ASTM C582-02
(Specification)Standard Specification for Contact-Molded Reinforced Thermosetting Plastic (RTP) Laminates for Corrosion-Resistant Equipment
Standard Specification for Contact-Molded Reinforced Thermosetting Plastic (RTP) Laminates for Corrosion-Resistant Equipment
ABSTRACT
This specification covers composition, thickness, fabricating procedures, and physical property requirements for glass fiber reinforced thermoset polyester, vinyl ester, or other qualified thermosetting resin laminates comprising the materials of construction for RTP corrosion-resistant tanks, piping, and equipment. This specification is limited to fabrication by contact molding. Laminates shall be classified according to type, class, and grade: Types I and II; Classes P and V. Tensile strength and tangent modulus of elasticity, flexural strength, glass content, thickness, hardness, chemical resistance, and surface flame-spread classification tests shall be performed to conform to the specified requirements.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers composition, thickness, fabricating procedures, and physical property requirements for glass fiber reinforced thermoset polyester, vinyl ester, or other qualified thermosetting resin laminates comprising the materials of construction for RTP corrosion-resistant tanks, piping, and equipment. This specification is limited to fabrication by contact molding.
Note 1—The laminates covered by this specification are manufactured during fabrication of contact-molded RTP tanks, piping, and other equipment.
Note 2—There is no similar or equivalent ISO standard.
1.2 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test method portion, Section 8, of this specification:This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
Designation: C 582 – 02
Standard Specification for
Contact-Molded Reinforced Thermosetting Plastic (RTP)
1
Laminates for Corrosion-Resistant Equipment
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C 582; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
3
1. Scope D 883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
D 2583 Test Method for Indentation Hardness of Rigid
1.1 This specification covers composition, thickness, fabri-
4
Plastics by Means of a Barcol Impressor
catingprocedures,andphysicalpropertyrequirementsforglass
D 2584 Test Method for Ignition Loss of Cured Reinforced
fiber reinforced thermoset polyester, vinyl ester, or other
4
Resins
qualified thermosetting resin laminates comprising the materi-
D 3681 Test Method for Chemical Resistance of “Fiber-
als of construction for RTP corrosion-resistant tanks, piping,
glass” (Glass-Fiber-ReinforcedThermosetting-Resin) Pipe
and equipment. This specification is limited to fabrication by
2
in a Deflected Condition
contact molding.
E84 Test Method for Surface Burning Characteristics of
NOTE 1—The laminates covered by this specification are manufactured 5
Building Materials
during fabrication of contact-molded RTP tanks, piping, and other
equipment.
3. Definitions
NOTE 2—There is no similar or equivalent ISO standard.
3.1 Definitions used in this specification are in accordance
1.2 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the
with Terminology D 883 unless otherwise indicated. The
test method portion, Section 8, of this specification: This
abbreviation for reinforced thermoset plastic is RTP.
standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns,
3.2 polyester—resins produced by the polycondensation of
if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user
dihydroxyderivatives and dibasic organic acids or anhydrides,
of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health
wherein at least one component contributes ethylenic unsat-
practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limita-
uration yielding resins that can be compounded with styryl
tions prior to use.
monomers and reacted to give highly crosslinked thermoset
copolymers.
2. Referenced Documents
3.3 vinyl ester—resins characterized by reactive unsatura-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
tion located predominately in terminal positions that can be
C 581 Practice for Determining Chemical Resistance of
compounded with styryl monomers and reacted to give highly
Thermosetting Resins Used in Glass Fiber Reinforced
crosslinked thermoset copolymers.
2
Structures Intended for Liquid Service
3
NOTE 3—These resins are handled in the same way as polyesters in
D 638 Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics
fabrication of RTP components.
D 695 Test Method for Compressive Properties of Rigid
3
Plastics 3.4 contact molding—a method of fabrication wherein the
D 790 TestMethodsforFlexuralPropertiesofUnreinforced glass-fiber reinforcement is applied to the mold, in the form of
and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materi- chopped strand mat or woven roving, by hand or from a reel,
3
als or in the form of chopped strands of continuous-filament glass
from a chopper-spray gun. The resin matrix is applied by
various methods, including brush, roller, or spray gun. Con-
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on
solidation of the composite laminate is by rolling.
Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.23 on Reinforced
Plastic Piping Systems and Chemical Equipment.
Current edition approved Nov. 10, 2002. Published January 2003. Originally
approved in 1965. Last previous edition approved in 1995 as C 582 – 95.
2 4
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.04. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.02.
3 5
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.01. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.07.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C 582–02
production process samples. They are not arbitrarily selected values.
4. Classification
4.1 Laminates shall be classified according to type, class,
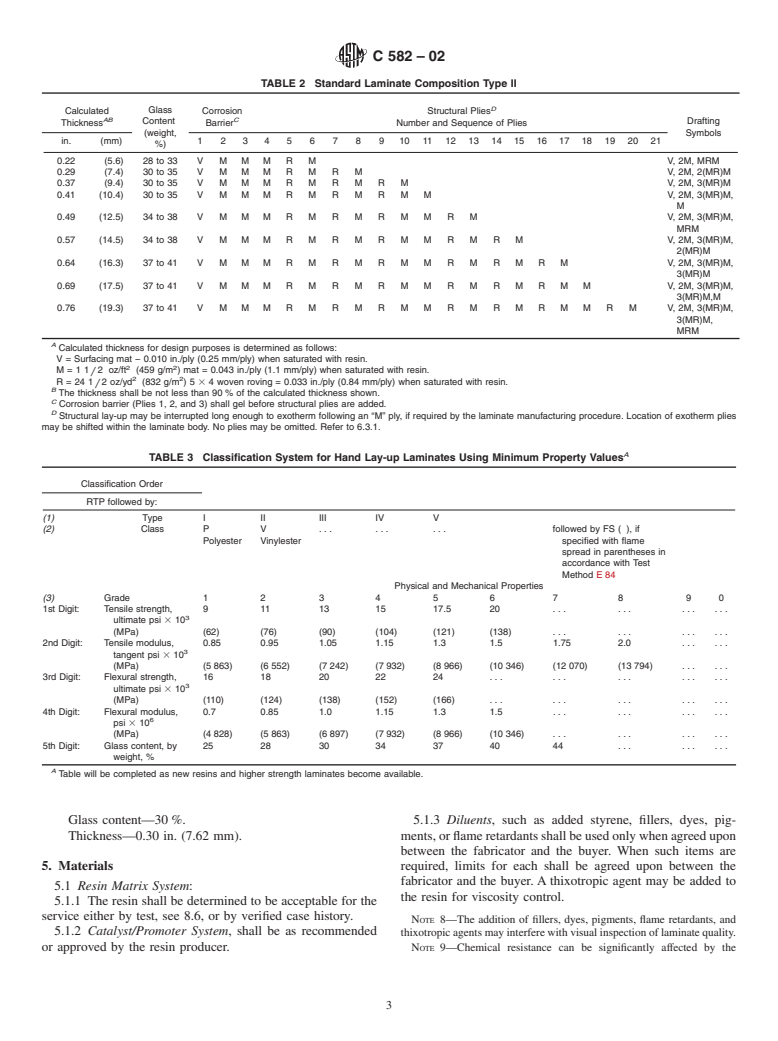
4.1.4 Thickness—Nominal, shall be designated by Arabic
and grade.
number in decimal hundredths of an inch. (See Table 1 and
4.1.1 Type—In Roman numerals, shall designate the rein-
Table 2 for standard thicknesses.)
forcement structure comprised of specific plies of glass fiber in
NOTE 7—Table 1 and Table 2 are for referenc
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.