for use in all locations, including tanks and areas exposed to the weather, and can be used lined or unlined.
NOTE 3—For Fig. 1(b), length of standoff legs may be unequal and angle of attachment may vary as required to suit conditions.
NOTE 4—Maximum length of standoff “L” shall be as follows: flat bar = 18-in.; pipe = 30-in.; and angle bar = 42-in.
FIG. 1 Split Cap Hangers
NOTE 1—For dimensions of hangers, see Table 2.
NOTE 2—These hangers are suitable for use in all locations, including tanks and areas exposed to the weather, and can be used lined or unlined.
1 1
NOTE 3—Install standard flat washers as necessary to unlined strap to provide ⁄32 in. to ⁄8 in. (0.8 mm to 3.2 mm) clearance for linear motion of piping
when required.
FIG. 2 Strap Hangers
F708 − 92 (2022)
NOTE 1—For dimensions of hangers, see Table 3.
NOTE 2—These hangers are suitable for use in all locations, including tanks and areas exposed to the weather, and are intended to be used unlined only.
NOTE 3—Weld as indicated for size 3-in. NPS and above. For 2 ⁄2-in. NPS and below, weld hanger on outside only.
FIG. 3 Welded Hangers
NOTE 1—For dimensions of hangers, see Table 4.
NOTE 2—These hangers are suitable for use in all locations, including tanks and areas exposed to the weather, and are intended to be used unlined.
FIG. 4 U-Bolt Hangers
F708 − 92 (2022)
NOTE 1—For dimensions of hangers, see Table 5.
NOTE 2—These hangers are limited to use on normally dry ferrous piping systems, such as sounding tubes. Air escapes and plumbing drains with a
wall thickness of 0.200 in. (5.1 mm) or more.
NOTE 3—These hangers should not be used where takedown is required or in the steering gear room, inner bottoms, fore peak, aft peak or deep tanks,
or other high vibration or inaccessible areas.
NOTE 4—For Fig. 5(b), length of standoff legs may be unequal and angle of attachment may vary as required to suit conditions.
FIG. 5 Welded Hangers
NOTE 1—For dimensions of hangers, see Table 6.
NOTE 2—These hangers are suitable for use in all locations, except tanks and areas exposed to the weather, and can be used lined or unlined.
FIG. 6 J-Band Type Hangers
F708 − 92 (2022)
NOTE 1—This hanger is suitable for use in all locations except tanks.
NOTE 2—This hanger is limited to use on pipe 4-in. NPS and below with a system operating temperature of 200 °F (93.3 °C) or less.
FIG. 7 Nelson Hanger
NOTE 1—These hangers are suitable for use in all locations, including tanks and areas exposed to the weather. When used in areas subject to high
corrosion, such as salt water ballast tanks or weather decks, stainless steel hanger components shall be used.
NOTE 2—These hangers are suitable for supporting single or multiple runs of piping 2 in. (50.8 mm) or smaller.
FIG. 8 Clamp Hanger Assembled with Mounting Channel
F708 − 92 (2022)
NOTE 1—These hangers are suitable for use in all locations, including tanks and areas exposed to the weather. When used in areas subject to high
corrosion, such as salt water ballast tanks or weather decks, stainless steel hanger components shall be used.
1 1
NOTE 2—These hangers are limited to use on pipe 1 ⁄4-in. NPS and below and tubing 1 ⁄2-in. outside diameter and below with a system operating
temperature of 300 °F (149 °C) or less.
NOTE 3—These hangers may be used for multiple pipe installations installed vertically, horizontally, or stacked using a welding plate, welding stud,
or attached to a mounting channel.
4,5
FIG. 9 Stauff Twin Clamp Hanger
NOTE 1—These hangers are suitable for use in all locations, except tanks, and should be coated with neoprene or other similar material when used to
support nonferrous tubing.
NOTE 2—These hangers are limited to use on tubing with an outside diameter of 1 ⁄8 in. (28.6 mm) or smaller with a system operating temperature
of 180 °F (82.2 °C) or less.
NOTE 3—Size and quantity of tubes may be varied provided they are arranged so as to be securely clamped.
FIG. 10 Crimp-On Weld Stud Hangers
F708 − 92 (2022)
NOTE 1—These hangers are suitable for use in all locations except tanks.
