ASTM D955-00
(Test Method)Standard Test Method of Measuring Shrinkage from Mold Dimensions of Thermoplastics
Standard Test Method of Measuring Shrinkage from Mold Dimensions of Thermoplastics
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Injection Molding—In injection molding, the difference between the dimensions of a mold cavity and of the molded specimen may vary according to the design of the mold and operation of the molding process. Factors such as mold and melt temperature, fill times, and packing conditions are known to affect shrinkage significantly. Adherence to the specified mold design (see 7.1) and specifications outlined in Practice D 3641 or ISO 294-4 or the appropriate material will improve the reproducibility of the test.
Compression Molding—In compression molding, the difference between the dimensions of a mold cavity and of the molded specimen may vary according to the design of the mold and operation of the molding process. Factors, such as the amount of material in charge, cooling time, and pressure application are known to affect shrinkage significantly. Adherence to the specified mold design (see 7.2) and specifications outlined in Practice D 4703 or ISO 293 or the appropriate material specifications will improve the reproducibility of the test.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method is intended to measure shrinkage from mold cavity to molded dimensions of thermoplastics when molded by compression or injection processes with specified process conditions.
1.2 This test method covers initial shrinkage measurements. The method also accommodates shrinkage at 24 and 48 h, which may be critical for some materials.
1.3 This method will give comparable data based on standard specimens and can not predict absolute values in actual molded parts with varying flow paths, wall thicknesses, pressure gradients and process conditions. Differences in mold shrinkage may also be observed between the three specimen geometries described in this test method.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are given for information only.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Note 1--This test method is technically identical to ISO 294-4 where Type D2 specimens are used except that pressure transducers are an option in this test method and required in ISO 294-4.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D955–00
Standard Test Method of
Measuring Shrinkage from Mold Dimensions of
1
Thermoplastics
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 955; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope* D 3641 Practice for Injection Molding ofTest Specimens of
4
Thermoplastic Molding and Extrusion Materials
1.1 This test method is intended to measure shrinkage from
D 4066 Specification for Nylon Injection and Extrusion
mold cavity to molded dimensions of thermoplastics when
4
Materials
molded by compression or injection processes with specified
D 4181 Specification forAcetal (POM) Molding and Extru-
process conditions.
4
sion Materials
1.2 This test method covers initial shrinkage measurements.
D 4549 Specification for Polystyrene Molding and Extru-
The method also accommodates shrinkage at 24 and 48 h,
5
sion Materials (PS)
which may be critical for some materials.
D 4703 Practice for Compression Molding of Thermoplas-
1.3 This method will give comparable data based on stan-
5
tic Materials into Test Specimens, Plaques, Sheets
dard specimens and can not predict absolute values in actual
D 4976 SpecificationforPolyethylenePlasticsMoldingand
molded parts with varying flow paths, wall thicknesses, pres-
5
Extension Materials
sure gradients and process conditions. Differences in mold
D 5947 Test Methods for Physical Dimensions of Solid
shrinkage may also be observed between the three specimen
5
Plastics Specimens
geometries described in this test method.
E 691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
6
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
standard. The values given in parentheses are given for
2.2 ISO Standards:
information only.
