ASTM D4617-96
(Specification)Standard Specification for Phenolic Compounds, (PF)
Standard Specification for Phenolic Compounds, (PF)
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers phenolic compounds suitable for molding.
1.2 This specification is intended to be a means of calling out plastic materials used in the fabrication of end items or parts. It is not intended for the selection of materials. Material selection should be made by those having expertise in the plastics field after careful consideration of the design and the performance required of the part, the environment to which it will be exposed, the fabrication process to be employed, the inherent properties of the material other than those covered by this specification, and the economics.
1.3 The properties included in this specification are those required to identify the compositions covered. There may be other requirements necessary to identify particular characteristics important to specialized applications. These will be agreed upon between the user and the supplier, by using the suffixes specified in Section 5.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.5 This standard should be used to measure and describe the properties of materials, products, or assemblies in response to heat and flame under controlled laboratory conditions and should not be used to describe or appraise the fire hazard or fire risk of materials, products, or assemblies under actual fire conditions. However, results of this test may be used as elements of a fire risk assessment which takes into account all of the factors which are pertinent to an assessment of the fire hazard of a particular end use.
1.6 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the test method portion, Section 13 of this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Note 1- ISO 800-1977(E) is similar but not equivalent to this specification. Product classification and characterization are not the same.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: D 4617 – 96
Standard Specification for
Phenolic Compounds (PF)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 4617; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
1.1 This specification covers phenolic compounds suitable 2.1 ASTM Standards:
for molding. D 256 Test Methods for Impact Resistance of Plastics and
1.2 This specification is intended to be a means of calling Electrical Insulating Materials
out plastic materials used in the fabrication of end items or D 570 Test Method for Water Absorption of Plastics
parts. It is not intended for the selection of materials. Material D 618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics and Electrical
selection should be made by those having expertise in the Insulating Materials for Testing
plastics field after careful consideration of the design and the D 638 Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics
performance required of the part, the environment to which it D 648 Test Method for Deflection Temperature of Plastics
will be exposed, the fabrication process to be employed, the Under Flexural Load
inherent properties of the material other than those covered by D 695 Test Method for Compressive Properties of Rigid
this specification, and the economics. Plastics
1.3 The properties included in this specification are those D 700 Specification for Phenolic Molding Compounds
required to identify the compositions covered. There may be D 790 Test Methods for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced
other requirements necessary to identify particular character- and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materi-
istics important to specialized applications. These will be als
agreed upon between the user and the supplier, by using the D 792 Test Methods for Specific Gravity (Relative Density)
suffixes specified in Section 5. and Density of Plastics by Displacement
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the D 796 Practice for Compression Molding Test Specimens of
standard. Phenolic Molding Compounds
1.5 This standard should be used to measure and describe D 883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
the properties of materials, products, or assemblies in response D 1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to
to heat and flame under controlled laboratory conditions and Plastics
should not be used to describe or appraise the fire hazard or D 1896 Practice for Transfer Molding Specimens of Ther-
fire risk of materials, products, or assemblies under actual fire mosetting Compounds
conditions. However, results of this test may be used as D 1898 Practice for Sampling of Plastics
elements of a fire risk assessment which takes into account all D 3419 Practice for In-Line Screw-Injection Molding of
of the factors which are pertinent to an assessment of the fire Test Specimens from Thermosetting Compounds
hazard of a particular end use. D 3892 Practice for Packaging/Packing of Plastics
1.6 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the D 4000 Classification System for Specifying Plastic Mate-
test method portion, Section 13 of this specification: This rials
standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, E 29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user Determine Conformance with Specification
of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health 2.2 Military Standard:
practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limita- MIL-STD-105 Sampling Procedures and Tables for Inspec-
tions prior to use. tion by Attributes
2.3 ISO Standard:
NOTE 1—ISO 800-1977(E) is similar but not equivalent to this speci-
fication. Product classification and characterization are not the same.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.01.
1 3
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-20 on Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.02.
Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.16 on Thermosetting Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02.
Materials. Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, Bldg. 4 Section D, 700
Current edition approved March 10, 1996. Published July 1996. Originally Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5094, Attn: NPODS.
published as D 4617 – 86. Last previous edition D 4617 – 91a. Available from American National Standards Institute, 11 West 42nd St., 13th
This edition includes the addition of an ISO equivalency statement. Floor, New York, NY 10036.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D 4617
ISO 8000-1977(E) conform to the requirements specified herein. The color and
form of the material shall be as agreed upon by the supplier and
3. Terminology
the user. Specification changes due to the effects of colorants
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of technical terms pertain- should be noted by both parties and, where necessary, covered
ing to plastics used in this specification see Terminology
by suffixes.
D 883.
