ASTM E1190-95(2007)
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Strength of Power-Actuated Fasteners Installed in Structural Members
Standard Test Methods for Strength of Power-Actuated Fasteners Installed in Structural Members
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
These test methods are intended to measure the anchoring capability and shear resistance of power-actuated fasteners to provide information from which applicable design values are to be derived for use in structural applications, such as in members of concrete, concrete masonry, and steel.
SCOPE
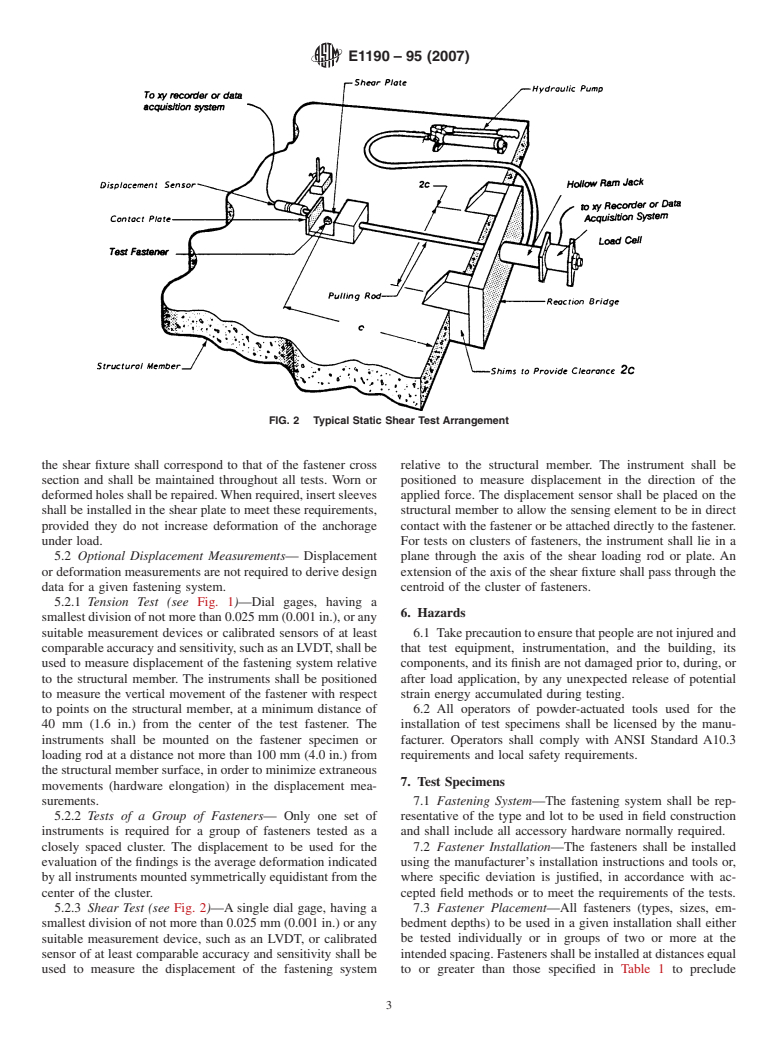
1.1 These test methods describe procedures for determining the static axial tensile and shear strengths of power-actuated fasteners installed in structural members made of concrete, concrete masonry, and steel.
1.2 These test methods are intended for use with fasteners that are installed perpendicular to a plane surface of the structural member.
1.3 Tests for combined tension and shear, fatigue, dynamic, and torsional load resistance are not covered.
1.4 The values stated in metric (SI) units are to be regarded as standard. The inch-pound units in parentheses are for information only.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazard statements are given in Section 6.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E1190 – 95 (Reapproved 2007)
Standard Test Methods for
Strength of Power-Actuated Fasteners Installed in Structural
1
Members
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E1190; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2.2 ANSI Standard:
ANSI A10.3 Safety Requirements for Powder-Actuated
1.1 These test methods describe procedures for determining
3
Fastening Systems
the static axial tensile and shear strengths of power-actuated
fasteners installed in structural members made of concrete,
3. Terminology
concrete masonry, and steel.
3.1 Definitions of general terms may be found in Terminol-
1.2 These test methods are intended for use with fasteners
ogy E631.
that are installed perpendicular to a plane surface of the
3.2 Descriptions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
structural member.
3.2.1 powder-actuated fastening system—a system that uses
1.3 Tests for combined tension and shear, fatigue, dynamic,
explosive powder to embed the fastener in structural elements.
and torsional load resistance are not covered.
3.2.2 power-actuated fastening system—a system that uses
1.4 The values stated in metric (SI) units are to be regarded
explosive powder, gas combustion, or compressed air or other
as standard. The inch-pound units in parentheses are for
gas to embed the fastener in structural elements.
information only.
3.2.3 drive pin—a nail-like metal fastener designed to
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
attach one material to another.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.2.4 threaded stud—a round metal-wire fastener, with a
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
pointed shank at one end and threads along the other end,
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
designed to be used as a removable fastening or in conjunction
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazard
with a threaded coupler.
statements are given in Section 6.
3.2.5 structural member—an element of a structural system
2. Referenced Documents such as a beam, column, or truss.
2 3.2.6 static load—a load or series of loads that are sup-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
ported by or are applied to a structure so gradually that forces
E4 Practices for Force Verification of Testing Machines
caused by change in momentum of the load and structural
E171 Specification for Atmospheres for Conditioning and
elements are negligible and all parts of the system at any
Testing Flexible Barrier Materials
instant are essentially in equilibrium.
E575 Practice for Reporting Data from Structural Tests of
3.2.7 tensile test—atestinwhichafastenerisloadedaxially
Building Constructions, Elements, Connections, and As-
in tension at a specified rate.
semblies
3.2.8 shear test—a test in which a force is applied perpen-
E631 Terminology of Building Constructions
dicularly to the axis of the fastener and parallel to the surface
of the structural member.
1
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E06 on
3.2.9 fastener spacing, s—the distance between the longi-
Performance of Buildings and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E06.13
tudinal axes of two fasteners in the same plane. Also, distance
on Structural Performance of Connections in Building Construction.
between longitudinal axis of fastener and nearest edge of
Current edition approved April 1, 2007. Published April 2007. Originally
´1
approved in 1987. Last previous edition approved in 2000 as E1190 – 95 (2000)
test-system supports (see s in Fig. 1).
. DOI: 10.1520/E1190-95R07.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
the ASTM website. 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
Copyright ©ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E1190 – 95 (2007)
FIG. 1 Typical Static Tension Test Arrangement
3.2.10 edge distance, c—the distance from the longitudinal shall be used for laboratory testing. If pressure gages are used
axis (center) of a fastener to the nearest edge of the structural for field testing, they shall be calibrated immediately prior to
member in which it is installed. use.
5.1.1 Tensile Test—A system suitable for applying tensile
3.2.11 embedment depth, h —the distanc
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.