NOTE 2—These hangers are limited to use
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation: F708 − 92 (Reapproved 2018) F708 − 92 (Reapproved 2022)An American National Standard
Standard Practice for
Design and Installation of Rigid Pipe Hangers
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F708; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A superscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
ε NOTE—The Keywords section was added editorially in September 2018.
1. Scope
1.1 This practice covers acceptable methods of fabricating and installing rigid pipe hangers used to support shipboard piping
systems with temperatures of 650°F (343°C)650 °F (343 °C) or less.
1.2 This practice provides guidance for the design of hanger caps, straps and standoffs, selection of hanger and hanger liner
materials, hanger bolting, and hanger spacing.
1.3 Other hanger designs may be used provided they result in an adequately supported vibration-free piping system and are
compatible with the intended system service and temperature limitations.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A307 Specification for Carbon Steel Bolts, Studs, and Threaded Rod 60 000 PSI Tensile Strength
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 liner, n—the material used to isolate a pipe from its hanger.
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F25 on Ships and Marine Technology and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F25.11 on Machinery
and Piping Systems.
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2018Oct. 1, 2022. Published October 2018October 2022. Originally approved in 1981. Last previous edition approved in 20142018 as
ɛ1
F708 – 92 (2014).(2018) . DOI: 10.1520/F0708-92R18E01.10.1520/F0708-92R22.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
F708 − 92 (2022)
3.1.2 rider bar, n—a protective strip of material installed between the pipe and the hanger where frequent linear movement of the
pipe is expected.
3.1.3 rigid pipe hanger, n—a device that transfers the load imposed by the piping, insulation, and system medium to the supporting
structure.
3.1.4 standoff, n—the rigid member that connects the hanger strap, saddle, or band to the supporting structure. A standoff is usually
made up of one or more pieces of flat bar, pipe, angle bar, or flanged plate to suit a specific location.
4. List of Pipe Hanger Styles
4.1 This practice incorporates 26 pipe hanger assemblies as shown on Figs. 1-12(c) as follows:
Hanger Fig. No.
Split cap hanger (single leg standoff) 1(a)
Split cap hanger (dual leg standoff) 1(b)
Split cap hanger (chair type) 1(c)
Strap hanger 2(a)
Strap hanger (assembled for clearance with rider bar) 2(b)
Strap hanger (assembled for clearance with TFE-fluorocarbon strip) 2(c)
Welded hanger (flat bar U-type) 3(a)
Welded hanger (round bar U-type) 3(b)
Welded hanger (square bar U-type) 3(b)
U-bolt hanger 4(a)
U-bolt hanger (assembled for clearance with rider bar) 4(b)
U-bolt hanger (assembled for clearance with TFE-fluorocarbon strip) 4(c)
Welded hanger (single leg standoff welded direct to pipe) 5(a)
Welded hanger (dual leg standoff welded direct to pipe) 5(b)
“J” band type hanger (insulated pipe) 6(a)
“J” band type hanger (bare pipe) 6(b)
Nelson hanger 7
Clamp hanger assembled with mounting channel 8
4,5
Poly-block twin clamp hanger (assembled with welding plate) 9(a)
4,5
Poly-block twin clamp hanger (assembled with welding stud) 9(b)
4,5
Poly-block twin clamp hanger (assembled with mounting channel) 9(c)
Crimp-on weld stud-type hangers 10
Banded weld stud-type hanger 11
Poly-block single-clamp hanger (assembled with welding plate) 12(a)
Poly-block single-clamp hanger (assembled with welding stud) 12(b)
Poly-block single-clamp hanger (assembled with mounting channel) 12(c)
5. Hanger Designs
5.1 Figs. 1-5 and Fig. 6(a) hangers are designs generally manufactured by shipyards or their subcontractors. See also Tables 1-6.
5.2 Fig. 6, Fig. 8, Fig. 10, and Fig. 11 hangers are commercially available from various vendors. Fig. 8, Fig. 10, and Fig. 11
hangers are primarily designed for use in supporting electrical cables, but are suitable for hanging small size pipe and tubing.
