ASTM F29-97(2017)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Dumet Wire for Glass-to-Metal Seal Applications
Standard Specification for Dumet Wire for Glass-to-Metal Seal Applications
ABSTRACT
This specification covers the properties and requirements for round, copper-coated 42 % nickel-iron wire, commonly known as dumet, intended primarily for sealing to soft glass. The wires shall conform to requirements stated for chemical composition, oxide coatings, dimension, internal and surface workmanship, and storage characteristics. Materials shall also undergo tests for thermal expansion, color of coating, diameter, reducible oxides, copper analysis, and metallography.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers round, copper-coated 42 % nickel-iron wire, commonly known as dumet, intended primarily for sealing to soft glass.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:F29 −97 (Reapproved 2017)
Standard Specification for
Dumet Wire for Glass-to-Metal Seal Applications
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationF29;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginal
adoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Materials With a Push-Rod Dilatometer
F14Practice for Making andTesting Reference Glass-Metal
1.1 This specification covers round, copper-coated 42%
Bead-Seal
nickel-ironwire,commonlyknownasdumet,intendedprimar-
ily for sealing to soft glass.
3. Ordering Information
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
3.1 The wire is usually supplied with a surface coating
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
consisting of a mixture of copper oxides and fused sodium
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
tetraborate (borax) which retards oxidation of the wire during
and are not considered standard.
sealing in glass and further aids wetting of the wire by the
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
glass. The composite wire may also be purchased as bare wire
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
for specific applications.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.2 Thesizeofthewire,ifapplicable,theboratecolorrange
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
designated as light, medium (regular), or dark, shall be
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
specified on each purchase order.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
3.3 Package sizes shall be agreed upon between the pur-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
chaser and the seller.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
4. Chemical Composition
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
4.1 The copper used in the manufacture of dumet shall be
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
99.90% minimum copper. Silver shall be included with the
2. Referenced Documents copper. The material shall be free of reducible oxides.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
4.2 The chemical composition of the nickel-iron core shall
B170Specification for Oxygen-Free Electrolytic Copper— be as shown in Table 1.
Refinery Shapes
5. Oxide Coating
D1535Practice for Specifying Color by the Munsell System
D1729Practice for Visual Appraisal of Colors and Color
5.1 The primary standards for the entire range of colors are
Differences of Diffusely-Illuminated Opaque Materials
dividedintothreegroupscoveringlight,medium(regular),and
E3Guide for Preparation of Metallographic Specimens
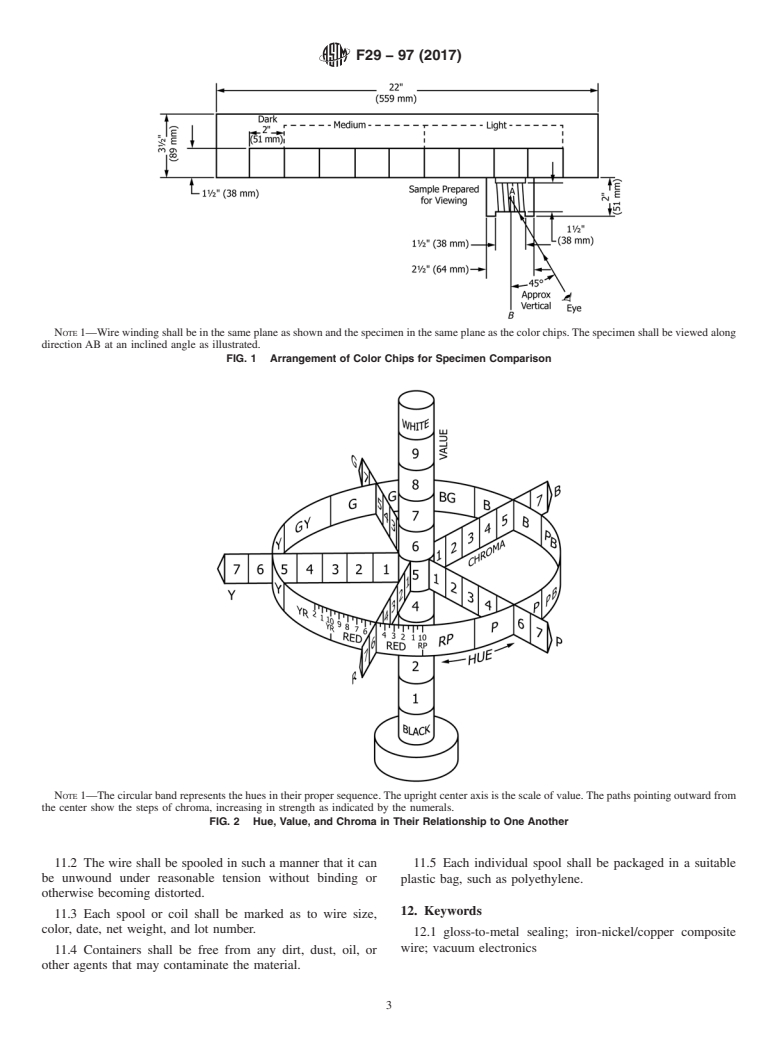
dark as shown, with their respective limits, in Fig. 1 and Table
E29Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
2 (Note 1). The color range of the specimens shall be
Determine Conformance with Specifications
determined in accordance with 9.2.