ISO 293 Plastics—Compression Moulding Test Specimens
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
7
of Thermoplastic Materials
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
ISO 294-3 Plastics—Injection Moulding of Test Specimens
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
7
of Thermoplastic Materials—Part 3: Small Plates
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
ISO 294-4 Plastics—Injection Moulding of Test
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Specimens—Part 4: Determination of Moulding Shrink-
NOTE 1—This test method is technically identical to ISO 294-4 where 7
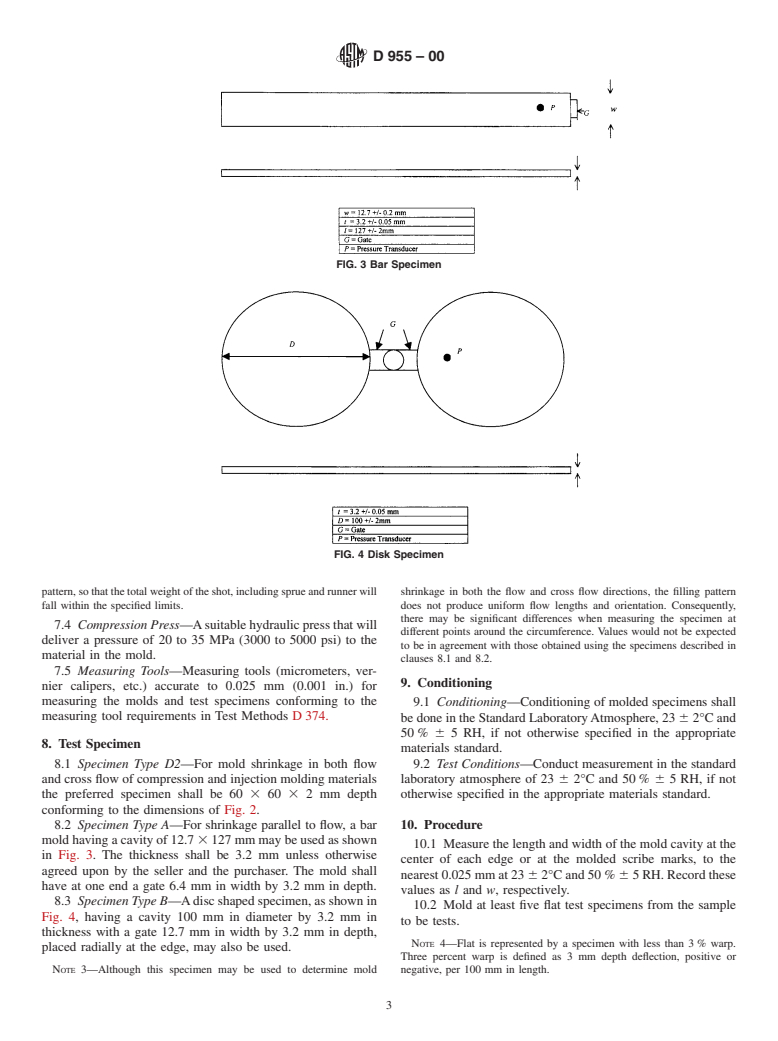
age
TypeD2specimensareusedexceptthatpressuretransducersareanoption
in this test method and required in ISO 294-4.
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—General definitions of terms applying to
2. Referenced Documents
this test method appear in Terminology D 883.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
D 374 Test Methods for Thickness of Solid Electrical Insu-
3.2.1 demolding, n—removing the specimens from the
2
lation
mold.
D 618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics and Electrical
3
Insulating Materials for Testing
4. Summary of Test Method
D 788 Classification System for Poly(Methyl Methacrylate)
4.1 The principle of this test method is to compare mold
3
(PMMA) Molding and Extension Compounds
cavity dimensions with specimen dimensions and report the
3
D 883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
differences in percent.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D20 on Plastics
4
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.09 on Specimen Preparation. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.02.
5
Current edition approved Nov. 10, 2000. Published January 2001. Originally Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.03.
6
published as D 955 – 48T. Last previous edition D 955 – 89 (1996). Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02.
2 7
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 10.01. Available from American National Standards Institute, 11 W. 42nd St., 13th
3
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.01. Floor, New York, NY 10036.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D955–00
3
Sp sprue molding volume = 30 000 mm
2
G gate projected area = 11 000 mm
lc = distance between the lines along which the test specimens are cut from
the runners
FIG. 1 Type D2
5. Significance and Use
5.1 Injection Molding—In injection molding, the difference
between the dimensions of a mold cavity and of the molded
Sp sprue
specimen may vary according to the design of the mold and
G gate
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.