ASTM D3117-03
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Wax Appearance Point of Distillate Fuels (Withdrawn 2010)
Standard Test Method for Wax Appearance Point of Distillate Fuels (Withdrawn 2010)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Wax appearance point is the temperature at which wax crystals begin to precipitate out of a fuel under specified cooling conditions. The presence of wax crystals in the fuel may restrict flow or plug the fuel filter. In critical fuel systems, wax appearance point may define the lower limit of acceptable operability.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the detection of wax in burner fuels, diesel fuels, and turbine engine fuels in the range from -26 to +2°C. It is applicable to a dark-colored oil if the stirrer can be seen under illumination.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements, see Section 7.
WITHDRAWN RATIONALE
This test method covers the detection of wax in burner fuels, diesel fuels, and turbine engine fuels in the range from -26 to +2°C. It is applicable to a dark-colored oil if the stirrer can be seen under illumination.
This test method is being balloted for withdrawal with no replacement because the test method is no longer in use, and there is no report from the CS92 ILCP.
Formerly under the jurisdiction of Committee D02 on Petroleum Products and Lubricants, this test method was withdrawn in May 2010.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation:D3117–03
Standard Test Method for
1
Wax Appearance Point of Distillate Fuels
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3117; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* cooling conditions. The presence of wax crystals in the fuel
may restrict flow or plug the fuel filter. In critical fuel systems,
1.1 This test method covers the detection of wax in burner
wax appearance point may define the lower limit of acceptable
fuels, diesel fuels, and turbine engine fuels in the range from
operability.
−26 to +2°C. It is applicable to a dark-colored oil if the stirrer
can be seen under illumination.
6. Apparatus
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
6.1 Specimen Tube—A double-walled (Dewar-type) jack-
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
eted tube with dimensions shown in Fig. 1.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
6.2 Temperature Measuring Device—Liquid-in-glass ther-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
mometerconformingtospecificationsforASTMThermometer
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard
62C in accordance with Specification E1, or any other tem-
statements, see Section 7.
perature measuring device with equal or better accuracy and
2. Referenced Documents equal temperature response.
2
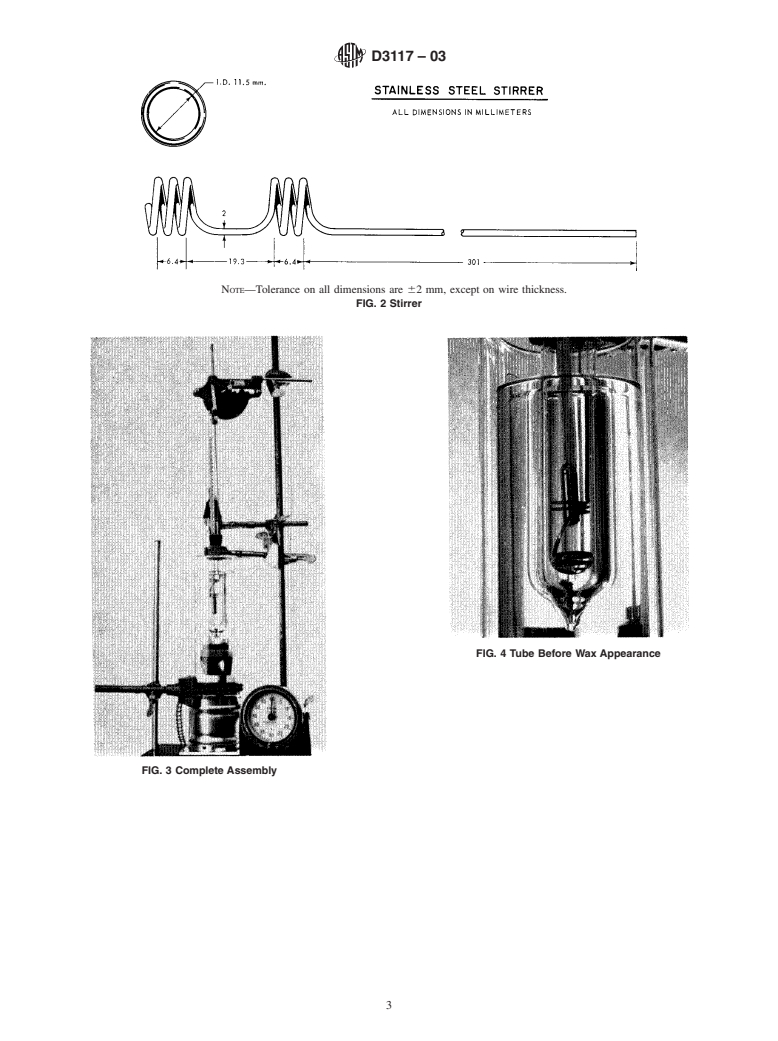
6.3 Stirrer Assembly—A stainless steel wire configured in
2.1 ASTM Standards:
the manner described in Fig. 2 and manipulated by a motor or
D445 Test Method for Kinematic Viscosity of Transparent
other suitable device in a vertical direction. The frequency of
and Opaque Liquids (and Calculation of Dynamic Viscos-
2
movement shall be 55 6 5 cycles/min with an amplitude of 50
ity)
2
6 5 mm. The stirrer shall be concentric with the temperature
D2386 Test Method for Freezing Point of Aviation Fuels
measuring device and shall be fitted with the moisture proof
D2500 Test Method for Cloud Point of Petroleum Products
3
collar specified in Test Method D2386. A No. 3, two-hole
neoprene rubber stopper shall be used to seal the top of the
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
specimen tube.
3. Terminology
6.4 Cooling Bath—Use an unsilvered vacuum flask having
minimum dimensions of 200-mm depth and 65-mm internal
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
diameter. The bath temperature, below −45°C, may be main-
3.1.1 wax appearance point—thetemperatureatwhichwax
tainedbyrefrigerationorsuitablefreezingmixtures(7.1).Bath
first begins to separate from the liquid when it is cooled under
temperature is monitored with an appropriate temperature
prescribed conditions.
measuring device such as ASTM Thermometer 6C.
4. Summary of Test Method
NOTE 1—Solid carbon dioxide chips (dry ice) and isopropanol is a
4.1 Aspecimen of distillate fuel is cooled under prescribed
recommendedmixtureforcoolant.Anexcessofdryiceshouldbeavoided
conditions while being stirred. The temperature at which wax to prevent obscuring the sample tube in a continuous stream of bubbles.
Isopropanolshouldbereplaceddailyorwhenlowtemperatureviscosityis
first appears is recorded as the wax appearance point.
noticeably higher than a fresh bath. Liquid nitrogen may also be used as
coolant instead of liquids cooled with solid carbon dioxide.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 Wax appearance point is the temperature at which wax 6.5 Illumination—A 150 to 230-mm long, 5 to 8-W fluo-
rescent tube shall be mounted behind the specimen to illumi-
crystals begin to precipitate out of a fuel under specified
nate it with transmitted light. Observations shall be made with
the sample tube between the observer’s eye and the lamp.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
6.6 Clock—Use a clock or other timing device readable to
Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
10 s to monitor the cooling rate.
D02.07 on Flow Properties.
Current edition approved March 10, 2003. Published May 2003. Originally
´1
approved in 1972. Last previous edition approved in 1996 as D3117–96 . DOI:
10.1520/D3117-03.
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.01.
3
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.03.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D3117–03
8.4 With the oil at 10°C or above, introduce a 25 6 1-mL
specimen into the tube. Add three drops of anhydrous isopro-
panol.
8.5 Adjust the stopper
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.