E53Test Method for Determination of Copper in Unalloyed
NOTE 1—Color chip 2.5R 3.90/8.0 may be included in the dark range
Copper by Gravimetry
merely to extend the color series for assisting the viewer in making a
E228Test Method for Linear Thermal Expansion of Solid
better decision regarding the cut-off point between medium (regular) and
dark dumet.
6. Thermal Expansion
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM-Committee F01 on
Electronics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F01.03 on Metallic
6.1 The nominal values for the average coefficient of linear
Materials.
thermal expansion shall be as follows when determined in
Current edition approved June 1, 2017. Published June 2017. Originally
accordance with 9.1:
approved in 1963. Last previous edition approved in 2012 as F29–97(2012). DOI:
−7
10.1520/F0029-97R17.
6.1.1 Core—63 to 72×10 in./in.·deg °C (mm/mm·deg
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
°C) over the temperature range of 30 to 400°C.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
−7
6.1.2 Copper—177 6 3.5×10 in./in.·°C (mm/mm·deg
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. °C) over the temperature range of 30 to 300°C.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
F29−97 (2017)
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements: Core Material
9.1.1 Heat the core rod specimen in a hydrogen atmosphere
Element Composition, % for1hat 900°C; then cool it from 900 to 200°C at a rate not
Nickel 41 to 43 exceeding 5°C/min.
Manganese 0.75 to 1.25
9.1.2 Determine the thermal expansion charateristics in
Silicon, max 0.30
accordance with Test Method E228.
Carbon, max 0.10
Sulfur, max 0.02
9.2 Color of Coating— Mount the color chips on a neutral
Phosphorus, max 0.02
Iron (by difference) remainder background (middle gray to white) as shown in Fig. 1. Wind
the specimen to be tested or compared on a flat surface similar
tothatshowninFig.1.Eachturnofthewireshouldlieparallel
TABLE 2 Color Ranges and Limits
and as close as possible to the preceding turn without overlap-
Medium (Regular)
ping. View the specimen in natural or artificial daylight in
Dark Range Light Range
Range
accordancewitheitherorbothMethodD1535,(Note3)orTest
Colors darker than chip 3.5R 3.5R 3.94/8.0 to 6.5R 7.5R 4.22/8.0 to 0.5YR
Method D1729, Fig. 2.
3.94/8.0 4.06/8.0, incl 4.56/8.0 incl
NOTE 3—Coated wire carries a mixture of copper oxides and fused
sodiumtetraborateonthesurfaceofthedumet,whichdissolves,whollyor
TABLE 3 Dimensional Tolerances in part, into the glass during the sealing operation. The sealing technique
is influenced by the amount of coating, and color has been established as
Diameter, in. (mm) Tolerance, in.
a means of estimating the thickness of this mixture.The color varies from
(mm)
a dark red-purple to a light yellow-red as the thickness decreases. The
0.007 to 0.013 (0.18 to 0.33) ±0.0003 (±0.008)
method,describedinTestMethodD1535,isbasedonthecolor-perception
Over 0.013 to 0.018 (0.33 to 0.46) ±0.0004 (±0.010)
attributes of hue, lightness, and saturation and is used as the means for
Over 0.018 (0.46) ±0.0005 (±0.013)
specifying color.This method employs the Munsell color-notation system
in which visual scales are assigned to each of the color-perception
attributes. In this system, the attributes are called hue, H, value, V, and
chroma,C,writtenintheformHV/C.Byusingacombinationofnumbers
andletters,apparentcolormaybeexactlyspecified.T
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: F29 − 97 (Reapproved 2012) F29 − 97 (Reapproved 2017)
Standard Specification for
Dumet Wire for Glass-to-Metal Seal Applications
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F29; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A superscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This specification covers round, copper-coated 42 % nickel-iron wire, commonly known as dumet, intended primarily for
sealing to soft glass.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
B170 Specification for Oxygen-Free Electrolytic Copper—Refinery Shapes
D1535 Practice for Specifying Color by the Munsell System
D1729 Practice for Visual Appraisal of Colors and Color Differences of Diffusely-Illuminated Opaque Materials
E3 Guide for Preparation of Metallographic Specimens
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to Determine Conformance with Specifications
E53 Test Method for Determination of Copper in Unalloyed Copper by Gravimetry
E228 Test Method for Linear Thermal Expansion of Solid Materials With a Push-Rod Dilatometer
F14 Practice for Making and Testing Reference Glass-Metal Bead-Seal
3. Ordering Information
3.1 The wire is usually supplied with a surface coating consisting of a mixture of copper oxides and fused sodium tetraborate
(borax) which retards oxidation of the wire during sealing in glass and further aids wetting of the wire by the glass. The composite
wire may also be purchased as bare wire for specific applications.
