ASTM D4476-97
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Flexural Properties of Fiber Reinforced Pultruded Plastic Rods
Standard Test Method for Flexural Properties of Fiber Reinforced Pultruded Plastic Rods
SCOPE
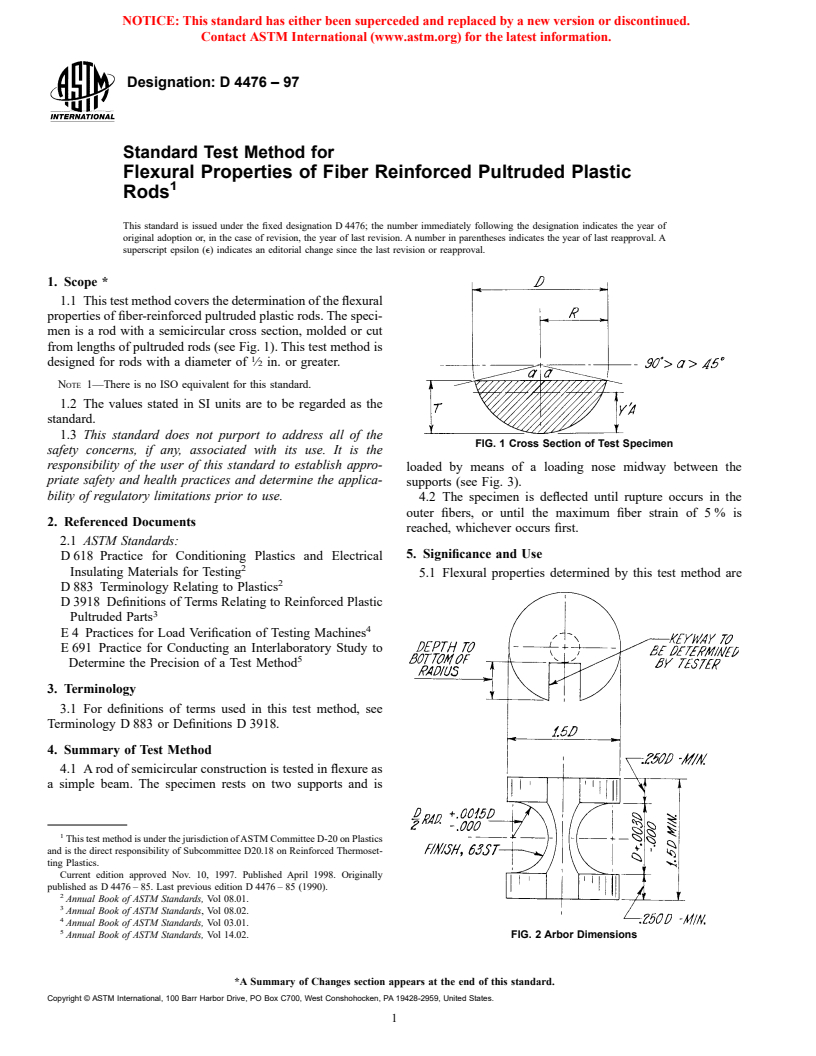
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the flexural properties of fiber-reinforced pultruded plastic rods. The specimen is a rod with a semi-circular cross section, molded or cut from lengths of pultruded rods (see Fig. 1). This test method is designed for rods with a diameter of 1/2 in. or greater.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.3 This standard may involve hazardous materials, operations, and equipment. This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems associated with its use. It is the responsibility of whoever uses this standard to consult and establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: D 4476 – 97
Standard Test Method for
Flexural Properties of Fiber Reinforced Pultruded Plastic
Rods
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 4476; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope *
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the flexural
properties of fiber-reinforced pultruded plastic rods. The speci-
men is a rod with a semicircular cross section, molded or cut
from lengths of pultruded rods (see Fig. 1). This test method is
designed for rods with a diameter of ⁄2 in. or greater.
NOTE 1—There is no ISO equivalent for this standard.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
FIG. 1 Cross Section of Test Specimen
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
loaded by means of a loading nose midway between the
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
supports (see Fig. 3).
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
4.2 The specimen is deflected until rupture occurs in the
outer fibers, or until the maximum fiber strain of 5 % is
2. Referenced Documents
reached, whichever occurs first.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5. Significance and Use
D 618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics and Electrical
Insulating Materials for Testing
5.1 Flexural properties determined by this test method are
D 883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
D 3918 Definitions of Terms Relating to Reinforced Plastic
Pultruded Parts
E 4 Practices for Load Verification of Testing Machines
E 691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
3. Terminology
3.1 For definitions of terms used in this test method, see
Terminology D 883 or Definitions D 3918.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 A rod of semicircular construction is tested in flexure as
a simple beam. The specimen rests on two supports and is
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-20 on Plastics
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.18 on Reinforced Thermoset-
ting Plastics.
Current edition approved Nov. 10, 1997. Published April 1998. Originally
published as D 4476 – 85. Last previous edition D 4476 – 85 (1990).