5.2.1 The Fig. 7 hanger is a specific design that has been patented by Nelson Division of TRW.
4,5
5.2.2 The Fig. 9 and Fig. 12 hangers are primarily designed for use when supporting multiple runs of pipe or tubing.
The sole source of supply of the apparatus known to the committee at this time is TRW Nelson Div., Toledo Ave. and E. 28th St., Lorain, OH 44055. If you are aware
of alternative suppliers, please provide this information to ASTM International Headquarters. Your comments will receive careful consideration at a meeting of the responsible
technical committee, which you may attend.
The sole source of supply of the apparatus known to the committee at this time is Stauff Corp., 41 Newman St., Hackensack, NJ 07601. If you are aware of alternative
suppliers, please provide this information to ASTM International Headquarters. Your comments will receive careful consideration at a meeting of the responsible technical
committee, which you may attend.
The sole source of supply of the poly-block hangers known to the committee at this time is Behringer Corp., 108 Jabez St., Newark, NJ 07105. If you are aware of
alternative suppliers, please provide this information to ASTM International Headquarters. Your comments will receive careful consideration at a meeting of the responsible
technical committee, which you may attend.
F708 − 92 (2022)
6. Materials and Manufacture
6.1 Hanger materials for straps, saddles, and U-bolts for Figs. 1-5 hangers and standoffs should be fabricated from commercial
quality carbon steel. The steel should be a weldable grade with a minimum tensile strength of 47 ksi (324 MPa) and capable of
being bent at room temperature through 90° to an inside radius equal to the material thickness without cracking on the outside of
the bend.
6.2 Hangers in Fig. 1, Fig. 6, Fig. 7, Fig. 10, and Fig. 11 are generally manufactured from carbon steel. Fig. 8 is furnished in carbon
steel and stainless steel. Fig. 9 and Fig. 12 hanger clamp halves are injected molded plastic furnished with carbon steel or stainless
steel hardware.
6.3 Bands and buckles for Fig. 6 and Fig. 11 hangers should be carbon steel electroplated zinc or stainless steel.
6.4 Hanger bolts and nuts should be regular series hex type electroplated zinc with unified national coarse threads Class 2 fit in
accordance with Specification A307, Grade B.
6.5 Table 7 is a listing of hanger liner materials generally used to isolate the pipe from the hanger (see 9.1.1).
7. Application and Limitations
7.1 Unless otherwise noted, application and limitations on the use of various style hangers should be as noted with each hanger
detail.
8. Hanger Spacing
8.1 Table 8 provides general guidance in determining pipe hanger spacing. Special consideration should be given to areas of
concentrated loads, such as risers, valves, or groups of fittings, and to piping configurations that could create rotational forces.
9. General Requirements
9.1 The following general requirements and conditions are applicable to all styles of hangers:
9.1.1 Hangers need not be lined unless the hanger and pipe are of dissimilar material, or when the system internal operating
temperature is 300°F (149°C)300 °F (149 °C) and over, or 50°F (10°C)50 °F (10 °C) and under and the heat transmitted to the
other side of the structure to which the hanger is attached may be objectionable. For hanger liner materials, see 6.5.
9.1.2 All hanger bolts within tanks or other inaccessible areas shall be secured with lock nuts, lock washers, or by some other
means.
9.1.3 Pipe hangers and standoffs located in areas subject to corrosion, such as in bilges, ballast tanks, and areas exposed to the
weather, should be zinc-plated or blasted and coated with inorganic zinc or coated with the same material as that of the surrounding
area.
9.1.4 Standoffs fabricated from pipe should not be used within tanks.
9.1.5 Where thermal growth of piping exceeds 0.100 in. (2.5 mm) or long runs of pipe are affected by ship flexing, such as long
runs on the weather deck, or long runs in longitudinal passageways, a metal rider bar attached to the pipe or a TFE-fluorocarbon
wear strip should be used in conjunction with a clearance type hanger, or other means should be provided to prevent chaffing of
the pipe.
9.1.6 Consideration should be given to thermal growth of the piping when selecting or locating hangers so as not to overstress
the piping or hangers.
