ASTM D7097-09
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Moderately High Temperature Piston Deposits by Thermo-Oxidation Engine Oil Simulation Test-TEOST MHT
Standard Test Method for Determination of Moderately High Temperature Piston Deposits by Thermo-Oxidation Engine Oil Simulation Test-TEOST MHT
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The test method is designed to predict the deposit-forming tendencies of engine oil in the piston ring belt and upper piston crown area. Correlation has been shown between the TEOST MHT procedure and the TU3MH Peugeot engine test in deposit formation. Such deposits formed in the ring-belt area of a reciprocating engine piston can cause problems with engine operation and longevity. It is one of the required test methods in Specification D 4485 to define API Category-Identified engine oils.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the procedure to determine the mass of deposit formed on a specially constructed test rod exposed to repetitive passage of 8.5 g of engine oil over the rod in a thin film under oxidative and catalytic conditions at 285°C. The range of applicability of the Moderately High Temperature Thermo-Oxidation Engine Test (TEOST MHT ) test method as derived from an interlaboratory study is approximately 10 to 100 mg. However, experience indicates that deposit values from 1 to 150 mg or greater may be obtained.
1.2 This test method uses a patented instrument, method and patented, numbered, and registered depositor rods traceable to the manufacturer and made specifically for the practice and precision of the test method.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3.1 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. Although not an SI unit, the special name, litre (L) is allowed by SI for the cubic decimetre (dm3) and the millilitre (mL) for the SI cubic centimetre (cm3).
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D7097 − 09
StandardTest Method for
Determination of Moderately High Temperature Piston
Deposits by Thermo-Oxidation Engine Oil Simulation Test—
1
TEOST MHT
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7097; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.1 This test method covers the procedure to determine the
mass of deposit formed on a specially constructed test rod
2. Referenced Documents
exposedtorepetitivepassageof8.5gofengineoilovertherod
5
2.1 ASTM Standards:
inathinfilmunderoxidativeandcatalyticconditionsat285°C.
D4485Specification for Performance ofActiveAPI Service
TherangeofapplicabilityoftheModeratelyHighTemperature
2
Category Engine Oils
Thermo-OxidationEngineTest(TEOSTMHT )testmethodas
D6335Test Method for Determination of High Temperature
derived from an interlaboratory study is approximately 10 to
Deposits by Thermo-Oxidation Engine Oil Simulation
100 mg. However, experience indicates that deposit values
Test
from 1 to 150 mg or greater may be obtained.
1.2 Thistestmethodusesapatentedinstrument,methodand
3. Terminology
patented, numbered, and registered depositor rods traceable to
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3
the manufacturer and made specifically for the practice and
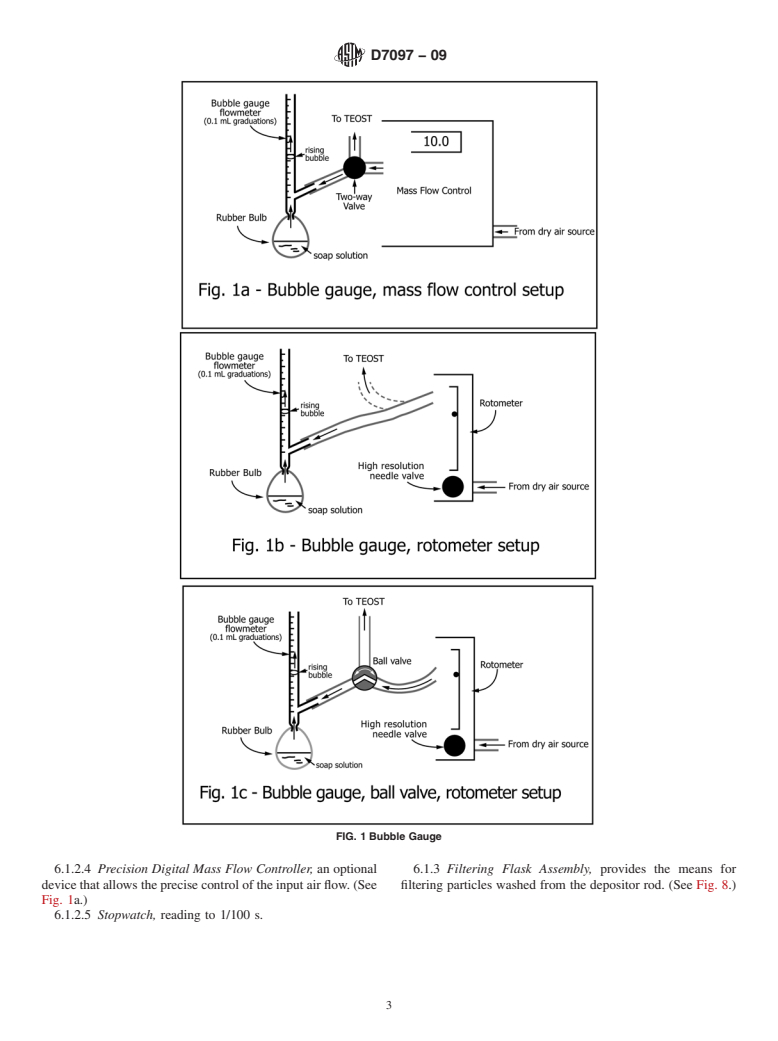
3.1.1 bubble airflow gauge, n—a precision bore glass tube
4
precision of the test method.