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.01.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.02.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.01.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02. FIG. 2 Arbor Dimensions
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D 4476
FIG. 3 Schematic of Flexural Test
especially useful for quality control and specification purposes. be sufficiently large to prevent contact of the specimen with the
5.2 The maximum axial fiber stresses occur on a line under sides of the nose. The supports shall consist of anvils to support
the loading nose. The use of the semicircular cross section the round section of the segment (see Fig. 2).
eliminates premature compression shear that has been noted in 6.3 Micrometers—Suitable micrometers for measuring the
three-point flexure tests on full-round rods. diameter of the test specimen to an incremental discrimination
5.3 Flexural properties may vary with specimen depth, of at least 0.025 mm (0.001 in.) shall be used.
temperature, atmospheric conditions, and differences in rate of
7. Test Specimen
straining.
7.1 The test specimen shall consist of a pultruded rod cut
5.4 Before proceeding with this test method, reference
into two parts so that the cross section of each part is smaller
should be made to the specification of the material being tested.
than a half-round section (see Fig. 1).
Any test specimen preparation, conditioning, dimensions, or
7.2 The specimen length shall be 16 to 24 times its thickness
testing parameters, or combination thereof, covered in the
or depth, plus at least 20 % of the support span to allow a
materials specification shall take precedence over those men-
minimum of 10 % overhang at the supports (see Fig. 3).
tioned in this test method. If there are no material specifica-
tions, then the default conditions apply.
NOTE 2—As a general rule, support span-to-depth ratios of 16 to 1 are
satisfactory when the ratio of the tensile strength to shear strength is less
6. Apparatus
than 20 to 1, but the support span-to-depth ratio should be increased for
6.1 Testing Machine—A properly calibrated testing ma- composite laminates having relatively low shear strength in the plane of
the laminate and relatively high tensile strength parallel to the support
chine that can be operated at constant rates of crosshead motion
span.
over the range indicated, and in which the error in the
load-measuring system shall not exceed 61 % of the maxi-
7.3 Number of Specimens—The number of test specimens is
mum load expected to be measured. It shall be equipped with
optional. However, a minimum of five specimens is required to
a deflection-measuring device. The stiffness of the testing
obtain a satisfactory average and standard deviation.
machine shall be such that the total elastic deformation of the
8. Conditioning
system does not exceed 1 % of the total deflection of the test
specimen during test, or appropriate corrections shall be made. 8.1 Conditioning—Condition the test specimen at 23 6 2°C
The load-indicating mechanism shall be essentially free of (73.4 6 3.6°F) and 50 6 5 % relative humidity for not less
inertial lag at the crosshead rate used. The accuracy of the
than 40 h prior to test in accordance with Procedure A of
testing machine shall be verified in accordance with Practices Practice D 618, for those tests where conditioning is required.
E4. In cases of disagreement, the tolerances shall be6 1°C
6.2 Loading Nose and Supports—The loading nose shall (61.8°F) and 62 % relative humidity. These conditions are
have cylindrical surfaces. In order to avoid excessive indenta- recommended for research and development trials, but not
tion or failure due to stress concentration directly under the necessarily for quality control. However, temperature control
loading nose, the radius of the nose shall be at least 6.4 mm ( ⁄4 to 22.26 5.6°C (72 6 10°F) is recommended for quality
in.) for all specimens. Larger-radius noses are recommended if control.
significant indentation or compressive failure occurs. The 8.2 Test Conditions—Conduct tests in the standard labora-
curvature of the loading nose in contact with the specimen shall tory atmosphere of 23 6 2°C (73.4 6 3.6°F) and 50 6 5%
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D 4476
relative humidity, unless otherwise specified in the test method
G = arc sine A, rad,
or in other specifications. In cases of disagreement, the
H =2A · B,
tolerances shall be6 1°C (61.8°F) and 62 % relative humid- g = T/R − relative thickness of specimen, m (in.),
ity. T = thickness of specimen, m (in.), and
D = original diameter of specimen, m (in.).
8.3 Preconditioning in other environments to simulate
specified conditions and durations is permissible.
NOTE 3—Eq 1 applies directly to materials for which the stress is
8.4 Testing in other environmental conditions is permis-
linearly proportional to strain up to the point of rupture and for which the
sible.
strains are small. Since this is not always the case, a slight error will be
introduced in the use of this equation. The equation will, however, be valid
9. Procedure
for comparison data and specification values up to the maximum fiber
strain of 5 % for specimens tested by the procedure herein described.
9.1 Use an untested specimen for each measurement. Mea-
NOTE 4—The preceding calculation is not valid if the specimen is
sure the diameter before cutting and depth of the specimen to
slipping excessively between the supports.
the nearest 0.025 mm (0.001 in.) at the center of the support
span.
11.2 Modulus of Elasticity:
9.2 Determine the support span to be used as described in
11.2.1 Tangent Modulus of Elasticity—The tangent modulus
Section 6 and set the support span to within 1 % of the
of elasticity, often called the “modulus of elasticity,” is the
determined value. ratio, within the elastic limit, of stress to corresponding strain,
9.3 Machine crosshead rate shall be 3 mm/min (0.1 in./min)
and shall be expressed in newtons per square metre (pounds-
for samples where D/2 is
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.