8. Detail Requirements
4. Classification
8.1 Test specimens for the various materials shall conform
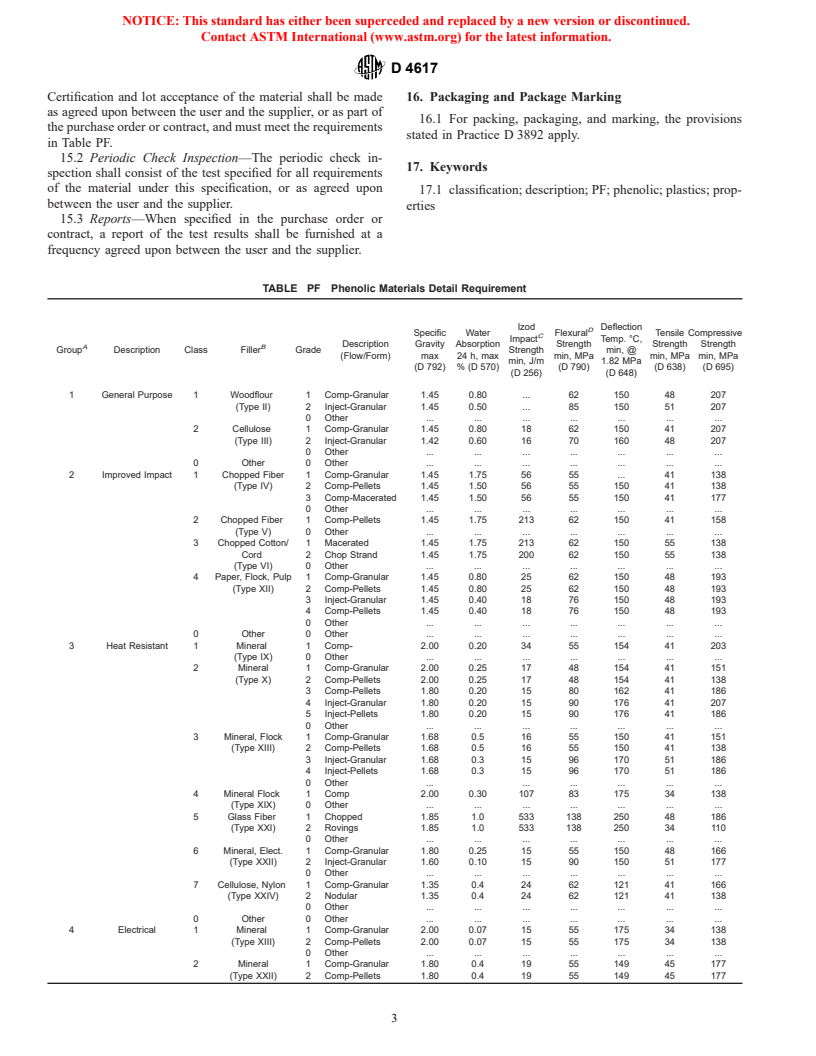
4.1 Phenolic compounds are classified into groups accord- to the requirements prescribed in Table PF and Table A, and
ing to their application. These groups are subdivided into suffix requirements as they apply.
classes and grades as shown in Table PF. 8.2 Observed or calculated values obtained from analysis,
measurement, or test shall be rounded off to the nearest unit in
NOTE 2—An example of this classification system is as follows:
the last right-hand place of figures used in expressing the
The designation PF 111 indicates:
specified limiting value in accordance with the rounding
PF = Phenol-Formaldehyde (Phenolic) as found in Terminology D 1600
method of Practice E 29. The value obtained is compared
1 = General Purpose (Group)
1 = Cellulose Filled, Type III (Class)
directly with the specified limiting value. Conformance or
1 = Compression Molding Grade with Requirements given in Table PF.
nonconformance with the specification is based on this com-
(Grade)
parison.
4.1.1 To facilitate the incorporation of future or special
materials, the “other unspecified” category (0) for group, class,
9. Sampling
and grade is shown in Table PF. The basic properties can be
9.1 Unless otherwise agreed upon between the user and the
obtained from Table A.
supplier, sample the materials in accordance with the sampling
4.2 Specific requirements for special or new phenolic com-
procedure prescribed in Practice D 1898. Adequate statistical
pounds shall be shown by a six-character designation. The
sampling shall be considered an acceptable alternative. A lot of
designation will consist of the letter A and the five digits
compound shall be considered as a unit of manufacture as
comprising the cell numbers for the property requirements in
prepared for shipment, and may consist of a blend of two or
the order they appear in Table A.
more production runs or batches of material.
4.2.1 Although the values listed are necessary to include the
10. Number of Tests
range of properties available in existing materials, users should
not infer that every possible combination of the properties
10.1 Conduct the number of tests as agreed upon between
exists or can be obtained.
the user and the supplier.
4.3 When the grade of the basic material is not known, or is
11. Specimen Preparation
not important, the use of “0” grade classification shall be used.
11.1 Mold the test specimens by compression in accordance
NOTE 3—An example of this classification system for a special phe-
with Practice D 796, by transfer in accordance with Practice
nolic compound is as follows:
D 1896, by injection in accordance with Practice D 3419, or as
The designation PF110A34130 indicates:
specified by the compound supplier.
PF110 = General-purpose injection molding grade phenolic from Table PF,
A = Table A property requirements,
12. Conditioning
3 = 50 MPa Tensile strength, min,
4 = 75 MPa Flexural modulus, min,
12.1 Condition test specimens in the standard laboratory
1 = 15 J/M Izod impact strength; min,
3 = 150°C Deflection temperature, min, and atmosphere in accordance with Procedure A of Practice D 618
0 = Unspecified.
before performing the required tests.
12.2 Conduct tests in the standard laboratory atmosphere of
NOTE 4—Specific
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.