marked in tenths of a millilitre used to measure accurately the
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as flow rate of air around and past the depositor rod and to
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
calibrate mass air flow controllers recommended for use in the
standard. procedure.
1.3.1 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
3.1.2 depositor rod deposits, n—particulate matter formed
standard.Although not an SI unit, the special name, litre (L) is
on the depositor rod surface by oxidation of the thin film of
3
allowed by SI for the cubic decimetre (dm ) and the millilitre
passingoilexposedtotherodtemperatureandair,andweighed
3
(mL) for the SI cubic centimetre (cm ).
after appropriate washing and drying to obtain the net mass
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
gain.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.1.3 filter deposits, n—particulates washed from the de-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
positor rod after the test and collected on a special multi-layer
filter cartridge.
2
3.1.4 TEOST , n—an acronym for Thermo-Oxidation En-
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
gine Oil Simulation Test.
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D02.09.0G on Oxidation Testing of Engine Oils.
3.1.5 total rod deposits, n—the mass of deposits collected
CurrenteditionapprovedJune1,2009.PublishedJuly2009.Originallyapproved
onthedepositorrodplusanymassofdepositswashedfromthe
in 2005. Last previous edition approved in 2006 as D7097–06a. DOI: 10.1520/
D7097-09.
depositor rod and later extracted on a filter.
2
TEOSTand MHTare registered trademarks of theTannas Co. (Reg. 2001396),
3.1.6 volatilized oil, n—oil vapor coalesced on the mantle
Tannas Company, 4800 James Savage Rd., Midland, MI 48642.
3
The sole source of supply of the apparatus known to the committee at this time wall, and subsequently collected in a vial.
is Tannas Company, 4800 James Savage Rd., Midland, MI 48642. If you are aware
3.2 Abbreviations:
of alternative suppliers, please provide this information to ASTM International
2
3.2.1 MHT , n—moderately high temperature.
Headquarters.Your comments will receive careful consideration at a meeting of the
1
responsible technical committee, which you may attend.
4
The TEOST instrument, method and rod are patented. Interested parties are
5
invited to submit information regarding the identification of an alternative(s) to this For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
patented technology to ASTM Headquarters. Your comments will receive careful contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
1
consideration at a meeting of the responsible technical committee, which you may Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
attend. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ---------
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D7097–06a Designation:D7097–09
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Moderately High Temperature Piston
Deposits by Thermo-Oxidation Engine Oil Simulation Test—
1
TEOST MHT
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 7097; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope *
1.1 This test method covers the procedure to determine the mass of deposit formed on a specially constructed test rod exposed
to repetitive passage of 8.5 g of engine oil over the rod in a thin film under oxidative and catalytic conditions at 285°C. The range
2
of applicability of the Moderately High Temperature Thermo-Oxidation Engine Test (TEOST MHT ) test method as derived from
an interlaboratory study is approximately 10 to 100 mg. However, experience indicates that deposit values from 1 to 150 mg or
greater may be obtained.
1.2 This test method uses a patented instrument, method and patented, numbered, and registered depositor rods traceable to the
3 4
manufacturer and made specifically for the practice and precision of the test method. Note1—ASTM International takes no
position respecting the validity of any patent rights asserted in connection with any item mentioned in this standard. Users of this
standard are expressly advised that determination of the validity of any such patent rights, and the risk of infringement of such
rights, are entirely their own responsibility.
1.3The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. Although not an SI unit, the special name, litre (L) is allowed
by SI for the cubic decimetre (dm
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3.1 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard.Although not an SI unit, the special name, litre (L) is allowed
3
3
by SI for the cubic decimetre (dm ) and the millilitre (mL) for the SI cubic centimetre (cm ).