9.1.7 Nonmetallic pipe should be hung in accordance with the manufacturer’s recommendations.
F708 − 92 (2022)
10. Workmanship, Finish, and Appearance
10.1 Finished hanger components shall have a workman-like appearance and be free of cracks or other injurious defects. Surface
scale, rust, welding slag, or any foreign material (such as oil) shall be removed before painting or coating.
11. Keywords
11.1 design; fabrication; installation; piping systems; rigid pipe hangers
F708 − 92 (2022)
NOTE 1—For dimensions of hangers, see Table 1.
NOTE 2—These hangers are suitable for use in all locations, including tanks and areas exposed to the weather, and can be used lined or unlined.
NOTE 3—For Fig. 1(b), length of standoff legs may be unequal and angle of attachment may vary as required to suit conditions.
NOTE 4—Maximum length of standoff “L” shall be as follows: flat bar = 18 in.; 18-in.; pipe = 30 in.; 30-in.; and angle bar = 42 in. 42-in.
FIG. 1 Split Cap Hangers
F708 − 92 (2022)
NOTE 1—For dimensions of hangers, see Table 2.
NOTE 2—These hangers are suitable for use in all locations, including tanks and areas exposed to the weather, and can be used lined or unlined.
1 1
NOTE 3—Install standard flat washers as necessary to unlined strap to provide ⁄32 in. to ⁄8-in. (0.8 in. (0.8 mm to 3.2-mm)3.2 mm) clearance for linear
motion of piping when required.
FIG. 2 Strap Hangers
NOTE 1—For dimensions of hangers, see Table 3.
NOTE 2—These hangers are suitable for use in all locations, including tanks and areas exposed to the weather, and are intended to be used unlined only.
NOTE 3—Weld as indicated for size 3-in. NPS and above. For 2 ⁄2-in. NPS and below, weld hanger on outside only.
FIG. 3 Welded Hangers
F708 − 92 (2022)
NOTE 1—For dimensions of hangers, see Table 4.
NOTE 2—These hangers are suitable for use in all locations, including tanks and areas exposed to the weather, and are intended to be used unlined.
FIG. 4 U-Bolt Hangers
NOTE 1—For dimensions of hangers, see Table 5.
NOTE 2—These hangers are limited to use on normally dry ferrous piping systems, such as sounding tubes. Air escapes and plumbing drains with a wall
thickness of 0.200 in. (5.1 mm) or more.
NOTE 3—These hangers should not be used where takedown is required or in the steering gear room, inner bottoms, fore peak, aft peak or deep tanks,
or other high vibration or inaccessible areas.
NOTE 4—For Fig. 5(b), length of standoff legs may be unequal and angle of attachment may vary as required to suit conditions.
FIG. 5 Welded Hangers
F708 − 92 (2022)
NOTE 1—For dimensions of hangers, see Table 6.
NOTE 2—These hangers are suitable for use in all locations, except tanks and areas exposed to the weather, and can be used lined or unlined.
FIG. 6 J-Band Type Hangers
F708 − 92 (2022)
NOTE 1—This hanger is suitable for use in all locations except tanks.
NOTE 2—This hanger is limited to use on pipe 4-in. NPS and below with a system operating temperature of 200°F (93.3°C)200 °F (93.3 °C) or less.
FIG. 7 Nelson Hanger
NOTE 1—These hangers are suitable for use in all locations, including tanks and areas exposed to the weather. When used in areas subject to high
corrosion, such as salt water ballast tanks or weather decks, stainless steel hanger components shall be used.
NOTE 2—These hangers are suitable for supporting single or multiple runs of piping 2 in. (50.8 mm) or smaller.
FIG. 8 Clamp Hanger Assembled with Mounting Channel
F708 − 92 (2022)
NOTE 1—These hangers are suitable for use in all locations, including tanks and areas exposed to the weather. When used in areas subject to high
corrosion, such as salt water ballast tanks or weather decks, stainless steel hanger components shall be used.
1 1
NOTE 2—These hangers are limited to use on pipe 1 ⁄4-in. NPS and below and tubing 1 ⁄2-in. outside diameter and below with a system operating
temperature of 300°F (149°C)300 °F (149 °C) or less.
NOTE 3—These hangers may be used for multiple pipe installations installed vertically, horizontally, or stacked using a welding plate, welding stud, or
attached to a mounti
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.