3.2 The size of the wire, if applicable, the borate color range designated as light, medium (regular), or dark, shall be specified
on each purchase order.
3.3 Package sizes shall be agreed upon between the purchaser and the seller.
4. Chemical Composition
4.1 The copper used in the manufacture of dumet shall be 99.90 % minimum copper. Silver shall be included with the copper.
The material shall be free of reducible oxides.
4.2 The chemical composition of the nickel-iron core shall be as shown in Table 1.
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM-Committee F01 on Electronics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F01.03 on Metallic Materials.
Current edition approved July 1, 2012June 1, 2017. Published August 2012June 2017. Originally approved in 1963. Last previous edition approved in 20092012 as
F29 – 97(2009).F29 – 97(2012). DOI: 10.1520/F0029-97R12.10.1520/F0029-97R17.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
F29 − 97 (2017)
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements: Core Material
Element Composition, %
Nickel 41 to 43
Manganese 0.75 to 1.25
Silicon, max 0.30
Carbon, max 0.10
Sulfur, max 0.02
Phosphorus, max 0.02
Iron (by difference) remainder
TABLE 2 Color Ranges and Limits
Medium (Regular)
Dark Range Light Range
Range
Colors darker than chip 3.5R 3.5R 3.94/8.0 to 6.5R 7.5R 4.22/8.0 to 0.5YR
3.94/8.0 4.06/8.0, incl 4.56/8.0 incl
TABLE 3 Dimensional Tolerances
Diameter, in. (mm) Tolerance, in.
(mm)
0.007 to 0.013 (0.18 to 0.33) ±0.0003 (±0.008)
Over 0.013 to 0.018 (0.33 to 0.46) ±0.0004 (±0.010)
Over 0.018 (0.46) ±0.0005 (±0.013)
5. Oxide Coating
5.1 The primary standards for the entire range of colors are divided into three groups covering light, medium (regular), and dark
as shown, with their respective limits, in Fig. 1 and Table 2 (Note 1). The color range of the specimens shall be determined in
accordance with 9.2.
NOTE 1—Color chip 2.5R 3.90/8.0 may be included in the dark range merely to extend the color series for assisting the viewer in making a better
decision regarding the cut-off point between medium (regular) and dark dumet.
6. Thermal Expansion
6.1 The nominal values for the average coefficient of linear thermal expansion shall be as follows when determined in
accordance with 9.1:
−7
6.1.1 Core—63 to 72 × 10 in./in.·deg °C (mm/mm·deg °C) over the temperature range of 30 to 400°C.
−7
6.1.2 Copper—177 6 3.5 × 10 in./in.·°C (mm/mm·deg °C) over the temperature range of 30 to 300°C.
7. Dimensional Tolerances
7.1 The specified diameters shall conform to the tolerances given in Table 3.
NOTE 1—Wire winding shall be in the same plane as shown and the specimen in the same plane as the color chips. The specimen shall be viewed along
direction AB at an inclined angle as illustrated.
FIG. 1 Arrangement of Color Chips for Specimen Comparison
F29 − 97 (2017)
8. Workmanship and Finish
8.1 Internal Condition—The internal structure of the composite material, including the bond area, shall be sound and free from
pipes, porosity, or discontinuities which might prevent the making of a satisfactory seal.
8.2 Surface Condition:
8.2.1 There shall be no areas of exposed core evident on the surface of the wire.
8.2.2 The wire shall contain no longitudinal scratches, folds, or lines of a depth greater than the width.
8.2.3 There shall be no oil, grease, or other surface contaminants on the wire.
8.2.4 The wire shall be looped or coiled over a mandrel five times the diameter of the wire. At least 75 % of the dumet area
shall be free from defects consisting of damaged borate, exposing the copper, when observed at 10× magnification.
8.2.5 The nickel-iron core shall be uniformly covered with 18 % to 28 % copper (by weight) and the ratio of maximum to
minimum sheath thickness shall not exceed 2.5 to 1 on any cross section.
NOTE 2—The sheath is defined as that area exclusive of the core.
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.