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
5
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 4485 Specification for Performance of Engine Oils
D 6335 Test Method for Determination of High Temperature Deposits by Thermo-Oxidation Engine Oil Simulation Test
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
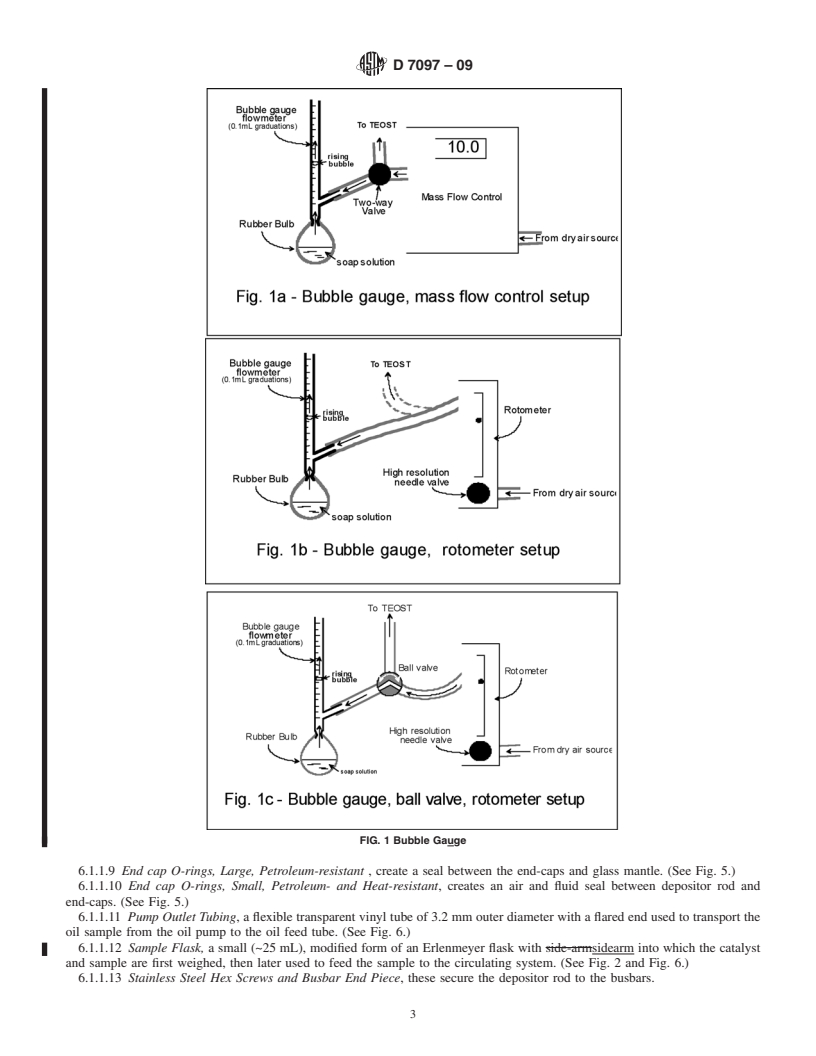
3.1.1 bubble airflow gagebubble airflow gauge, n—a precision bore glass tube marked in tenths of a millilitre used to measure
accurately the flow rate of air around and past the depositor rod and to calibrate mass air flow controllers recommended for use
in the procedure.
3.1.2 depositor rod deposits, n—particulate matter formed on the depositor rod surface by oxidation of the thin film of passing
oil exposed to the rod temperature and air, and weighed after appropriate washing and drying to obtain the net mass gain.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D02.09.0G
on Oxidation Testing of Engine Oils.
Current edition approved Dec.June 1, 2006.2009. Published January 2007.July 2009. Originally approved in 2005. Last previous edition approved in 2006 as D 7097–06a.
2
TEOST and MHT are registered trademarks of the Tannas Co. (Reg. 2001396).
2
TEOST and MHT are registered trademarks of the Tannas Co. (Reg. 2001396), Tannas Company, 4800 James Savage Rd., Midland, MI 48642.
3
The sole source of supply of the apparatus known to the committee at this time is Tannas Company, 4800 James Savage Rd., Midland, MI 48642. If you are awareof
alternative suppliers, please provide this information toASTM International Headquarters. Your comments will receive careful consideration at a meeting of the responsible
technical committee, which you may attend.
4
The TEOST instrument, method and rod are patented. Interested parties are invited to submit information regarding the identification of an alternative(s) to this patented
technology to ASTM Headquarters. Your comments will receive careful consideration at a meeting of the responsible technical committee, which you may attend.
5
For referencedASTM stan
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.