ASTM D6579-06
(Practice)Standard Practice for Molecular Weight Averages and Molecular Weight Distribution of Hydrocarbon and Terpene Resins by Size-Exclusion Chromatography
Standard Practice for Molecular Weight Averages and Molecular Weight Distribution of Hydrocarbon and Terpene Resins by Size-Exclusion Chromatography
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The MW averages and the MWD are important characteristics of a resin. They may be used for a variety of correlations for fundamental studies, processing, or product applications. The MW and MWD values may also be used for production quality control of resins.
Limitations—Comparison of SEC molecular weight values should be made only if the data were obtained under identical chromatographic conditions.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice covers the determination of apparent molecular weight (MW) averages and molecular weight distributions (MWD) for THF-soluble hydrocarbon and terpene resins by size-exclusion chromatography (SEC). This technique is not absolute; it requires calibration with standards of known molecular weight. This practice is applicable to resins containing molecular-weight components that have elution volumes falling within the elution volume range defined by polystyrene standards.Note 1
SEC is also known as gel permeation chromatography (GPC).
1.2 SEC systems employ low-volume liquid chromatography components and columns packed with relatively small (generally 3 to 20 m) microporous particles. High-performance liquid chromatography instrumentation and automated data handling systems for data acquisition and processing are also required.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D6579–06
Standard Practice for
Molecular Weight Averages and Molecular Weight
Distribution of Hydrocarbon and Terpene Resins by Size-
1
Exclusion Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6579; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* D3016 Practice for Use of Liquid Exclusion Chromatogra-
phy Terms and Relationships
1.1 This practice covers the determination of apparent
D6440 Terminology Relating to Hydrocarbon Resins
molecular weight (MW) averages and molecular weight distri-
butions (MWD) for THF-soluble hydrocarbon and terpene
3. Terminology
resins by size-exclusion chromatography (SEC). This tech-
3.1 For definitions of size-exclusion chromatography terms,
nique is not absolute; it requires calibration with standards of
see Practice D3016.
known molecular weight. This practice is applicable to resins
3.2 For definition of terpene resin, see Terminology D804.
containing molecular-weight components that have elution
3.3 For definitions of resin terms, see Terminology D6440.
volumes falling within the elution volume range defined by
polystyrene standards.
4. Summary of Practice
NOTE 1—SECisalsoknownasgelpermeationchromatography(GPC).
4.1 In this practice, a dilute solution of a hydrocarbon or
terpene resin sample is injected into a liquid mobile phase
1.2 SEC systems employ low-volume liquid chromatogra-
containing the same solvent used to prepare the resin solution.
phy components and columns packed with relatively small
The mobile phase transports the resin into and through a
(generally 3 to 20 µm) microporous particles. High-
chromatography column (or set of columns connected in
performance liquid chromatography instrumentation and auto-
series) packed with a rigid or semirigid, porous substrate that
mated data handling systems for data acquisition and process-
separates the molecules according to their size in solution. A
ing are also required.
detector monitors the eluate as a function of elution volume (or
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
time). Upon emerging from the column(s), the fractions of
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
size-separated molecules are detected and their elution vol-
only.
umes (or times) and (usually) concentrations recorded.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
Through calibration, the elution volumes (or times) are con-
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
verted to apparent molecular weights, and various molecular
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
weight parameters for the sample resin are calculated from the
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
molecular weight/concentration data.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
5. Significance and Use
2. Referenced Documents
2
5.1 The MW averages and the MWD are important charac-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
teristics of a resin. They may be used for a variety of
D804 Terminology Relating to Naval Stores, Including Tall
correlations for fundamental studies, processing, or product
Oil and Related Products
applications. The MW and MWD values may also be used for
production quality control of resins.
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint and
5.2 Limitations—ComparisonofSECmolecularweightval-
Related Coatings, Materials, and Applications and is the direct responsibility of
ues should be made only if the data were obtained under
Subcommittee D01.34 on Pine Chemicals and Hydrocarbon Resins.
identical chromatographic conditions.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2006. Published November 2006. Originally
approved in 2000. Last previous edition approved in 2000 as D6579 – 00. DOI:
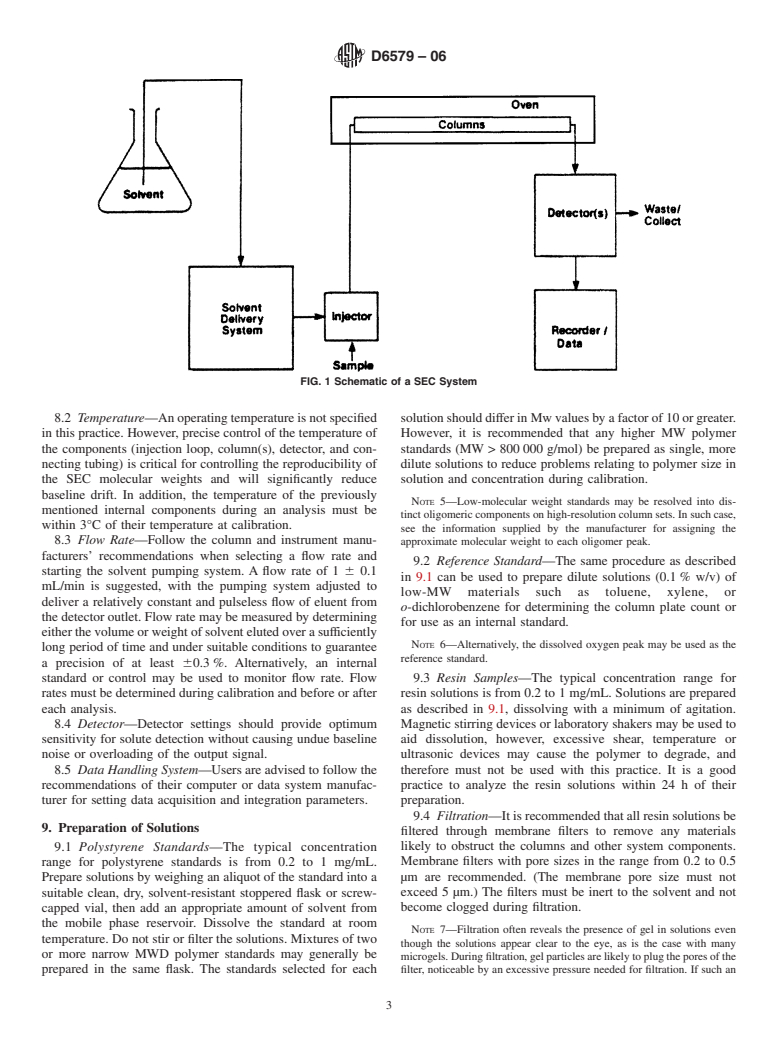
6. Apparatus
10.1520/D6579-06.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
6.1 Solvent Reservoir—The solvent reservoir must hold
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
sufficient solvent to ensure consistency of composition for a
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. number of analyses. The reservoir should isolate the solvent
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6579–06
NOTE 3—The principal disadvantage of the differential refractometer is
from the atmosphere, permit control of the environment in
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.